The electric vehicle (EV) market is witnessing phenomenal growth. The number of electric cars in use globally rose 43% in 2020 to above 10 million. What's more, with 4.5 million electric cars, China has the highest number of EV cars in the world. Undeniably, the growth potential of electric vehicles cannot be overemphasized.
With low-cost, quality manufacturing potential, as well as a huge domestic market, Chinese EV makers look set for long-term growth. Here are five Chinese EV stocks to consider buying right now.
NIO Inc.
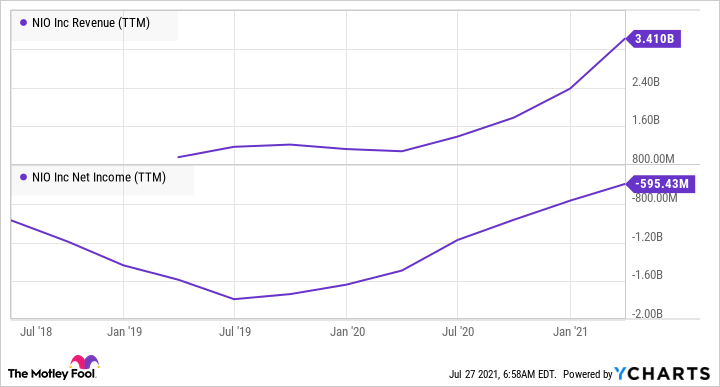
Founded in 2014, NIO (NIO 3.49%) started commercial deliveries in June 2018. NIO delivered 21,896 vehicles in Q2 2021, an increase of 112% year over year. NIO is building a new plant in Hefei, China. The company currently only sells vehicles in China, but it plans to expand to international markets. NIO is growing its revenue impressively and its net income is trending in the right direction.
NIO Revenue (TTM) data by YCharts
NIO uses Jianghuai Automobile Group's manufacturing facility to carry out its production. Jianghuai Automobile is a leading state-owned automobile manufacturer in China with a 50-year history. The facility has an annual production capacity of 120,000 units. That offers significant benefits to NIO, as it need not set up a plant from scratch, which requires considerable time, resources, and the presence of a robust supply chain.
XPeng Inc.
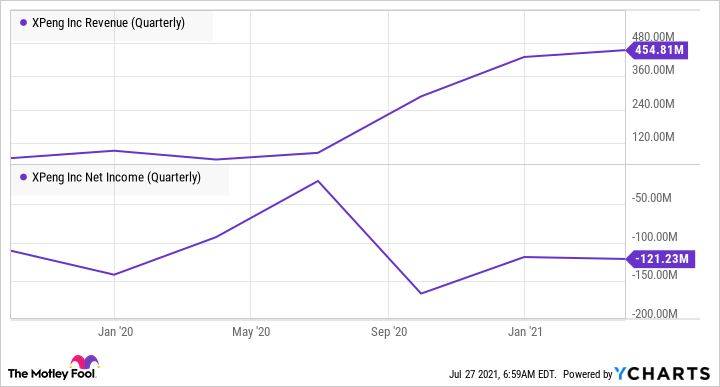
Founded in 2015 in Guangzhou, XPeng (XPEV -1.39%) began deliveries to customers in 2018. It was listed in the U.S. in August 2020. The company delivered 17,398 electric vehicles in Q2 2021, up from 13,340 deliveries in Q1. The company's revenue grew significantly in the last few quarters, in-line with the growth in its vehicle deliveries. In addition to EVs, XPeng's key focus is on developing an autonomous driving system.
XPEV Revenue (Quarterly) data by YCharts
XPeng has a manufacturing plant in Zhaoqing that became operational in May 2020. Prior to that, the company carried out its manufacturing at a plant of another automaker, Haima, which has over three decades of experience in auto manufacturing. Some of its models are still manufactured at one of Haima's plants. Such an arrangement allows XPeng to produce quality products with minimal capital investment. Its Zhaoqing plant has a capacity of 100,000 units while Haima's plant has a capacity of 150,000 units. Further, XPeng plans to construct two new plants each with a capacity of 100,000 units.

Image source: Getty Images.
BYD Company
BYD Company (BYDDY 2.01%) makes both internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles as well as electric vehicles. It is also involved in battery and photovoltaic businesses and developing rail transport. Founded in 1995, the company entered the automobile segment in 2003. In 2020, automobiles and related products contributed to 53% of the company's revenue. BYD has been growing its revenue rapidly and has been making profits for years.
BYDDY Revenue (TTM) data by YCharts
In Q2, BYD delivered 99,828 new energy vehicles, which included plug-in hybrid vehicles as well as buses and other commercial vehicles. Excluding plug-in hybrid and commercial vehicles, BYD delivered 54,841 passenger battery electric vehicles in Q2. That's much higher than EVs delivered by NIO or XPeng. By comparison, BYD delivered 42,716 ICE vehicles in Q2. So, the company's sales of electric vehicles exceeded that of its ICE vehicles.
In the first half of 2021, the sales volume of electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles grew 155% compared to the first half of 2020. By comparison, ICE sales volume dropped around 6%. It shows that BYD is increasingly shifting to EVs, which should make up a progressively higher portion of the company's sales and profits. However, the stock isn't valued like other Chinese EV stocks.
NIO Market Cap data by YCharts
As the above graph shows, BYD's price-to-sales ratio is lower than other top Chinese EV stocks, making it more attractive tha others from a valuation standpoint.
Li Auto
Founded in 2015, Li Auto (LI -3.79%) started commercial production in November 2019. It currently targets the premium SUV segment of the Chinese EV market. The company's manufacturing facility is in Changzhou and has an annual capacity of 100,000 units, expandable to 200,000 units with additional machinery. Li delivered 17,575 EVs in Q2 2021, up 166% year over year. The deliveries exceeded the company's guidance of 14,500 to 15,500 vehicles for the quarter.
LI Revenue (Quarterly) data by YCharts
The company has reported handsome revenue growth in the short period since its listing in the U.S.
Niu Technologies
Niu Technologies (NIU 0.97%) differs from other EV stocks, as the company sells electric scooters. Founded in 2014, Niu has already sold around 1.8 million electric scooters worldwide. It sells scooters, bicycles, mopeds, and motorcycles in more than 45 countries. The company's revenue has grown rapidly over the years and it has been profitable for two years.
NIU Revenue (TTM) data by YCharts
Niu Technologies has benefited from being an early mover in a fast-growing market segment. In Q2 2021, Niu sold 252,998 electric scooters, up 58% year over year. Of these, 246,018 were sold in China. Niu is expanding its production capacity and expects it to double to 2 million units by the end of 2021 from 1 million units at the end of March.
To conclude, all of the above EV stocks look very promising. Even so, investors should consider the risks involved in international investing before making an investment decision.