Since cryptocurrencies are decentralized and not under the control of financial institutions, they need a way to verify transactions. One method many cryptos use is proof of stake (PoS).
Proof of stake is a type of consensus mechanism used to validate cryptocurrency transactions. With this system, owners of the cryptocurrency can stake their coins, which gives them the right to check new blocks of transactions and add them to the blockchain.
This method is an alternative to proof of work, the first consensus mechanism developed for cryptocurrencies. Since proof of stake is much more energy-efficient, it has gotten more popular as attention has turned to how crypto mining affects the planet.
Understanding proof of stake is important for those investing in cryptocurrency. Here's a guide to how it works, its pros and cons, and examples of cryptocurrencies that use it.
How does proof of stake work?
How does proof of stake work?
The proof-of-stake model allows owners of a cryptocurrency to stake coins and create their own validator nodes. Staking is when you pledge your coins to be used for verifying transactions. Your coins are locked up while you stake them, but you can unstake them if you want to trade them.
When a block of transactions is ready to be processed, the cryptocurrency's proof-of-stake protocol will choose a validator node to review the block. The validator checks if the transactions in the block are accurate. If so, they add the block to the blockchain and receive crypto rewards for their contribution. However, if a validator proposes adding a block with inaccurate information, they lose some of their staked holdings as a penalty.
As an example, let's look at how this works with Cardano (ADA 4.51%), a major cryptocurrency that uses proof of stake.
Anyone who owns Cardano can stake it and set up their own validator node. When Cardano needs to verify blocks of transactions, its Ouroboros protocol selects a validator. The validator checks the block, adds it, and receives more Cardano for their trouble.
Mining power in proof of stake
Mining power in proof of stake
Mining power in proof of stake depends on the amount of coins a validator is staking. Participants who stake more coins are more likely to be chosen to add new blocks.
Each proof-of-stake protocol works differently in how it chooses validators. There's usually an element of randomization involved, and the selection process can also depend on other factors such as how long validators have been staking their coins.
Although anyone staking crypto could be chosen as a validator, the odds are very low if you're staking a comparatively small amount. If your coins make up 0.001% of the total amount that has been staked, then your likelihood of being chosen as a validator would be about 0.001%.
That's why most participants join staking pools. The staking pool's owner sets up the validator node, and a group of people pool their coins together for a better chance of winning new blocks. Rewards are split among the pool's participants. The pool owner may also take a small fee.
Proof of stake vs. proof of work
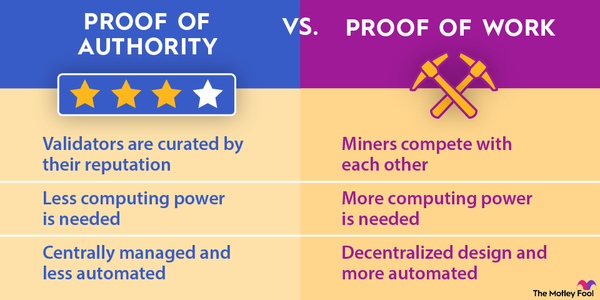
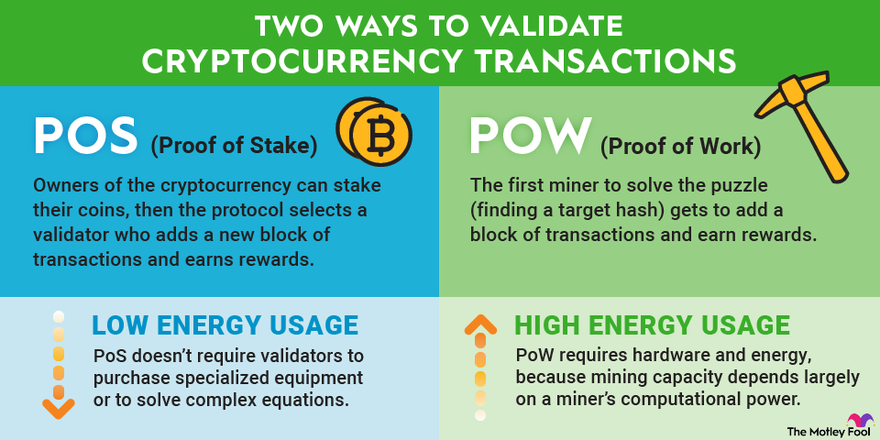
Proof of stake and proof of work are the two most common types of consensus mechanisms cryptocurrencies use. Proof of work was the method of choice for early cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin (BTC 5.56%), while proof of stake originated in 2012 with Peercoin (CRYPTO:PPC) and has become a common choice for altcoins.
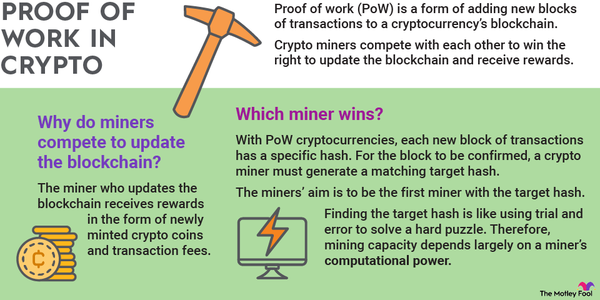
The biggest difference between proof of stake and proof of work is their energy usage. Proof of work requires miners to compete to solve complex mathematical problems. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add a block of transactions and earn rewards. This results in mining devices around the world computing the same problems and using substantial energy.
Since proof of stake doesn't require validators to all solve complex equations, it's a much more eco-friendly way to verify transactions.
Related investing topics
Pros and cons of proof of stake in crypto
Pros and cons of proof of stake in crypto
Here are the pros and cons of the proof-of-stake model:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Energy-efficient. | Not as proven in terms of security as proof of work. |
| Provides fast and inexpensive transaction processing. | Validators with large holdings can have excessive influence on transaction verification. |
| Doesn't require special equipment to participate. | Some proof-of-stake cryptocurrencies require locking up staked coins for a minimum amount of time. |
Proof-of-stake coins list
Proof-of-stake coins list
Here are examples of major cryptocurrencies that use proof of stake:
- Cardano is a research-driven blockchain platform that prioritizes security and sustainability.
- Tezos (XTZ 4.2%) is a programmable blockchain designed with an on-chain upgrade mechanism for adaptability.
- Algorand (ALGO 5.74%) uses a two-tier blockchain structure to offer processing speeds of 1,000 transactions per second.
Because of how it works, proof of stake benefits both the cryptocurrencies that use it and their investors. Cryptocurrencies that use proof of stake are able to process transactions quickly and at a low cost, which is key for scalability. Investors can stake their crypto to earn rewards, providing a form of passive income. And the fact that proof of stake is environmentally friendly means it will likely continue to grow more popular as a consensus mechanism.