Understanding the Cash Coverage Ratio and How to Calculate It
If your company has no debt requiring an interest payment, the cash coverage ratio is not useful. However, for those of you carrying debt with interest expense, it can be extremely useful.
The cash coverage ratio is an accounting ratio that is used to measure the ability of a company to cover their interest expense and whether there are sufficient funds available to pay interest and turn a profit.
Overview: What is the cash coverage ratio?
For companies that have interest expenses that need to be paid, the cash coverage ratio is used to determine whether the company has sufficient income to cover them.
Unlike the times interest earned ratio, which includes non-cash expenses such as depreciation and amortization in its calculation, the cash coverage ratio adds back any non-cash expenses to determine debt repayment capability.
All of the information you need to calculate the cash coverage ratio can be found in your income statement. For better financial statement accuracy, it’s always better to use accounting software to manage your financial transactions.
Types of coverage ratios
Coverage ratios are used as a method to measure the ability of a company to pay its current financial obligations. Along with the cash coverage ratio, there are a variety of other coverage ratios that can be used.
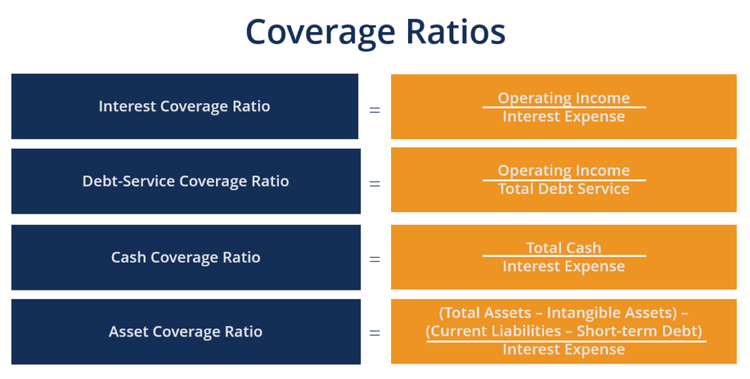
Several coverage ratios can be used to measure a company’s ability to pay its financial obligations. Image source: Author
1. Interest coverage ratio
Similar to the cash coverage ratio, the interest coverage ratio measures the ability of a business to pay interest expense on any debt that is carried.
However, unlike the cash coverage ratio, the interest coverage ratio uses operating income, which includes depreciation and amortization expense, when calculating the ratio results.
2. Debt service coverage ratio
The debt service coverage ratio takes a more encompassing approach by looking at the ability to pay not only interest expense but all debt obligations, including principal and interest on any loan.
3. Asset coverage ratio
Instead of using only cash and cash equivalents, the asset coverage ratio looks at the ability of a business to repay financial obligations using all assets instead of only cash or operating income.
How to calculate the cash coverage ratio
The formula for calculating the cash coverage ratio is:
(Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) + Depreciation Expense) ÷ Interest Expense = Cash Coverage Ratio
Before calculating the cash ratio, you’ll first have to calculate EBIT. The formula for calculating EBIT is:
Total Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold - Operating Expenses = EBIT
Once you’ve calculated EBIT, you‘ll need to add back any depreciation or amortization expenses. For example, if your EBIT number is $60,000, and your depreciation expense is $4,000, the total you’ll use to calculate your cash coverage ratio is $64,000.
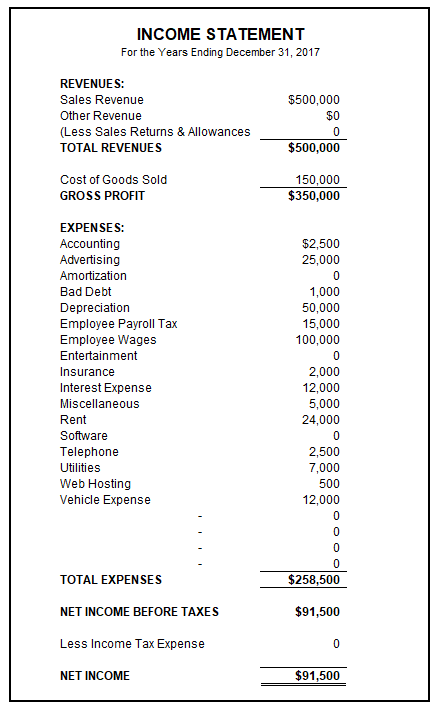
The income statement shows EBIT, or net income before taxes, which is used to calculate the cash coverage ratio. Image source: Author
Let’s go ahead and calculate the cash coverage ratio using the numbers from the income statement above. First we’ll take the net income amount of $91,000 and add depreciation expense of $50,000 back into the equation. We’ll then divide the total of $141,500 by the interest expense:
($91,500 + $50,000) ÷ $12,000 = 11.79
This result means that the business in question can cover its interest expenses nearly 12 times over, leaving more than enough in cash to cover other obligations.
The cash coverage ratio can be even more useful if tracked over time to determine trends. It is frequently used by lending institutions to determine whether a business is financially able to take on more debt.
The higher your cash coverage ratio, the better the financial condition your business is in. But how do you know when you should be concerned?
Any time that your cash coverage ratio drops below 2 can signal financial issues, while a drop below 1 means your business is in danger of defaulting on its debts. While a ratio of 1 is sufficient to cover interest expenses, it also means that there’s not enough cash to pay other expenses.
Business owners should aim for a ratio of 2 or above, which means that interest expenses can be covered two times over.
FAQs
-
If you have a very small business, or do not have any interest expense, you can forego calculating the cash coverage ratio. But if you do have interest expenses, the cash coverage ratio can be useful in determining if you have adequate income to cover them.
-
No. The cash ratio formula looks at current assets such as cash and cash equivalents and divides that total by current liabilities to determine whether your business can pay off short-term debt. The cash coverage ratio is more specialized and uses net income rather than cash assets.
It only takes into consideration the ability of your business to pay interest expense. While many small businesses would find the cash ratio useful, only those with debt repayment and interest expenses will need to use the cash coverage ratio.
-
Coverage ratios are used to measure the ability of your company to pay financial obligations. These obligations can include interest expense payments or all debt obligations, including the repayment of principal and interest.
While coverage ratios can be useful for businesses, particularly if calculated at regular intervals, coverage ratios are primarily used by lenders and other financial institutions to determine whether a company has the financial capacity to take on more debt.
Should you use the cash coverage ratio in your business?
The cash coverage ratio is not a ratio typically run by a small business bookkeeper. If you’re a sole proprietor or a very small business with no debt on the books, other accounting ratios are much more useful, such as current ratio or quick ratio.
However, if you have current debt and interest expense, calculating this ratio can be important, particularly if you’re looking to assume more debt with a large purchase or business expansion.
As with any ratio, it’s important to view the results cautiously, understanding that an accounting ratio often represents just a single area of your business. However, they are a helpful tool and can provide you with insight into business liquidity, which is an important metric for anyone who owns a business.
Alert: our top-rated cash back card now has 0% intro APR until 2025
This credit card is not just good – it’s so exceptional that our experts use it personally. It features a lengthy 0% intro APR period, a cash back rate of up to 5%, and all somehow for no annual fee! Click here to read our full review for free and apply in just 2 minutes.
Our Research Expert
We're firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. The Ascent does not cover all offers on the market. Editorial content from The Ascent is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.
Related Articles
View All Articles