How Cross-Selling Can Increase the Lifetime Value of Your Clients
E-commerce marketing of your store comes down to two basic functions: acquiring new customers and maximizing their lifetime value. Most marketing strategies will focus on acquisition, and most e-commerce strategies will highlight maximization of the return on each customer.
E-commerce technology has made it easy to start an online business, so your next challenge is to acquire prospects at a reasonable cost and maximize the average value of your customers. For the latter, let’s concentrate on lifetime value: the profits you make over the entire relationship you have with a client.
You can increase lifetime value via repeat purchases and prolonging the customer relationship. You can also maximize the value by increasing the size of each order. Enter the upsell and the cross-sell.

For e-commerce, the two basic marketing functions can be summarized as client acquisition and lifetime value maximization. Image source: Author
Overview: What is cross-selling?
Cross-selling is when a user is purchasing a product, and the vendor proposes an additional complementary product. So, here I am on Amazon, looking for hiking boots because I am going on a family vacation in the mountains.
Amazon uses various techniques to increase the order value of each client. Some recommendations on the bottom of the page are cross-sell proposals: “Looking for hiking boots? Users who bought these boots often bought this pair of socks with them.”
The technology Amazon uses is called “collaborative filtering” -- it looks at the purchase history of others who bought the product previously and identifies additional products often purchased by them.
Want to see an example of cross-selling? Search for a product on Amazon and click on the products it proposes. Check out some ink jet printers, some hiking boots, and how about a tent?
Or even better: Look for the category of the product you sell, and explore the cross-sell and upsell opportunities Amazon presents.
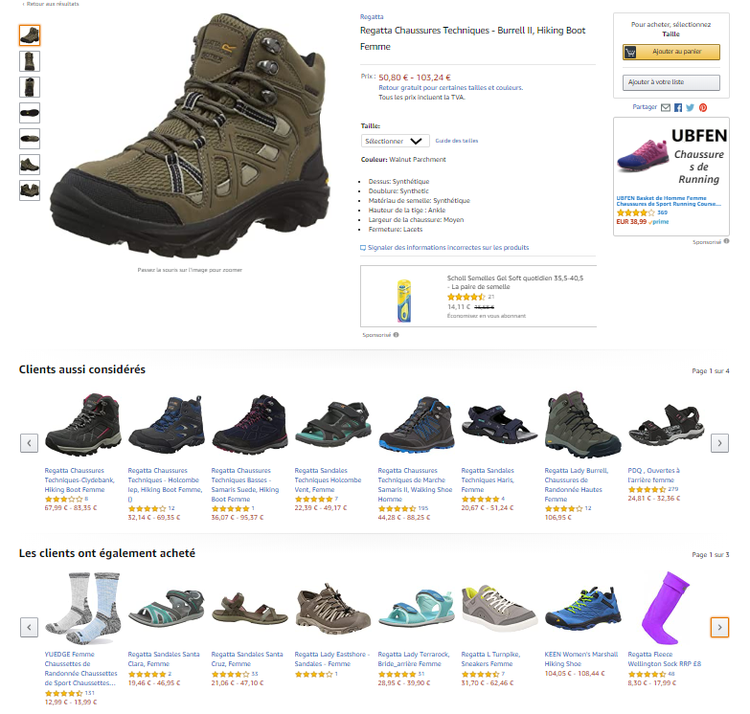
Amazon excels at cross-selling and always proposes complementary products. Image source: Author
Cross-selling vs. upselling: What's the difference?
To maximize client revenue during the buying process, you can use two similar techniques: upselling for buying a more expensive alternative and cross-selling for buying additional products. Sometimes it’s a fine line between the two approaches.
For example, you could consider the coffee capsules you buy with a coffee machine as either. You could argue that selling extra ink cartridges for a printer and batteries for any electronic device are upselling techniques.
- The clear-cut upsell is when the customer is convinced to buy a more expensive model or adding options on the basic product: You were going to buy a mini and you ended up buying a maxi.
- The clear-cut cross-sell is when you buy another product on top of the one you went shopping for. Cross-selling in retail is when you buy a pair of trousers and the salesperson persuades you to buy a shirt to go with it.
How does cross-selling work?
Amazon was first to explore cross-selling opportunities online, and they generalize it throughout their platform. When a user looks at a product, there is always one or more additional suggestions for other products.
They are typically presented under the main product presentation. Users scroll down, and once they’ve read the information about the product itself, they may be open to more suggestions.
This is where first upsell and next cross-sell opportunities can be presented if not already presented in a banner. Amazon is a prime example of a website experience that never ends: There is always an additional suggestion, an offer, a reminder of something you already looked at, so you don’t leave the platform.
How many times have you bought more products on Amazon than you originally intended? Me too.
6 cross-selling tips and best practices for small businesses
The most basic cross-selling approach is to enrich the product database with an extra field which holds information for related products. You can do this during the product positioning process. Collaborative filtering can be applied to a large dataset of purchase histories.
However, it’s much more complex. It allows you to recommend products based on buying behavior: “Users who liked the product you are buying also bought the following products: A, B, C.”
Cross-selling products in your online store impacts both design and functionality. On leading e-commerce platforms like Shopify or BigCommerce, this added functionality comes with the store template or via an app.
It requires real work to activate it. With this in mind, let’s look at some of the ways you can start cross-selling in your online store.
Tip 1: Hard code related products
In your product catalog, each entry comprises a product title, one or more images, a description, and perhaps a list of technical specifications. Your product database may already contain one or more fields to enter information about related products.
To use this approach, it helps to analyze past orders to see what products were often bundled or bought together.
If the online store is designed to always show one or two products, make sure you have enough information about related products so you don’t deteriorate the user experience with empty spaces or repetitive suggestions.
Tip 2: Cross-selling apps for e-commerce platforms
Most e-commerce platforms don’t offer native cross-selling functionality. Instead, they can be part of a store template or provided in a specific app for that purpose. The apps work as plug-ins and base recommendations either on relations you define, or on the buying history they have access to and can analyze.
The technology is evolving, as machine learning is used by more developers. Artificial intelligence improves their predictions of what second or third product a user may buy.
Don’t get carried away by the promises, though. If your product catalog is small, and you don’t have a lot of buying history data, their predictions will be of limited value.
Tip 3: Complementary product advertising
What if you don’t sell the best complementary products suggested? On Amazon, cross-selling can be done via advertising on other sellers’ product pages. When a user is looking for a product, complementary products are proposed in ads.
It works both ways: There are likely to be cross-selling ads on your own Amazon product page too.

On Amazon, advertising can be targeted to complementary products and perform a cross-selling function. Image source: Author
Tip 4: Post-purchase cross-selling
Many online store owners feel uncomfortable interrupting the user in their decision-making process.
I’m sure I’m not the only one who’s considered outright abandoning a flight ticket purchase when I have to click through an additional baggage upsell, an insurance upsell, a hotel booking cross-sell, and a car rental cross-sell page.
You can let the user complete the purchase and then suggest a cross-sell. Some tools allow you to do this via a thank-you page or a thank-you email. Your CRM tool may do this.
You will still need to define what complementary product to propose, but you can automate parts of the process and easily measure effectiveness and return.
Tip 5: Play around with machine learning
Have you been blinded by sales talk and frustrated by failed promises of great results with cross-selling solutions? Maybe it’s time to build your own.
Machine-learning algorithms and online database tools are inexpensive and can be used with any product catalog. You will need to get your hands dirty but will discover a wealth of opportunities. But before you do, make sure you have a significant dataset, the basic technical skills required, and patience.
Tip 6: Partnerships for bundling
Finally, why not partner up with providers of complementary products. You can pool marketing resources to have a stronger impact and both parties could get access to the other partner’s client database.
Cross-selling works for many, but not for all
Cross-selling is a basic and well-mastered technique for increasing average order value among merchants. It works best when you have a large catalog and buying history from your clients.
To make it work for you, start with the most basic forms before investing in dynamic and algorithm solutions. In today’s competitive environment, maximizing the value of each customer is essential. A well-organized cross-selling solution can help you do that.
Alert: our top-rated cash back card now has 0% intro APR until 2025
This credit card is not just good – it’s so exceptional that our experts use it personally. It features a lengthy 0% intro APR period, a cash back rate of up to 5%, and all somehow for no annual fee! Click here to read our full review for free and apply in just 2 minutes.
Our Research Expert
We're firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. The Ascent does not cover all offers on the market. Editorial content from The Ascent is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.
Related Articles
View All Articles