Asset management is a service offered by financial companies to oversee their clients' financial assets. Many asset managers decide how to administer a client's assets based on their investment strategy. Here's a closer look at asset management, what asset management firms do, how they make money, and some examples of asset managers.

What is asset management?
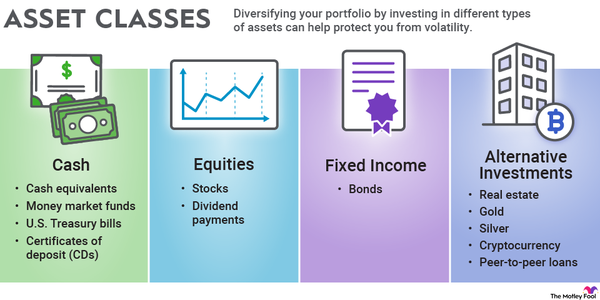
Asset management oversees financial assets owned by other organizations or individuals. An asset manager allocates a client's investments across the different asset classes based on their stated goals, strategy, and risk tolerance. Those asset classes include:
- Cash: Cash assets include cash equivalents, money market funds, U.S. Treasury bills, and certificates of deposit (CDs). Cash investments seek to preserve an investor's money.
- Fixed income: Fixed-income investments include various types of bonds like savings bonds, municipal bonds, Treasury bonds, and corporate bonds. Fixed-income investments strive to generate income for an investor at a fixed annual rate.
- Equities: Equity is an ownership interest in a business or other financial investment with capital appreciation potential. Equity investments include stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and mutual funds. Equity investments aim to deliver higher returns than fixed income through price appreciation.
- Alternative Investments: Alternative investments are investments offered outside the traditional banking system or public markets. Alternatives include real estate, precious metals, cryptocurrency, private equity, hedge funds, commodities, art, and forex (foreign exchange). Alternative investments aspire to produce higher returns than traditional equity and fixed-income investments.
What does an asset management firm do?
An asset manager oversees their client's financial assets and allocates them across the various asset classes based on their client's investment strategy, risk profile, and situation. Asset managers aim to grow their clients' assets by investing the money into fixed-income, equity, or alternative investments while taking on risks appropriate for their client's needs.
There are several types of asset managers, including:
- Registered Investment Advisers (RIAs): These firms advise clients on managing their portfolios and may make changes on a client's behalf.
- Investment brokers: These companies enable clients to buy stocks and other securities on their platforms. They don't make changes to a client's portfolio on their behalf but serve as a custodian over their assets.
- Financial advisors: These financial professionals advise clients on how to manage their assets. Some actively manage client accounts, while others only serve in an advisory role.
- Robo-advisors: These platforms use a computer program to automatically monitor and allocate assets on behalf of clients.
How do asset management companies make money?
Companies engaged in asset management typically charge clients administration fees for managing their assets. The most common structure is to levy fees based on a percentage of the assets under management (AUM). The average asset management fee is around 1% of a client's portfolio value. So, if a client had a $1 million portfolio, the asset manager would earn $10,000 in administration fees each year.
Some asset managers may also charge a fee for each trade they make on a client's behalf. Asset managers might also earn a commission for selling certain financial products to their clients, like mutual funds, insurance products, or annuities.
Finally, some asset managers earn a percentage of the return they generate for investors above a certain threshold. These profit-based earnings are known as a “promote” in a real estate investment and “carried interest” in private equity, hedge funds, and venture capital funds. For example, if a private real estate investment achieves its return threshold, the deal's sponsor will often split the profits with investors above that level (usually 70% to 80% to investors and 20% to 30% to the sponsor as their promote income).
Examples of asset management companies
Several companies focus on providing asset management services to clients. Some focus on managing traditional asset classes like fixed income and equities, while others concentrate on alternatives.
BlackRock (BLK 0.69%) is the biggest asset management firm. The company had nearly $8.6 billion in AUM at the end of 2022. That was down about 14% from the prior year due to falling asset values. The company provides asset management services to retail, ETF, and institutional clients across equity, fixed income, multi-asset, alternatives, and cash management products. Blackrock generated $17.9 billion of revenue in 2022, which included administration fees and other revenue sources like performance fees and advisory revenue.
Blackstone (BX -0.03%) is the largest alternative asset manager. The company ended 2022 with $975 billion in AUM (up 11% year over year) across real estate, private equity, hedge fund solutions, and private credit and insurance. Blackstone's clients include institutional and high-net-worth investors. The company produced $4.4 billion of fee-related earnings in 2022. In addition, Blackstone realized $3 billion of performance and investment income, which includes carried interest earned from its various funds.