Are You Well-Paid? Compare Your Salary to the Average U.S. Income
KEY POINTS
- National average income: The median household income in 2024 was $83,730, up 4% from the previous year.
- Highest paying jobs: 4 of the 5 highest paying jobs by median are all in the medical field and earn over $200,000 per year.
- U.S. income by gender: The median male earnings in 2024 was $71,090 compared to $57,520 for women.
The median household income in 2024 was $83,730, up 4% from the previous year, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. That's the first meaningful change in income, and increase, in recent years, when accounting for inflation.
While your industry and position largely dictate your earnings, you may want to know how your salary compares to the national average income of your peers or the general population. After all, the more you make, the more you can (usually) save for an emergency or retirement.
Wonder no more. Here's a deep dive into Americans' earnings by factors such as occupation, age, gender, and location so you can get a sense of how your paycheck stacks up.
Average U.S. household income: $121,000
The average U.S. household income in 2024 was $121,000, while the median household income was $83,730.
Adjusting for inflation, median household income rose 4% from 2023.
When the median is considerably lower than the average, it means that there are outliers on the top end. A few people who make a lot of money boost the average. The median income, $83,730 is a more accurate representation of typical household earnings.
Here's a more in-depth breakdown of what U.S. households are making:
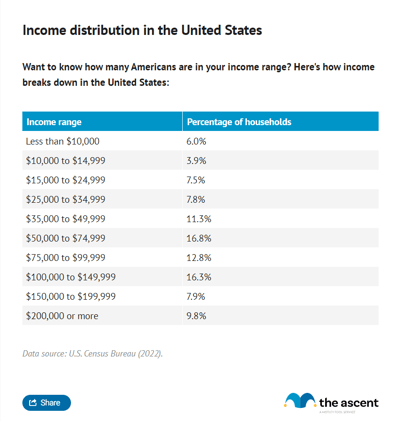
Forty-five percent of American households earn less than $75,000 per year. Forty-three percent earn $100,000 or more.
Average U.S. income versus average U.S. salary
With few exceptions, we aren't reporting the median and average salary in this article. Instead we're mostly reporting income. The U.S. Census Bureau tracks earnings, composed mostly of salary and wages, and income, which includes all sources of money that people bring in.
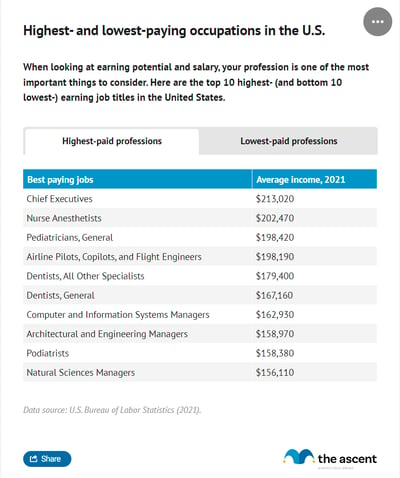
Lowest and highest paying jobs
The industry you work in largely influences your earnings potential. Not surprisingly, most of the top paying occupations require advanced degrees and specialized training. Here are the 10 highest-paying occupations and lowest-paying careers.
U.S. income by gender
The gender pay gap persists, with men continuing to out-earn women. Men earned a median salary of $71,090 while women earned $57,520, 81% of men's salaries.
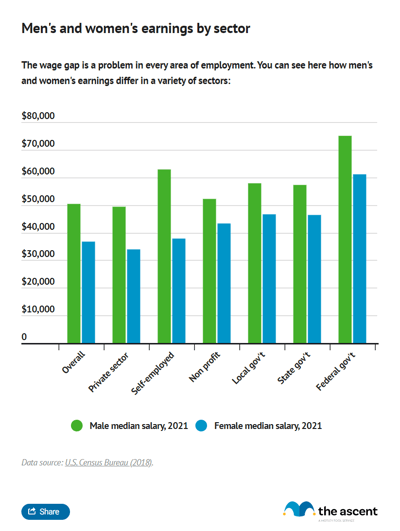
Men's earnings grew faster than women's from 2023 to 2024, 3.8% versus 1.5%, according to the Census Bureau.
Women's earnings have on average grown at a faster rate than men's since 1960 and the gender pay gap has shrunk from women earning about 60% of what men earned to 76% today.
The persistent gender pay gap is primarily a result of two issues: women earning less than men for the same jobs and women being more likely to have lower-paying jobs than men. The latter is more common than the former.
Another contributing factor is women more often than men taking time away from their careers after giving birth.
U.S. metro areas with the highest pay
Despite a shift towards remote work in recent years, breaking down median household income by metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs) reveals that geography still plays a significant role in earnings.
Americans in the San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland, California MSA earned a median income $125,105 in 2024 while those in the Middlesborough-Corbin, Kentucky MSA earned a median income of $46,740.
It's no surprise that other high-tech, high-cost-of-living regions like the the Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue MSA, Denver, and Boston and its metro area are among the 10 regions with the highest median incomes.
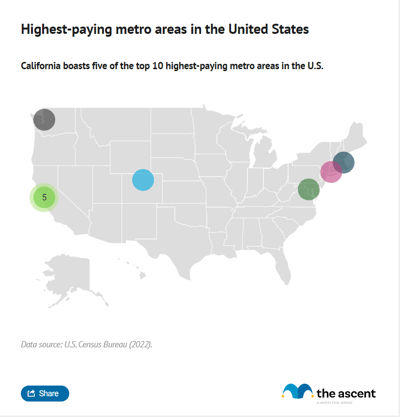
Of course, it's easy to be tempted to move to one of these metros in the hopes of snagging a massive pay boost. But remember, some of these cities are among the most expensive in the country to live in, so what you might gain in earnings, you'll likely end up spending on rent and other expenses. You may be better off finding a city that's known for high salaries and a low cost of living.
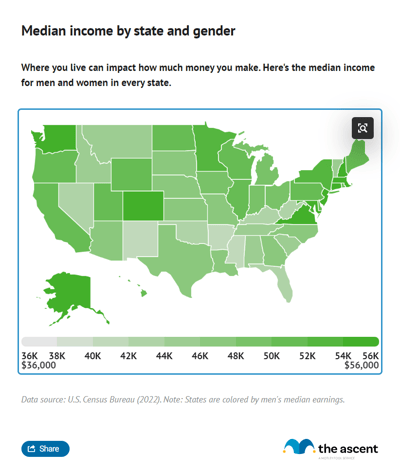
Median income by state
Income also varies by state -- the median household income in Massachusetts was $113,900 in 2024, while the median household income in Mississippi was roughly half that, at $55,980.
U.S. median income by family size
The average family income changes based on the number of people in your household. Larger families come with more expenses.
Here's how median family income in the U.S. income breaks down by family size:
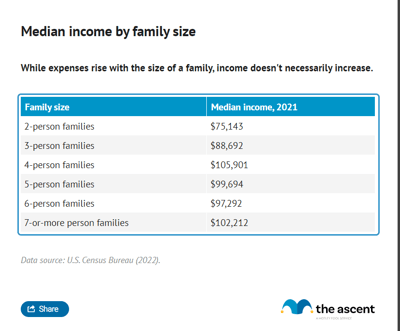
U.S. median family income peaks with four-person families at $139,900 and levels off at around $121,000 for families of five or larger. The largest jump in median income occurs between families of two and three.
The average family income is also highest for four-person families at $178,500.
U.S. income by number of wage earners
The number of wage earners in a family naturally affects median household income. The median income for families with one wage earner is $71,720, while with two wage earners the median income roughly doubles to $142,200.
Families with more wage earners unsurprisingly have a higher median income, although returns diminish above two wage earners. This is likely because high school or college-age children make up the additional wage earners and bring in much less than their parents.
The same trend is seen when looking at average income by wage earners. On average, families with one wage earner bring in $106,700, two wage earners net $182,700.
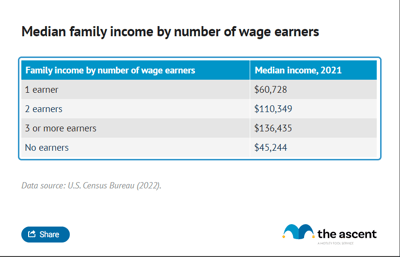
U.S. income by age
As workers progress in their careers their median income generally rises. But median income by age peaks before declining as Americans near retirement.
Here's a breakdown of median U.S. household income by age group:
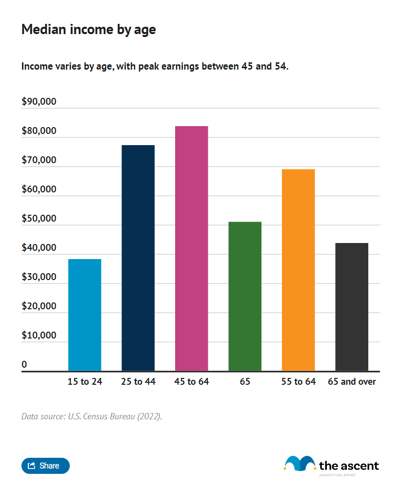
Americans earn most when they're aged 45 to 54 ($116,800), and they earn least when they're aged 15 to 24 ($60,310) or 65 or older ($56,680).
U.S. income by race
Looking at median household income by race, Asian Americans earn the most, making $121,700 a year, while Black or African American earners make the least, bringing in a median of $56,020. White Americans have a median income of $92,530. The median income of Hispanic Americans is $70,950.
Average incomes follow the same pattern. Asian Americans have the highest average income, $170,300, followed by white Americans ($129,800), Hispanic Americans ($99,340), and Black Americans ($56,020).
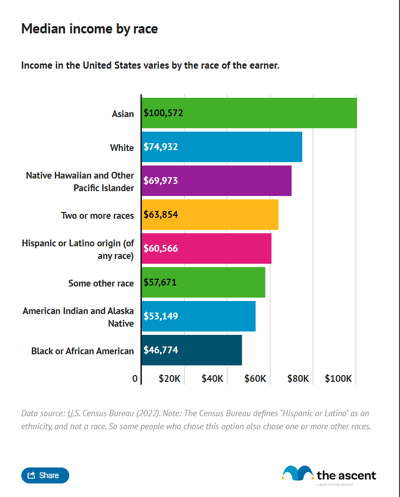
Examining income by race in America reflects racial disparities in education and opportunity more generally.
For example, fewer Black Americans aged 25 and older have completed high school or have a bachelor's degree than any other race other than Hispanic Americans, according to Pew. Meanwhile, a higher percentage of Asian Americans have reached those educational milestones than any other race, per Pew.
A similar percentage of white and Asian Americans live in poverty, while a much higher percentage of Black and Hispanic Americans live in poverty, which can make it more difficult to move up the income ladder.
U.S. income by education
Education plays a significant role in income. Those with a college degree or higher earn significantly more than those without one.
The median income for those with a high school diploma is $50,640 while those with a bachelor’s degree or higher earn $91,250, according to the Census Bureau.
How does your income stack up?
Now that you have a better sense of how much Americans earn on a national level and how those earnings break down by factors such as gender, race, age, occupation, and location, you can take a closer look at your circumstances and see if any changes are in order.
Drastic changes may not be necessary to earn more. If you're happy with your line of work and enjoy the area you live in, try learning new job skills to make yourself a more valuable employee. Doing so could result in a nice raise.
Similarly, research salary data for your industry and present it to your employer if you see that you're statistically underpaid given your position and line of work. And finally, don't hesitate to dust off your resume and see what opportunities are out there. You may find that there's a nearby company that will pay you what you're worth if your current employer won't.
And, of course, don't forget that it's not always how much money you make -- it's how you use it.
How to stretch your income
Here are a few steps you can take to passively boost your savings and make the most of your income:
- Pay down debt: Debt can make it difficult to save or invest.
- Budgeting apps can help uncover ways to cut costs and focus funds on paying off debt. Review our best budgeting apps to get organized and start saving.
- Balance transfer credit cards can simplify paying off credit card debt. We've compiled some of the best balance transfer credit cards to help you save while paying off debt.
- Personal loans can be used to consolidate high-interest debt into a single, likely lower-interest, line of credit. Our experts have reviewed and ranked some of the best personal loans for debt consolidation.
- A mortgage refinance could potentially net thousands in savings. Check out our list of some of the best mortgage refinance lenders to see if you can save.
2. Align credit card rewards with spending: Translate recurring expenses into cash back or other rewards by finding a credit card that fits your spending. If you're thinking of applying for a credit card, our experts have compiled some of the best credit cards.
3. Open a high-yield savings account: Review the best high-yield savings accounts to find a solution that keeps your money accessible and growing.
4. Open a brokerage account to invest for the long term: If you're interested in starting your investment journey, our experts put together a list of some of the best stock brokers.
-
Sources
- Pew (2021). "Racial and ethnic gaps in the U.S. persist on key demographic indicators."
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (2024). "May 2024 National Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates."
- U.S. Census Bureau (2024). American Community Survey - Table S1901, "Income in the Past 12 Months (in 2022 Inflation-Adjusted Dollars)."
- U.S. Census Bureau (2024). American Community Survey - Table S1903, "Income in the Past 12 Months (in 2022 Inflation-Adjusted Dollars)."
- U.S. Census Bureau (2025). Current Population Survey - Table A-1, A-2, and A-6 "Income in the United States: 2024."
- U.S. Census Bureau (2025). Current Population Survey - Table FINC-01, "Family Income in 2024."
Our Research Expert
Motley Fool Stock Disclosures
The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.