If you’ve ever used public Wi-Fi, say at a coffee shop, airport, or library, you’re vulnerable to a form of cyber threat called the man-in-the-middle attack (MITM).
The MITM attack is nefarious because it’s difficult to detect, and it gives a cybercriminal complete access to view your internet activities, including your emails.
For this reason, adopt the best endpoint security software to protect your computing devices. Read on to learn more about dealing with MITM attacks.
Overview: What is a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack?
The name of this cyberattack describes the scenario. There’s you, the website or person you’re connecting to online, and the criminal in between called the man in the middle (sometimes referred to, appropriately, as the monster in the middle).
The criminal hacks into the internet connection you’re using and spies on your online activities. You never know the criminal is there until they take action.
The MITM attack consists of two phases: interception and decryption.
- Interception kicks off the attack. In this phase, the cybercriminal works to intercept your online activities before you reach your intended destination.
- The decryption phase consists of the criminal quietly decoding stolen data and decrypting secure connections so you can’t tell there’s a monster in the middle.
The attack begins with the criminal gaining access to an IT network. A criminal can easily infiltrate a public Wi-Fi with no security.
They may even create an unsecured public Wi-Fi network. The criminal controls this network, using it to lure unsuspecting victims like a spider using its web to catch flies.
A MITM attack can redirect you from the website you wanted to visit to a fake one created to steal your login credentials. The criminal can even intercept your messages and respond to them without you realizing there’s an intruder.
A MITM attack can occur against individuals or businesses. For a business, a criminal uses this type of attack to infiltrate a company’s IT network, where they can quickly cause widespread damage.
The goal is to collect your personal information, such as passwords and bank accounts, or your company’s proprietary data. The criminal can use this information to steal money or your identity, make unauthorized purchases with your accounts, or simply wreak havoc.
Because victims aren’t aware they were compromised, a criminal can quietly perform their activities for weeks or months without detection. The IT security industry calls this type of attack an advanced persistent threat (APT).
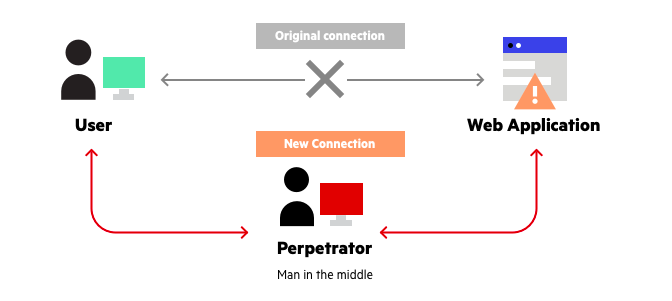
A man-in-the-middle attack intercepts and redirects your internet connection. Image source: Author
How to detect a MITM attack: 3 signs and symptoms
Since the criminal’s goal is to avoid detection, a MITM attack is extremely difficult to identify. You can pay security experts to execute threat hunting on a regular basis.
Otherwise, how do you discover you’re the victim of a MITM attack? A few telltale signs exist. Look for these warning signs that a cybercriminal is snooping into your connections.
1. Fake websites
Criminals use a MITM attack to send you to a web page or site they control. Since they only have access to your internet connection and the traffic coming from your device and not the contents of your computer, they need to trick you to get the information they want, such as your account login.
That’s where a fake website comes into play; they use it to make you think you’re at your intended destination. They also use fake sites to promote a free software download, but you’re actually downloading some type of malware used to gain access to your computer files.
To protect yourself, look for “https” at the start of the URL for every website you visit. If you’re going to a well-known site, such as your bank, and you don’t see the “https” protocol, it’s a cybercriminal trying to trick you.
Another sign of a fake website is its use of a URL that’s subtly different from the legitimate one. For example, you might be trying to get to google.com, but instead, you see a slight variation such as go0gle.com. That’s a sign your connection was intercepted and your traffic rerouted to the criminal’s fake site.
2. Intrusive popups
You go to a website, and suddenly a popup appears with an urgent message. It could claim your device is infected with a virus, or your computer needs a critical update. This dire warning insists you click a link to download a fix immediately.
Like the fake website scenario, if you click the link, you’re actually downloading malware. Unlike a fake website, the site you’re visiting may be legitimate. It’s the popup that the criminal inserted as part of their MITM attack.
3. Suspicious certificates
Every legitimate website has a certificate issued by a certification authority that verified the identity of the website owner. Browsers check for this certificate and warn you if it’s missing, invalid, or expired.
If your browser displays a certificate warning, it’s a sign you’re going to a website inserted by a criminal as part of a MITM attack. You should not proceed to the site.
Sometimes, a legitimate website forgets to renew this certificate. Don’t take a chance. Always avoid sites without updated certificates.
5 ways to prevent MITM attacks
The best way to stop MITM attacks is to take preventive steps. Read on to learn how to prevent cyberattacks such as MITM by adopting these actions.
1. Secure connections
A secure internet connection is your first line of defense. To that end, only visit websites with a secure HTTP connection using SSL (Secure Socket Layer) technology. The additional SSL protection prevents MITM attacks.
These sites are easily identified since the URL starts with “https://,” and not “http://.” Many browsers also show a padlock icon in the URL field as an indicator of a secure site. The HTTPS URL uses port 443 by default, which differs from the default port 80 used by unsecured sites.
Sticking with secure websites isn’t all you need to do. Avoid using any unsecured public Wi-Fi connections. With no security, these connections are easy for a criminal to hack and insert themselves between you and the websites you’re visiting.
Also avoid public Wi-Fi if security is lax, such as at a coffee shop. All a criminal needs to do is ask the barista for the Wi-Fi password. That’s no better than an unsecured network.
2. VPN
One of the best practices for network security is to use a VPN (virtual private network) when connecting online. A VPN encrypts the data you send online.
This encryption stops the MITM attack from infiltrating your network traffic. Even if a criminal manages to access your network, the encrypted data blocks them from reading your messages or knowing which websites you’re going to.
Every business should know how to set up a VPN and provide VPN software to staff, particularly those working remotely.
Another VPN benefit: If you must connect to public Wi-Fi, doing so through a VPN provides protection.
3. Endpoint security
Despite your best efforts, you or your staff can fall prey to MITM attacks. These attacks combine with malware to gain unrestricted access to your device or IT network.
Leverage strong endpoint security software to protect against these threats. The best security software, such as Kaspersky Endpoint Security, checks potentially dangerous websites and emails to help you avoid falling victim to a cyberattack. If your device or network becomes infected with malware, this security software steps in to defend you.
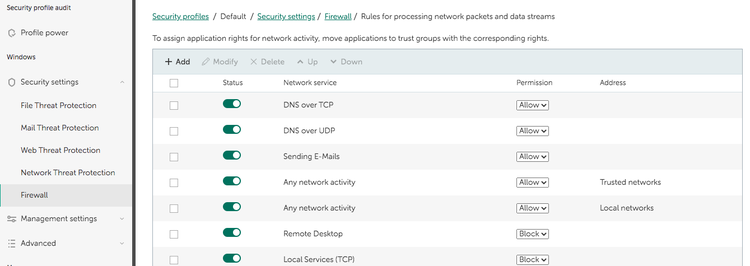
Kaspersky offers many security options, such as extensive rules for your firewall settings. Image source: Author
4. Multi-factor authentication
If you’re tricked by a MITM attack and the criminal gains your login credentials through a fake website, all is not lost if you use multi-factor authentication (MFA).
MFA is a security enhancement where you not only need your username and password to log into your account, you also use another form of verification. Examples include entering a PIN (personal identification number) or a special code texted to your mobile phone.
By requiring multiple ways to verify your identity beyond an easily stolen login, you block a criminal from gaining access to your information or money.
5. Education
Businesses are particularly vulnerable to MITM and other cyberattacks. Organizations are attractive targets for criminals, and unsuspecting employees can unwittingly open doors for these villains.
Educate staff members, particularly remote workers, about the dangers of a MITM attack. Let them know best practices, such as implementing a VPN, before going online and advise them to avoid public Wi-Fi networks.
Have a plan to routinely educate and remind your team about the latest cyber threats. The more you build safe online habits with your staff, the less likely your business suffers consequences from cyberattacks.
A last word about MITM attacks
MITM attacks are likely to grow more common as we connect additional devices to Wi-Fi networks. From the internet-connected smart doorbell to online protection systems, cybercriminals have increasing opportunities to hack our networks. And many of these newer devices have little or no security.
Adopting a preventive mindset and strictly adhering to secure connections will help to keep you, your business, and your staff safe from MITM and other cyber threats.
Our Small Business Expert
We're firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. The Ascent does not cover all offers on the market. Editorial content from The Ascent is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.