A balance sheet, like a profit and loss statement (income statement) and cash flow statement, is designed to be distributed to people outside of a company.
Bookkeepers and accountants should be preparing a balance sheet at the end of every accounting period particularly since GAAP rules require all U.S. corporations to issue a balance sheet report.
Used widely in accounting, balance sheet totals can provide business owners with solid information on the financial health of their business. In fact, balance sheets are used both internally and externally for a variety of reasons, including calculating working capital and monitoring operating expenses.
Balance sheet totals can also be used when performing any kind of accounting calculations such as accounting ratios or creating projections for your business. You’ll also find fixed costs such as loans and notes payable on a balance sheet.
Overview: Balance sheet definition
A balance sheet is a statement that shows the assets, liabilities, and equity of a business at a particular time. The statement is designed to show exactly what a company owns, what it owes, and how much money has been invested into the company by owners and investors.
A balance sheet is not affected by adjusting journal entries or closing entries, nor does your balance sheet directly affect your net income and your cash flow statement.
The balance sheet formula
If you’re familiar with popular accounting terms, you know that all of your general ledger accounts need to be classified as one of the following:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Income
- Expenses
- Equity/Capital
While income and expense accounts are found on your income statement, the balance sheet provides a summary of your business’ asset, liability, and equity accounts, providing the foundation for the balance sheet formula, which you remember is:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Unlike a cash flow statement or adjusted trial balance, the balance sheet is not typically used to create a budget or manage business expenses, but is instead designed to help business owners monitor assets, liabilities, and equity properly.
Elements of the balance sheet
The balance sheet offers three main elements: assets, liabilities, and equity, with the asset and liability elements further divided into two sections. The five elements include:
1. Assets
Assets are anything that your business owns. Examples of assets include cash accounts, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, furniture, and stock.
Assets are usually divided into two categories on your balance sheet, current assets and long-term assets. Current assets are considered anything that can be converted into cash quickly.
2. Long-term assets
Also known as fixed assets, long-term assets include land, machinery, equipment, as well as intangible assets such as patents and trademarks.
3. Liabilities
Liabilities are considered obligations that your business has. For example, liabilities include accounts payable, interest payable, wages and salary payable, and customer deposits.
Like assets, liabilities are divided into two categories on your balance sheet: current liabilities and long-term liabilities. Current liabilities are considered anything that is due to be paid within a year’s time.
4. Long-term liabilities
Long-term liabilities are obligations that will not be paid off in the coming year. Examples of long-term liabilities include loans and notes payable, though some notes payable may be considered a current liability if they are due and payable within a year.
5. Equity
Equity represents the amount of money that you or your investors have invested in the business. Also called capital, the equity account represents a company’s net worth. Added together with the liability total, it should match or balance with your total assets.
6. Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The assets on your balance sheet should always balance with the total of your company’s liabilities plus equity.
Example of a balance sheet
Midway Services Balance Sheet 12/31/2020
| ASSETS | |
|---|---|
| Current Assets | |
| Cash | $125,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | $ 80,000 |
| Inventory | $ 75,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $280,000 |
| Fixed Assets | |
| Building | $300,000 |
| Equipment | $100,000 |
| Total Fixed Assets | $400,000 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $680,000 |
| LIABILITIES | |
| Current Liabilities | |
| Accounts Payable | $ 45,000 |
| Interest Payable | $ 11,000 |
| Taxes Payable | $ 15,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $ 71,000 |
| Long Term Liabilities | |
| Notes Payable | $ 165,000 |
| Total Long Term Liabilities | $236,000 |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | |
| OWNER’S EQUITY | |
| Capital | $295,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $149,000 |
| TOTAL OWNER’S EQUITY | $444,000 |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & OWNER’S EQUITY | $680,000 |
How to create balance sheets for your small business
The easiest, most accurate way to create a balance sheet is by using accounting software. However, you can still create a balance sheet even if you’re using a manual accounting system or spreadsheet software. Here are a few options:
Method #1: By hand
Unless you have a very small business, it can be extremely difficult to prepare a balance sheet manually. However, if you are tracking your accounting transactions in separate ledgers, it is possible. First, you would take your current cash account balance and place that under current assets.
Any accounts receivable balances you may have would be placed under the current header as would any inventory you have in stock. Add these totals to arrive at your total current assets amount.
Next, if you’re tracking fixed assets, you’ll want to include the total of your fixed assets. Add your current and fixed asset totals to arrive at your assets total.
Next, you’ll follow the same process to calculate current and long-term liabilities. Items such as accounts payable are considered current liabilities, while notes payable or bank loans are considered long-term liabilities. Add these two figures together to come up with total liabilities.
Finally, you’ll need to calculate the amount of money you have invested in the company. Any money invested by others will also need to be included. You’ll add the equity number to the total liabilities number.
Your manual balance sheet should look like this:
| Assets | Amount |
|---|---|
| Cash | $ 12,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | 13,000 |
| Inventory | 5,000 |
| Fixed Assets | 16,000 |
| Total Assets | 46,000 |
| Liabilities & Equity | Amount |
| Accounts Payable | $ 9,000 |
| Notes Payable | 13,000 |
| Owner/Investor Equity | 24,000 |
| Total Liabilities & Equity | 46,000 |
Method #2: Use accounting software
By far, the easiest, and most accurate way to produce a balance sheet is to use accounting software. By tracking all of your transactions in your accounting software application, you can have an accurate balance sheet in seconds.
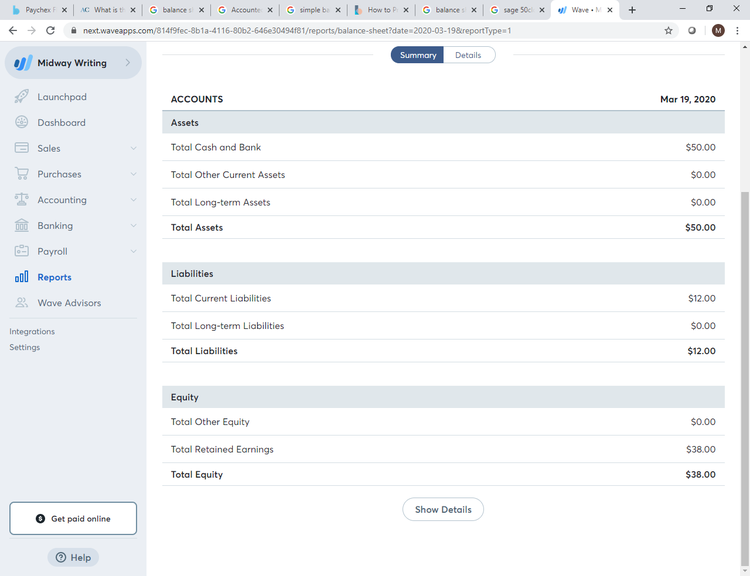
Wave Accounting offers both summary and detailed balance sheets. Image source: Author
From time-tested accounting software applications such as QuickBooks Desktop and Sage 50cloudaccounting (formerly Peachtree) to newer applications such as Wave Accounting and Xero, using accounting software is the best way to produce accurate financial statements such as a balance sheet.
Method #3: Spreadsheet
Preparing a balance sheet using spreadsheet software is really the same as preparing a balance sheet manually since you’ll still have to manually enter the totals, just as you did when using the manual method.
While having a template can speed the process considerably, you’ll still have to calculate the number and run the risk of error.
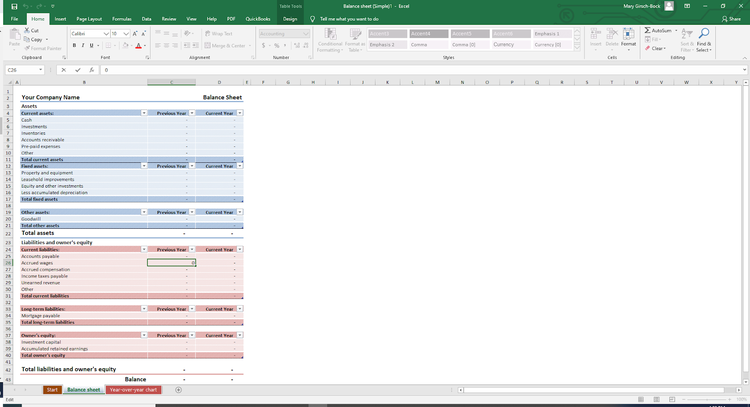
Microsoft Excel offers a balance sheet template for those not using accounting software. Image source: Author
Final thoughts on the balance sheet
The balance sheet, like the cash flow statement and the income statement, are all required by GAAP rules. The balance sheet is designed to display assets, liabilities, and equity totals for a business at any specific time, making it particularly valuable to financial institutions, current and potential investors, and company management.
If you’re struggling to create a balance sheet using a manual system or spreadsheet software, why not consider moving to accounting software, which makes it easy to create all the financial statements you need for your business.
Our Small Business Expert
We're firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. The Ascent, a Motley Fool service, does not cover all offers on the market. The Ascent has a dedicated team of editors and analysts focused on personal finance, and they follow the same set of publishing standards and editorial integrity while maintaining professional separation from the analysts and editors on other Motley Fool brands.