The primary insurance amount is the monthly payment someone will receive from Social Security if they claim their benefit at full retirement age. The amount is based on past earnings, adjusted for inflation. The primary insurance amount is used to determine a claimant's monthly benefit based on the age at which they claim.
What is a primary insurance amount?
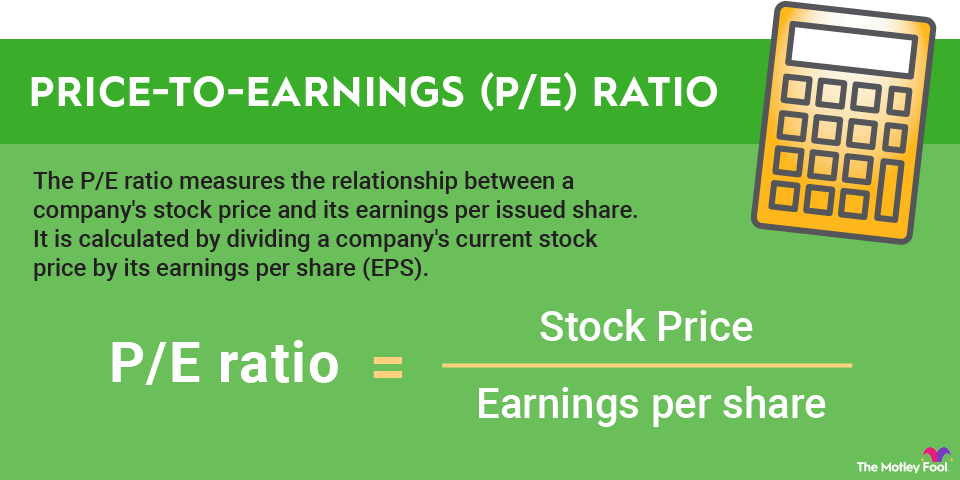
A primary insurance amount, or PIA, is the monthly Social Security benefit you'll receive at full retirement age.
The Social Security Administration uses a formula to determine an individual's primary insurance amount based on their past earnings. It indexes earnings for inflation and determines a percentage of your past earnings to pay out as a Social Security retirement benefit.
The PIA is used as the base benefit for calculating how much to pay if someone claims early or delays Social Security beyond full retirement age.
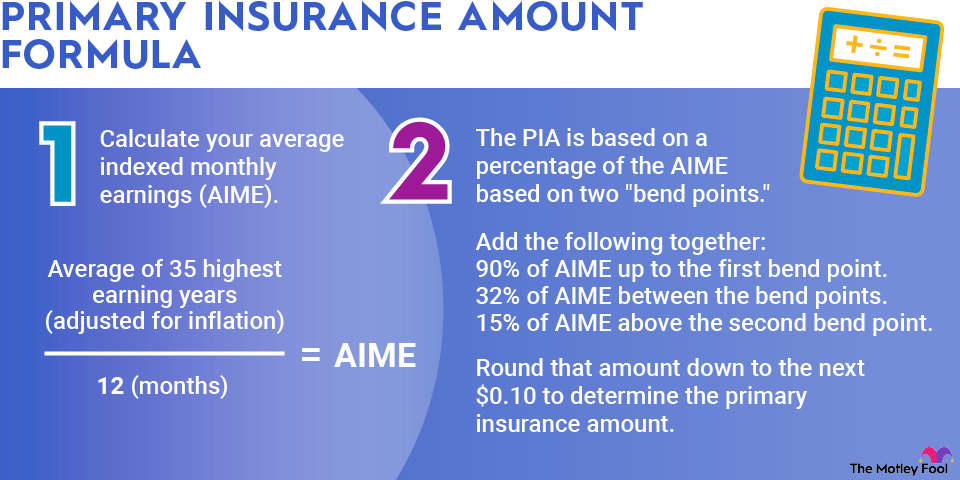
Primary insurance amount formula
The primary insurance amount formula first requires calculating the average indexed monthly earnings (AIME).
The AIME takes the average of a person's 35 highest-earning years adjusted for inflation and divides by 12, the number of months in a year. The inflation index is based on the national average salary from two years prior.
After calculating the AIME, the primary insurance amount is based on a percentage of the AIME based on two "bend points." The calculation takes the sum of the following:
- 90% of AIME up to the first bend point.
- 32% of AIME between the bend points.
- 15% of AIME above the second bend point.
For 2023, the bend points are $1,115 and $6,721.
The amount is then rounded down to the next $0.10 to determine the primary insurance amount.
Maximizing the primary insurance amount
Maximizing the primary insurance amount requires earning a high income for 35 years during your career.
There's a maximum amount of income that pays Social Security tax. The amount changes every year, adjusting for inflation. For 2025, the maximum is $176,100 in taxable wages.
Since the AIME is based on your top 35 years of earnings, it'll require you to reach a highly paid position relatively early in life and continue working for a long time.
The maximum primary insurance amount in 2025 is $4,018.
Related investing topics
Example of the primary insurance amount
If you've reached all the qualifications to claim Social Security benefits, you'll be interested in determining your primary insurance amount.
The first step is gathering an earnings history. Anyone can view their Social Security statement online by setting up an account with the Social Security Administration. Once you've established an account, you can view your entire earnings record.
Take your annual wages and multiply them by the percentage increase in the average wage index since the year they were earned. The SSA provides that data on its website.
Then, select the 35 highest-earning years, add them together, and divide by 420 (the number of months in 35 years). If you don't have 35 years of earnings, add all your earnings and divide by 420.
That's your AIME. Let's say your AIME came out to be $7,000.
The next step is to calculate the primary insurance amount.
Use the bend points to make the calculation. So, in this example, you'll take 90% of $1,115 (the first bend point in 2023) plus 32% of $5,606 (the difference between the bend points) and 15% of $279, the amount above the second bend point. The sum total is $2,839.27. You round that down to $2,839.20 to get your primary insurance amount.
You can also use the tools on the Social Security Administration's website to determine your PIA, but understanding the factors that go into it and how it's calculated can help you make better decisions on how long to work and when to claim Social Security.