The semiconductor industry has played a pivotal role in the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) technology. From training popular AI models to running inference applications in data centers to powering AI workloads on edge devices such as smartphones, personal computers, and cars, semiconductors do the heavy lifting by performing large amounts of calculations quickly.
Different types of chips are tackling AI workloads in the applications mentioned above. They include central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), and specialized chips known as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). Companies that design these chips, such as Nvidia, Advanced Micro Devices, and Broadcom, have seen solid acceleration in growth in recent years.

Image source: Getty Images.
It's important to note, however, that all the above-mentioned names are fabless chipmakers, which means that they only design the chips and don't manufacture them. The manufacturing is done by their foundry partner -- Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM 2.66%). Popularly known as TSMC, this Taiwan-based foundry giant has played a pioneering role in the spread of this technology.
Let's see why TSMC is probably the most important semiconductor company out there and has the potential to redefine the AI industry by the end of the decade.

NYSE: TSM
Key Data Points
TSMC's advanced nodes play a key role in the expansion of AI
TSMC's fabrication plants produce chips using different process nodes. Advanced process nodes tend to pack more transistors into a single chip. As a result, these chips can deliver more computing power and reduce energy consumption simultaneously.
Nvidia's A100 data center GPU, which was used for training ChatGPT, was manufactured on TSMC's 7-nanometer (nm) process node. Nvidia is now reportedly using TSMC's 4nm process node to manufacture its latest generation of Blackwell AI GPUs. These new GPUs deliver a significant jump in performance and power efficiency over the previous generation of chips that were based on a 5nm process.
So, TSMC enabled Nvidia to enhance the performance of its latest processors by moving to a better process node. As a result, companies designing chips using TSMC's advanced process nodes can train bigger models and run AI inference applications more efficiently in data centers. At a time when AI models are becoming more efficient and concerns are being raised about the amount of power consumed by AI data centers, the need for advanced computing chips that TSMC makes is going to increase.
This is precisely the reason TSMC has been able to consistently increase its share of the global foundry market. It controlled an impressive 70.2% of the global foundry market in the second quarter, up by 260 basis points from Q1.
The second-place foundry player, Samsung, has a market share of just 7.3%. That's not surprising as the Korean company's process nodes are reportedly inferior to TSMC's in terms of performance. But TSMC isn't done pushing the envelope yet.
More advanced process nodes are on the way
TSMC's 3nm nodes are being widely used by Apple, Qualcomm, and other chip designers. The company is expected to start producing chips on an even better 2nm process node this year, promising a 15% improvement in transistor density over the 3nm node. As a result, TSMC's 2nm chips could reduce power consumption by 25% to 30% and enhance performance by 10% to 15% over the prior-generation chips.
But that's not where the company is going to stop. TSMC management estimates that it can move to a 1.6nm chip node by the end of 2026, followed by a 1.4nm node in 2028. The company claims that the 1.4nm process "will offer up to a 15% speed improvement at the same power, or up to a 30% power reduction at the same speed, along with more than a 20% increase in logic density" as compared to the 2nm process.
And finally, TSMC estimates that it can move to an even smaller 1nm node by 2030. What this means is that TSMC's customers can make even more powerful chips in the future with lower power consumption. This should ideally enable TSMC to increase its share of the global foundry market in the long run, setting the company up for outstanding growth going forward.
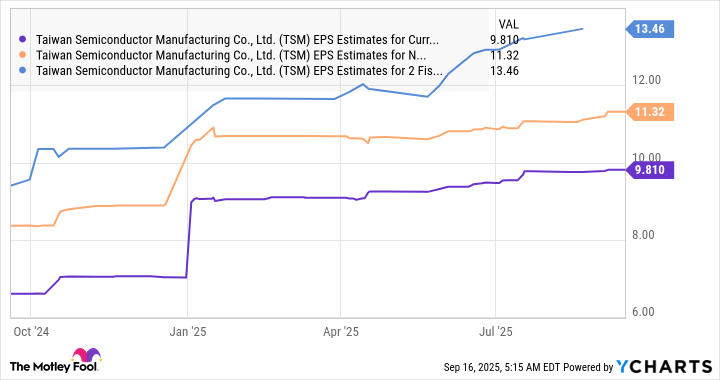
Not surprisingly, consensus analyst estimates project TSMC's earnings growth will accelerate.
Data by YCharts.
It can sustain this healthy growth rate through the end of the decade thanks to its product roadmap discussed above. Assuming TSMC can increase its earnings at an annual rate of 20% in 2029 and 2030, its bottom line could hit $19.38 per share in 2030 (from $13.46 in 2028). Multiplying that by the tech-heavy Nasdaq-100 index's forward earnings multiple of 26 points toward a stock price of $511 after five years, a potential jump of 92% from current levels.
Given that TSMC stock trades at just 22 times forward earnings right now, investors are getting a great deal on this semiconductor stock. They should consider buying TSMC stock right away, considering its attractive valuation, as the company's ability to redefine the industry with even more advanced chips over the next five years could lead to stronger-than-expected earnings growth, and that could result in a sharper jump in its stock price than predicted above.