A debit card is a payment card linked to a bank account, most often a checking account. You can use it to withdraw cash at ATMs and to make purchases at merchants that accept this type of payment method. When you use your debit card, the money for the transaction is deducted from your bank account.

Understanding debit cards
Debit cards normally come with checking accounts and money market accounts. Some banks and credit unions also offer savings accounts with debit cards, although this is fairly uncommon. Financial institutions generally issue your debit card when you open your account. You may need to activate your debit card, and you'll need to set up a personal identification number (PIN) that you enter for transactions.
Your bank account balance is the amount you can spend with your debit card, unless you opt into overdrafts, which can carry an additional fee. Many banks also have debit card purchase limits and ATM withdrawal limits. These limits and other important information will be in your debit card agreement.
Debit cards versus credit cards
Debit cards and credit cards are the two most common types of payment cards in the U.S., and they look very similar. However, they have several notable differences.
A credit card is a revolving line of credit. When you use a credit card, you're borrowing money from the card issuer and must pay it back later. The card issuer can charge you interest, although credit cards typically have a grace period during which you can pay off your balance without having to pay interest. You may not be able to withdraw cash with a credit card, and even if you can, it's rarely a good idea. Credit card cash advances have extra fees and high interest rates.
With a debit card, you're spending your own money. Since you're not borrowing anything, there's no interest and no risk of getting into debt. However, debit cards are also lacking some of the benefits that credit cards offer. You can't build credit using a debit card, like you can with a credit card. Debit cards also don't have the kind of rewards and bonus opportunities available with many credit cards. But for those who struggle to manage credit without going into debt, a debit card is often the safer option.
How to use a debit card
Since your debit card is linked to your bank account, it's important to keep track of your balance. A mobile banking app is an easy way to do this and prevent declined transactions or overdrafts.
For security, never share your PIN with anyone. If your debit card is lost or stolen, report it to your bank right away. Your bank can then cancel the card and send you a replacement. Reporting a lost debit card promptly also limits your liability for debit card fraud.
When you need to withdraw cash, try to do it at an ATM that's in your bank's network. In-network ATM withdrawals usually don't have any additional fees. If you use an out-of-network ATM, you could be charged ATM fees. Check your bank's website or mobile banking app to find in-network ATM options.
Related investing topics
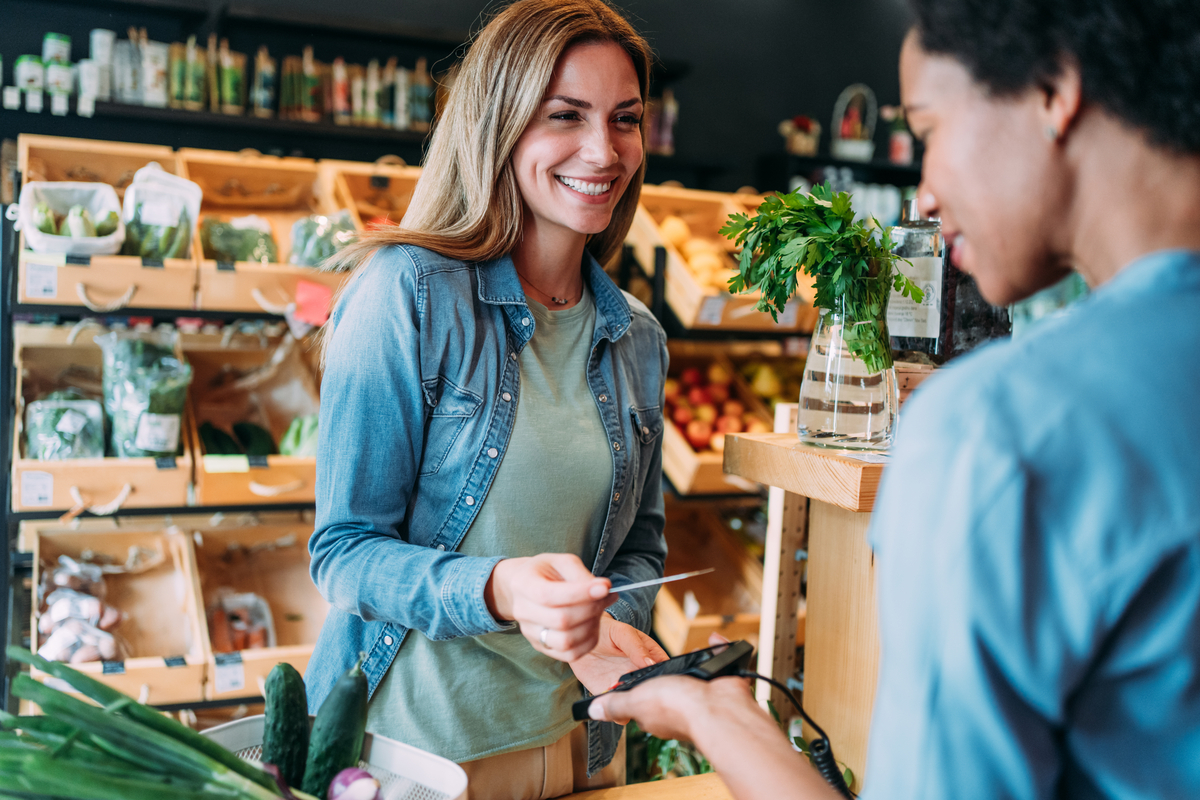
Example of a debit card transaction
Imagine you have $1,000 in your checking account. You go to the grocery store and ring up a bill of $200. You also decide you want to get $50 in cash back, which is an option that's available when you pay by debit card.
You tap, insert, or swipe your debit card at the payment terminal, enter the PIN, and choose the option to get $50 in cash back. Your total transaction amount is $250 with the cash back and the $200 in groceries. Your bank would approve the purchase and deduct $250 from your checking account, leaving you with $750. As you can see, using a debit card is a straightforward process.