It might not look like it based on Transocean's (RIG +1.02%) most recent earnings reports, but the company is making some very large strides to improve its position in the rig market. While once seen as a company with an extremely old, ineffective fleet, Transocean now looks younger, leaner, and ready to position itself for the upturn in the offshore market.
In fact, Transocean is so confident in its current position that it thinks it can do something that has been almost completely unheard of in recent years: According to executives in its fourth-quarter earnings call, it's ready to make an acquisition. Here are some notable quotes from the call that illustrate what management is thinking.

Image source: Getty Images.
Taking the lion's share of the market
There hasn't been a lot of new work for rigs out there. So even the shortest, cheapest contract can be helpful in putting some cash in the coffers. According to Transocean CEO Jeremy Thigpen, the company has actually been doing a rather remarkable job of capturing what little work that is available:
I'd also like to thank our marketing contracts team, which in 2016 despite intense competition, won roughly one-third of the contracted global floater fixtures. The combination of our long-standing and deep customer relationships, our global footprint, our excellent operational performance and our internal confidence to offer innovative commercial models helped us to capture market share in this challenging market without bidding below cash breakeven dayrates. Of note, we were also able to secure contracts for two cold-stacked rigs when our competitors had hot rigs that were available.
It may not be showing up much in the bottom line of Transocean's results, but keeping rigs working at even the most modest profits will go a long way for any rig company, especially since we have yet to hit the bottom of the market.
Changing the game
As the offshore rig industry goes through this deep downturn, one of the silver linings is that it is forcing companies to think of better ways to operate. One thing that Transocean is looking to do is coordinate more with its suppliers and equipment manufacturers to lower operational downtime and maintenance costs. According to Thigpen, the company is trying a novel approach:
[W]e are more closely collaborating with our supply partners, and leveraging our respective strength to further enhance our riser inspection maintenance program and proven optimized [blowout preventer] performance, further improve reliability and reduce the total cost of ownership over the lives of the assets. We will accomplish these joint objectives by migrating our service model to reflect actual use in lieu of a more traditional calendar-based approach to service and maintenance. This reliability-centered approach has been approved by [Det Norske Veritas], and being embraced by the respective [original equipment manufacturers]. Ultimately, through closer collaboration, coordination and the aligning of incentives, we are confident that we can further improve rig uptime while reducing our operating costs.
Transocean isn't the only company taking this kind of approach to equipment performance. In 2016, Diamond Offshore (DO +0.00%) signed an agreement with General Electric (GE +2.65%) where it sold its blowout preventers back to GE and, in exchange, will lease them from GE. The idea here is that the OEM will have a better understanding of the equipment itself and will be more in tune with the maintenance needs. It also puts skin in the game for the OEM, as it is only paid for when the equipment is in use.
This seems to be a trend taking hold across the industry, so don't be surprised if we see more offshore rig owners move toward these equipment leasing options in the future.
The turning point
Probably the thing that investors care about more than anything else is when we can expect the market to turn for offshore operators. Based on Thigpen's statements, 2017 isn't going to be the year. Integrated oil and gas companies (think ExxonMobil and Chevron) represent the bulk of offshore development money, and those players don't have much of their budget dedicated to offshore work and reserve replacement. But Thigpen's more optimistic about 2018:
As we looked toward 2018, we're increasingly encouraged. The [integrated oil companies], which represent the majority of the offshore and specifically, the Deepwater market, recognize that their future is ultimately dependent on reserve replacement and production growth, yet 2017 will represent the third consecutive year of reduced capital spending and underinvestment in core high-return assets. As such, we expect the natural course of accelerating depletion to narrow the gap between the supply and demand of oil, and place upward pressure on its price, ultimately encourage incremental activity. Additionally, by 2018, we as an industry, will have further streamlined our organization and our processes, realizing additional performance improvement in cost savings that will result in even lower breakeven for our customers.
Still turning over the fleet
Transocean has been the most aggressive company in terms of scrapping older rigs that probably won't have much use in the future. The demands from operators today mean only the highest-specification rigs get work. As much work Transocean has done in right-sizing its fleet, Thigpen admits there is still lots of progress left to be made by the industry as a whole:
Still, with approximately 315 floaters in the current market, which includes those under construction, we as an industry remain oversupplied, even when considering the more optimistic estimates of recovery. Although we cannot accurately predict what others will do as the market unfolds, we will continue to be very pragmatic in evaluating both our rigs rolling off contract and our assets that are currently stacked. As we identify rig that no longer fulfills our fleet strategy and/or does not best address what we believed to be our customers' specific demand, we will continue to quickly make the decision to recycle it.
Transocean's most recent rig report showed it had nine older rigs that are only deepwater and midwater capable.These are the most likely candidates to be recycled. Some are still under contract, though, so don't expect them to be sent to the scrap yard before their contracts are up.
Time to buy?
This was probably the most interesting quote from the whole earnings call. Thanks to Transocean's efforts to right size the fleet, delay delivery of some rigs under construction, and maintain a strong balance sheet, Thigpen actually sees a ripe opportunity to make some acquisitions:
In addition to retiring less-marketable assets, there is a significant number of high specification rigs, either in the possession of the stressed market participants or shipyards that could enhance our overall fleet and competitive position. We will continue to evaluate these assets, and remain ready to act under the right circumstances.
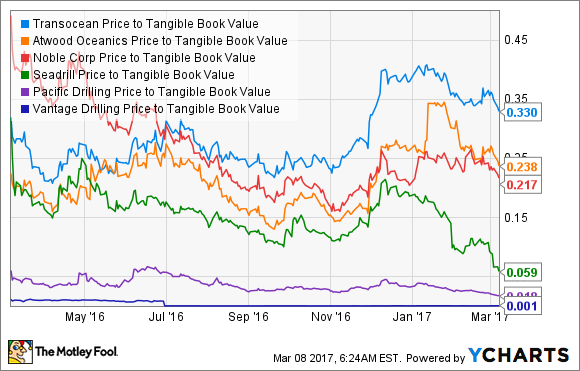
Thigpen went on to say that there two ways Transocean can deal with this. Either it can use cash to take over a shipyard delivery that was supposed to go to another player, or it could use its equity to absorb a competitor. Using equity today isn't ideal -- shares are trading for the absurdly cheap valuation of 0.31 times tangible book value -- but even that low share price is better than some of its peers.
RIG Price to Tangible Book Value data by YCharts.
If the company is going to make those kinds of deals, though, CFO Mark Mey thinks the company will need to act fast to get the best deal possible.
[Y]ou cannot wait too long because the opportunity may not be there for you. So you have to make a pre-emptive strike. I think Transocean, given our marketing presence and market intelligence, we probably have the best information out there, and probably get a look before most people do. So I think when we do decide to go out and strike, you can read that as a sign that we think the market is certainly troughed and improving from there.
Transocean has pretty much been the only company as of late to discuss the possibility of making an acquisition right now, which shows what kind of strength it has in the market in general. If this isn't a sign that the company is one of the best-positioned to bounce back in the offshore drilling industry, I'm not sure what is.