Gross margin vs. gross profit: What is the difference?
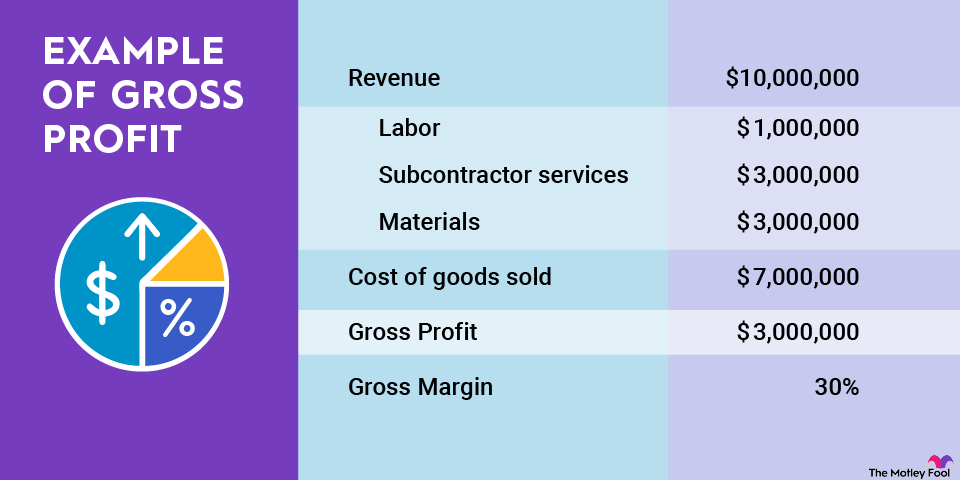
There can be some confusion between gross margin and gross profit. Gross profit is a measure of absolute value, while gross margin is a ratio. Gross profit is simply the difference between a company's sales and its direct selling costs, and a company's gross margin is its gross profit expressed as a percentage of sales. Gross margin puts gross profit into context by taking the company's sales volume into account.
How to use gross margin to evaluate a company
Margins are metrics that assess a company's efficiency in converting sales to profits. Different types of margins, including operating margin and net profit margin, focus on separate stages and aspects of the business. Gross margin gives insight into a company's ability to efficiently control its production costs, which should help the company to produce higher profits farther down the income statement.
Calculating gross margin is useful for comparison purposes. Determining a company's gross margins for multiple reporting periods provides insight into whether the company's operations are becoming more or less efficient. Determining the gross margins of multiple companies within the same industry is another type of comparison, and it can help you to understand which market participants have the most efficient operations.
What are the limitations to gross margin?
While calculating gross margin can be helpful for evaluating a company's reporting periods or similar companies, the metric has more limited value when comparing companies in different industries. Capital-intensive industries, like manufacturing and mining, often have high costs of goods sold, which translates to relatively low gross margins. Others, like the tech industry, that have minimal costs of goods typically produce high gross margins.
Related investing topics