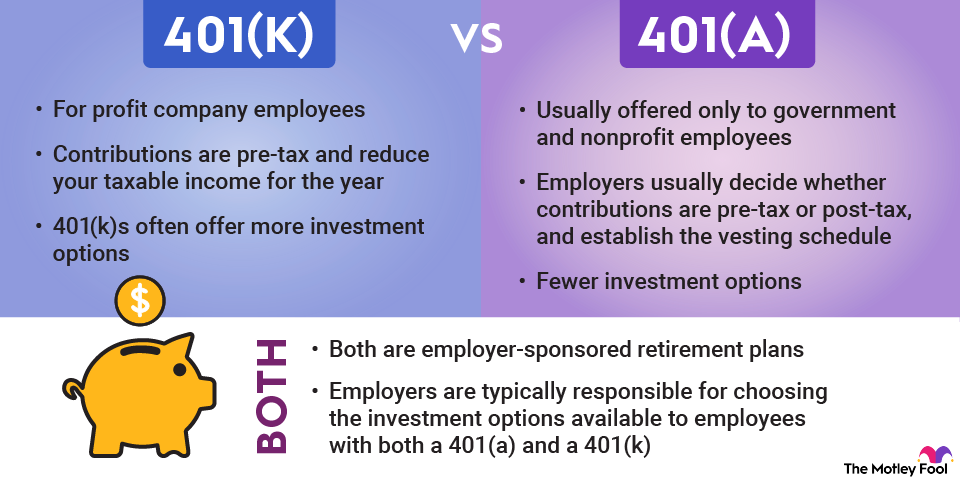
Any mandatory contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, while voluntary contributions are made with after-tax money. Voluntary employee contributions are capped at 25% of the worker’s income. In 2023, only the first $330,000 of income can be considered for the purposes of calculating contributions, up from $305,000 in 2022.
When you leave an employer that offers a 401(a) plan, you’re allowed to roll over your money into an individual retirement account (IRA) or another qualified retirement plan, such as a 401(k), 403(b), or a different employer’s 401(a).
But if you withdraw your money before age 59 ½, expect to pay a 10% penalty on top of income taxes. Your employer is required to withhold 20% of an early withdrawal for tax purposes, so if you took a $20,000 distribution, you’d only receive $16,000. Depending on your plan’s rules, a 401(a) loan may be allowed.
If the account is funded with pre-tax dollars, you’ll owe income taxes on distributions when you retire. You’ll also be required to take required minimum distributions (RMDs) at age 73. However, under the Secure Act 2.0, RMD age will increase to 75 by 2033.
Related investing topics