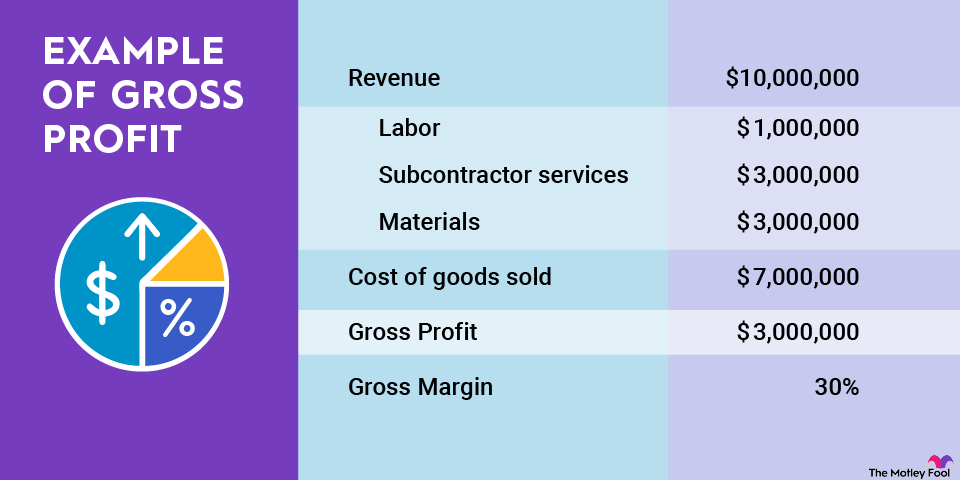
What you get is the proportion of each dollar of revenue that the company retains as gross profit. The raw number is a decimal ratio, which you can convert into an easy-to-read percentage. Simply multiply it by 100.
A higher gross profit margin indicates that the company is generating more gross profit for each dollar of revenue, while a lower margin means it's retaining less profit at this stage.
Why is gross profit margin important?
Gross profit margin is a useful financial metric because it reveals a company's ability to generate profit from its core operations. By understanding the gross profit margin, investors can gain insights into a company's cost structure, pricing strategy, and operational efficiency.
A higher gross profit margin suggests that the company is efficiently managing its cost of goods sold. That could be a result of efficient production processes, strategic sourcing, or favorable pricing. On the other hand, a lower margin might indicate systemic trouble or a dramatically different business plan in the same categories.
You should also weigh a company's gross profit margin against those of its competitors. Can this company demand a much higher gross margin than its head-to-head rivals? Cool -- you’re looking at a market leader that can charge a premium price for its products or services.
You also should keep an eye out for large changes over time -- and especially for sudden jumps or drops. Dig deeper to find the underlying reasons for those unexpected shifts. In many cases, you’ll learn something important about the business model this way.