Operating margin measures the percentage of revenue a company keeps as operating profit. This is an important metric because it indicates to investors the profitability of a business and offers a convenient way to compare competing businesses or different industries.
What is operating margin?
To understand operating margin, sometimes called operating profit margin, first let's define operating profit. Operating profit equals revenue minus the cost of goods sold and operating expenses, which typically include selling, general, and administrative costs; sales and marketing; research and development; and depreciation and amortization. EBIT, or earnings before interest and taxes, is sometimes used as stand-in terminology for operating income.
Operating margin differs from net profit margin, which is the bottom line figure, because net profit subtracts for expenses like interest and taxes in addition to non-core business activities like gains or losses on investments and revaluations of debt. Because operating margin is much more consistent across reporting periods than net profit margin, it's a better reflection of the strength of the underlying business.
Gross margin, also distinct from operating margin, is another important profitability ratio investors should know. Gross margin is the measure of gross profit divided by revenue, with gross profit equal to revenue minus the cost of goods sold.
How to calculate operating margin
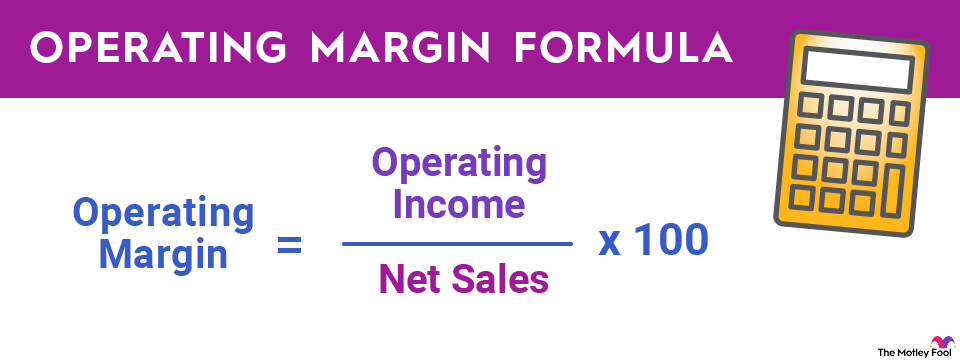
The simple equation to calculate operating margin is:
Operating Margin = (Operating Income / Net Sales) x 100
Let's take a look at a real-world example from Apple's (AAPL +1.23%) financial statements to demonstrate how to easily compute the operating margin of any company. The chart below shows results from Apple's fiscal 2021 first quarter.
Revenue | $111.4 billion |
Cost of Goods Sold | $67.1 billion |
Gross profit | $44.3 billion |
Gross margin | 39.8% |
Operating expenses | |
Research and development | $5.2 billion |
Selling, general, and administrative expenses | $5.6 billion |
Operating profit | $33.5 billion |
Operating margin | 30.2% |
In the example above, Apple's operating margin of 30.2% is found by dividing its operating profit of $33.5 billion by its revenue of $111.4 billion and multiplying that amount by 100. The company's operating margin is lower than its gross margin because operating margin accounts for fixed expenses like research and marketing that do not vary with manufacturing output.
As you can see, Apple's operating margin is phenomenal at more than 30% and just 9.6% below its gross margin. This operating margin shows the strength of the company's business and illustrates why it's one of the most valuable companies in the world.
Related investing topics
What operating margin doesn't tell you
Even though knowing a company's operating margin is helpful, it doesn't account for every expense the company bears. One-time restructurings, impairments, and other charges are also typically missing from operating income, as are income tax expenses. Interest cash flows and any impacts, positive or negative, from foreign currency exchange are also accounted for farther down the income statement.
A company's operating margin also doesn't tell you anything about its growth rate. Fast-growing companies often have low or even negative operating margins because they are spending aggressively on initiatives like marketing and product development to expand the business and reinvesting any profits back into the company. Conversely, a low-growth business such as tobacco giant Altria (MO -0.20%) is likely to have a comparatively high operating margin since the company and industry are both mature. It's important to consider operating margin as just one metric among other considerations such as the industry and the company's growth.
Still, calculating operating margin is the best way to get a sense of a company's or a core business unit's profitability. You can compare operating margins for the same company across multiple time periods and also compare operating margins for different companies in the same industry.
Operating margins are a simple concept, but they convey a lot of information. By giving you a deeper understanding of an income statement, operating margins serve a valuable purpose for all stock investors.