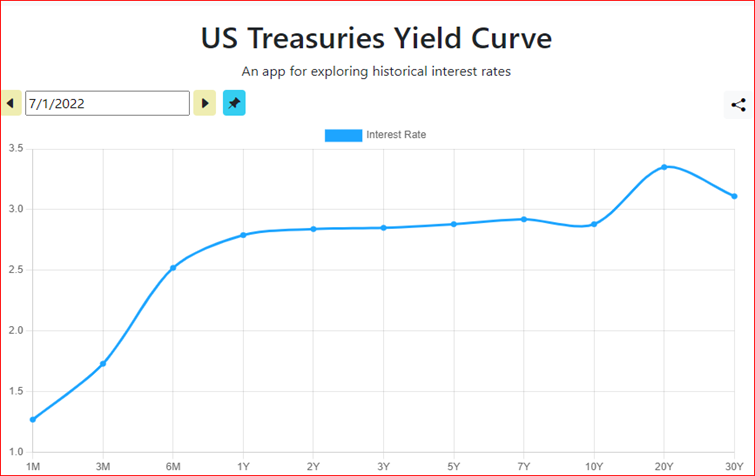
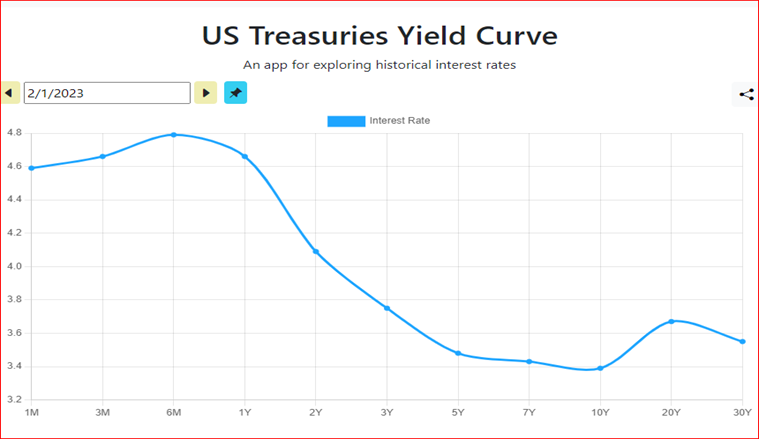
Why is the yield curve important?
Although the yield curve is an important indicator of future economic trends, individual investors can benefit from it as well. Brokers generally recommend investors start with a portfolio consisting of 60% equities and 40% fixed-income investments, such as bonds. U.S. governments and corporations reported almost $53 trillion in outstanding bonds at the end of 2021, about the same amount as the total value of U.S. stocks.
For most investors, however, the question isn’t whether to buy bonds; it’s whether to buy bonds that mature sooner or bonds that mature later. Short-term bonds are generally less risky but have lower yields. Longer-term bonds usually have higher yields, but their value can fluctuate.
Enter the yield curve. The most basic analysis of the yield curve involves finding a combination of safety and profitability that suits your risk appetite and investment timeline. But the yield curve doesn’t always operate in a completely linear fashion. Sometimes higher interest rates can be found with short-term bonds. When this happens, analysts refer to the inverted yield curve, typically signaling hard times are coming.
Related investing topics