One of the oft-mentioned uses for Bitcoin (BTC +1.04%) is as an inflation hedge, and it's sometimes referred to as "digital gold" for that reason. The idea is that as prices rise due to inflation, Bitcoin could potentially maintain its value better than fiat currency.
Ethereum (ETH +0.63%), the second-largest cryptocurrency, has more uses than Bitcoin because of its smart-contract capabilities. But its success so far has also made it popular as a way to hedge against inflation, so they have that in common. Let's see which of these top cryptocurrencies is more up to that task.

Image source: Getty Images.
Bitcoin is a deflationary asset
Bitcoin has a fixed maximum supply of 21 million coins, and 19.9 million are already in circulation. New coins are released through Bitcoin mining, which is its method of validating transactions. Once all 21 million coins are mined, which should happen around 2040, no more will be created.
This built-in scarcity is the main argument for Bitcoin as an inflation hedge. Like gold, it doesn't have an unlimited supply.

CRYPTO: BTC
Key Data Points
It's worth noting, however, that it doesn't have all the benefits of gold. Gold has real-world utility, not just in jewelry but also in electronics, dentistry, and other areas. Bitcoin is simply a piece of code stored on a blockchain network -- a very valuable piece of code right now, but still code.
Gold is also much more established than Bitcoin as a store of value. People have been using gold for thousands of years and will likely continue to do so. Bitcoin has only been around since 2009. Last but not least, gold is far less volatile than Bitcoin, which has lost over 50% of its value on multiple occasions.
Ethereum has a unique way of handling inflation
Most cryptocurrencies are either inflationary, meaning their supply increases over time, or deflationary, meaning the supply remains the same or decreases. Ethereum can be inflationary or deflationary depending on the level of activity on its blockchain network.
Ethereum doesn't have a supply limit, and up to 18 million new ETH tokens can be issued per year. However, in August 2021, its EIP-1559 upgrade introduced a token-burning mechanism. When network activity is high, this mechanism burns (destroys) a portion of the ETH tokens used to pay transaction fees.
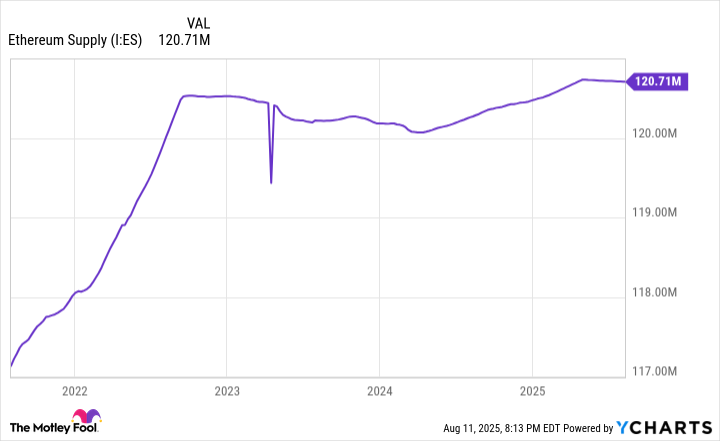
While Ethereum's supply initially increased following this upgrade, it has leveled off. As you can see in the chart below, it has been around 120 million for the last two years.
Ethereum supply data by YCharts.
Ethereum shares some of Bitcoin's drawbacks as an inflation hedge. It has an even shorter track record, having only been around since 2015, and is also extremely volatile. This year alone, it has lost over 50% of its value, and then rebounded to gain over 180%.
Which cryptocurrency is the better inflation hedge?
I would pick Bitcoin over Ethereum, and any other cryptocurrency, for hedging against inflation. It's the oldest, most proven cryptocurrency, and it makes up nearly 60% of the entire market. The fact that it has a hard ceiling on its supply also gives it an edge in preserving value.

CRYPTO: ETH
Key Data Points
That said, if you're strictly looking for an inflation hedge, you're probably better off investing in gold or stocks. A good inflation hedge is an asset that maintains its value. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and most other cryptocurrencies are too volatile, considering they can drop by 20% or more in a matter of weeks. Gold and stocks can dip during downturns, too, but they tend to be sturdier assets, particularly if you go with low-volatility stocks.
Although they may not be the ideal inflation hedge, Bitcoin and Ethereum can make sense as investments. The former is getting more and more popular as a digital store of value, and the latter is the most widely used blockchain platform. They're risky, but if you want to add digital assets to your portfolio, they may each be worth a small investment.