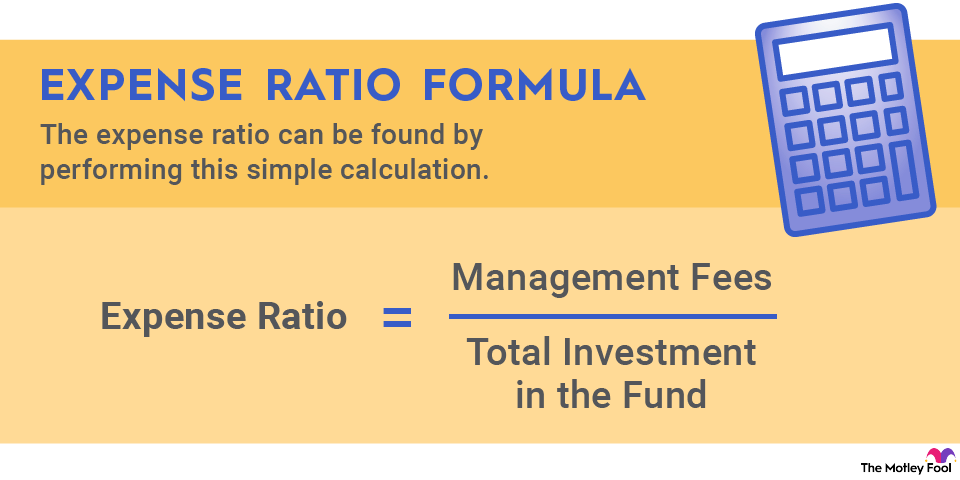
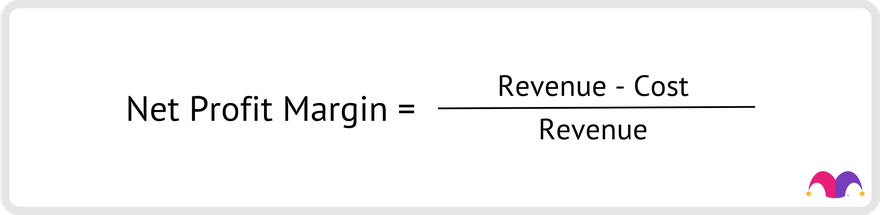
How to evaluate a company using net profit margin
Net margin can help investors compare a company's performance across reporting periods and among its competitors. If a company undertakes a strategic initiative to increase its profitability, then investors can calculate net profit margin to evaluate whether that initiative is delivering results. If the company's net margin is in decline, then investors can use that information to recognize deteriorating financial health.
A company with a higher net profit margin than those of its peers is more efficiently converting revenue into profit. If a company's net margin is lower than those of its industry peers, then that could be a sign it is financially weaker or less efficient than its rivals.
What are the limitations to net profit margin?
While net profit margin is a useful metric, it has some limitations. For example, it is not a good gauge for comparing companies in different sectors. That's because in some industries, low-single-digit net profit margins are considered quite good, while in other sectors, double-digit net profit margins are the norm.
Another limitation of the net margin metric is that it can vary greatly across reporting periods due to the potentially outsized effects of one-time events. Asset sales can temporarily boost income, inflating the net margin. Likewise, one-time expenses can weigh heavily on a company's profitability for a reporting period. Because of this, it's important to understand the factors that influence net profit during any given period to determine whether calculating net margin is appropriate to evaluate the company.
Net profit margin is just one of many metrics that investors can use to analyze a company, and it is certainly not the sole metric that determines the worthiness of a stock investment.
Related investing topics