Cost of Debt
Interest Rate
About the Author
The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.
Invest better with The Motley Fool. Get stock recommendations, portfolio guidance, and more from The Motley Fool's premium services.
Student loans are used by millions of people to attend colleges and universities in the United States. As of 2023, Americans had $1.78 trillion in outstanding federal and private student loan debt, and more than 45 million borrowers had federal student loans.
Student loans are one of the most flexible and beneficial types of loans, but they are also one of the most complex. So, there’s a lot that future, current, and former college students should know about how student loans work, how they are repaid, and more.
Student loans are designed to help students (and their parents) at colleges and universities cover the cost of attendance to obtain a degree or certificate. There are several different types of student loans, some offered by government agencies and some by private lenders. Student loans consist of a lender allowing you to borrow money in exchange for the promise of repayment, with interest.
In many cases, student loans are paid directly to the college or university, and any overage can then be distributed to the borrower. Additionally, student loans often have borrowing limits. In the case of federal direct loans, student loans have annual maximums that depend on the student's year in school and dependent status, while other types of loans may only be limited by the school's published cost of attendance.
There are two main categories of student loans: federal and private. Federal student loans refer to any student loan originated by the U.S. Department of Education, while private loans refer to student loans made by a financial institution, such as a bank or other lender.
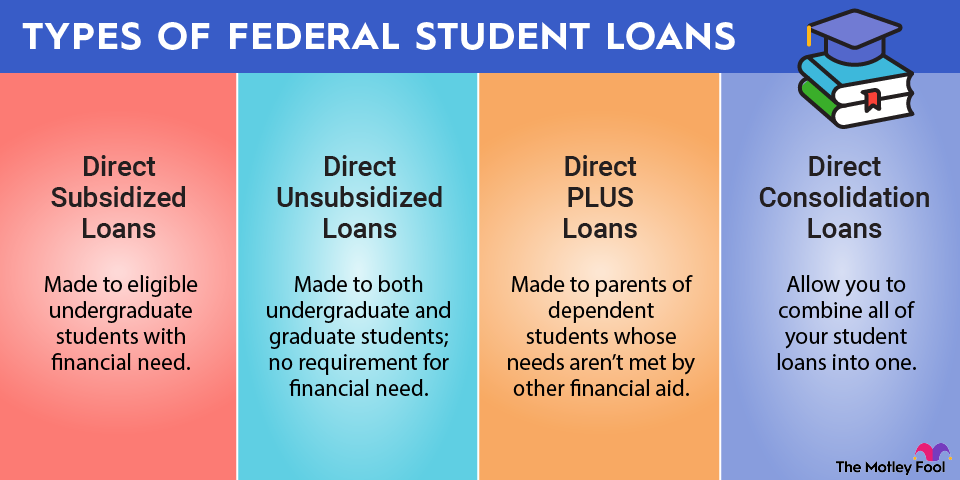
Within the category of federal student loans, there are several different types. There are four loan types under the Federal Direct Loan program:
With private lenders, the application process for student loans can vary from one lender to the next. But for federal student loans, it is a pretty straightforward process.
Complete and submit the FAFSA, which is the Free Application for Federal Student Aid. This is the form you'll use to qualify for federal loans and grants, as well as several other types of need-based student aid.
You'll receive a financial aid offer from your school based on the information in your FAFSA. This will include any federal student loans for which you qualify.
You can choose to accept the entire amount of student loans you're offered, a reduced amount, or not at all. The financial aid letter you receive will detail the process for accepting student loans.
The next step is to sign your loan agreement, which essentially is a legal document that says you promise to repay your loans as agreed. You'll also complete "entrance counseling," which will give you some general information about how your student loans work.
In certain circumstances, federal student loans can be paused. This can either be specific to you as a borrower or a pause granted to a large group or even all federal student loan borrowers (as happened during the COVID-19 pandemic). Private loans may be able to be paused as well in times of financial hardship, but this depends on the lender.
With federal loans, the two main types of pauses are deferment and forbearance. Both involve temporarily suspending payment obligations, but there are some subtle differences.
A deferment typically requires some sort of reason, such as being enrolled in school or being unemployed. Deferments can last for various lengths of time and must be granted if you have a valid reason. During periods of deferment, interest doesn't accrue on subsidized federal loans.
A forbearance can be granted for as long as 12 months at a time, with no set maximum, and no specific qualification is required. It is up to your loan servicer whether or not to grant forbearance, although it typically is a fairly automatic process. During periods of forbearance, interest will continue to accumulate on all loans.
It's also worth noting that in times of financial hardship, enrolling in an income-driven payment plan (more on these in a bit) can have the same effect. These plans cap your monthly payment at a certain percentage of your discretionary income -- and it could be as low as $0 if you're unemployed or underemployed.
With federal student loans, there are several different repayment options, and they can be classified into four basic categories.
The standard repayment plan is a 10-year repayment plan with a fixed monthly payment. When you graduate (or leave school) and your grace period expires, this is the default repayment option. In a nutshell, if you make monthly payments for 10 years under the standard repayment plan, your loans will be paid off in full at the end of the 10-year period.
The graduated repayment plan is a 10-year repayment plan that has lower initial payments, but its monthly payments increase every two years. It is designed for people who anticipate their earnings to increase significantly during the first several years of their careers.
The extended plan has a fixed monthly payment but a longer, 25-year repayment term. It allows borrowers to get a lower monthly payment than under the standard plan.
The Department of Education offers several different income-driven repayment plans that set the borrower's required monthly payment based on their annual income, loan balance(s), and family size. There are five income-driven plans available to most federal student loan borrowers:
Income-driven repayment plans are the best option for the vast majority of student loan borrowers. Not only do they typically result in the lowest monthly payments, but borrowers must be enrolled in income-driven repayment to qualify for public service loan forgiveness (PSLF) and several other programs. And, within the realm of income-driven plans, virtually all borrowers will find the lowest payments under the SAVE plan.
With private student loans, the repayment options depend on the company that made the loan and its terms. Most private student loans have a set repayment length and do not offer income-driven options, although some may allow you to lengthen your repayment term to lower your payment -- for example, switching from a 10-year to a 15-year repayment term. If you're curious about repayment options for your private student loans, the best course of action is to contact your lender.
There are many different scholarships and grants available to help cover the cost of higher education. Some are merit-based, while others are need-based. There are many potential places to look for these programs, but here are some good starting points:
Federal work study provides part-time jobs for students who have financial need. You'll need to apply for aid and qualify for these jobs, and the amount you earn cannot exceed your total work-study award.
Alternatively, students can obtain part-time employment elsewhere to earn money towards the cost of attending school. In most cases, it isn't practical to completely cover the cost of a college degree through part-time jobs, but it can certainly help lower the amount of money you need to borrow.
Another method of raising money for college is to crowdfund, which means starting a campaign online (usually through social media) to ask for friends, family, and social media followers to contribute funds for a specific purpose. There are several popular crowdfunding platforms, some of which specialize in education funding, so this could be worth looking into as well.
Student loans are a complex financial instrument, and there is a lot to learn to navigate the student loan process in a way that maximizes your ability to access funds, minimizes repayment obligations, sets you up for loan forgiveness, and more.