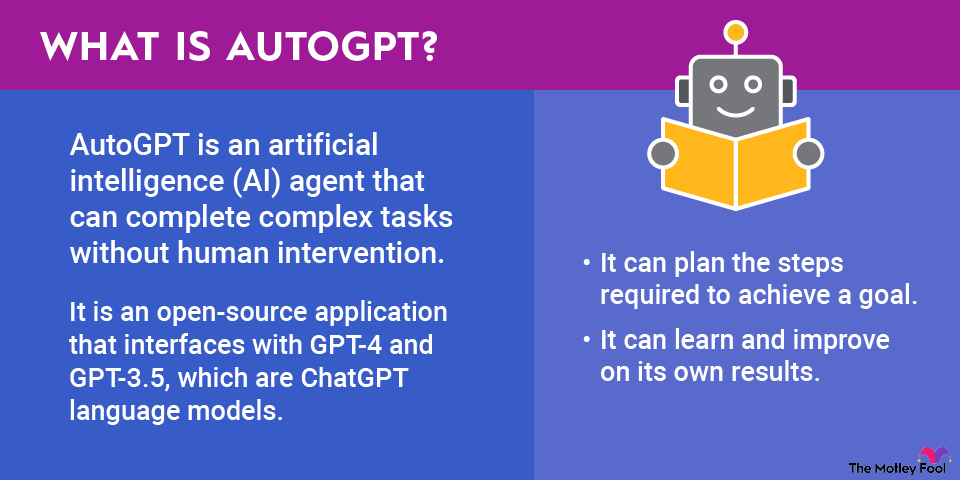
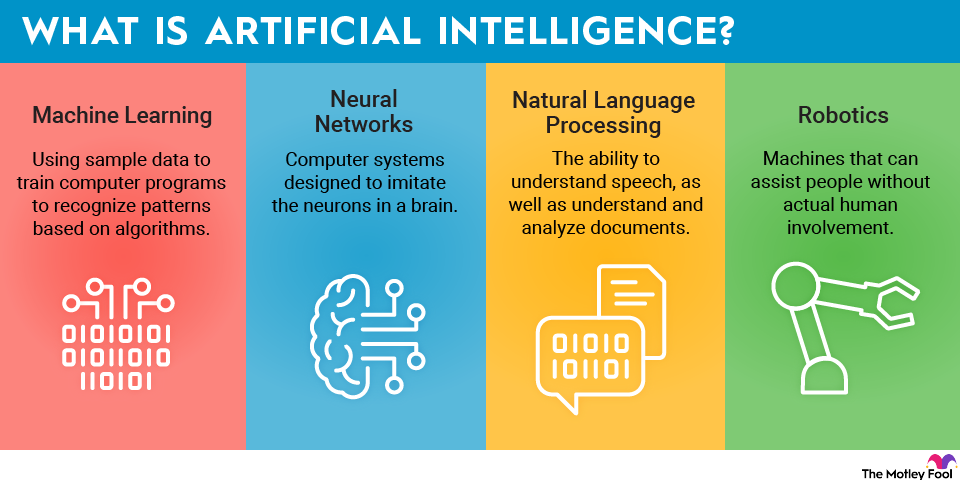
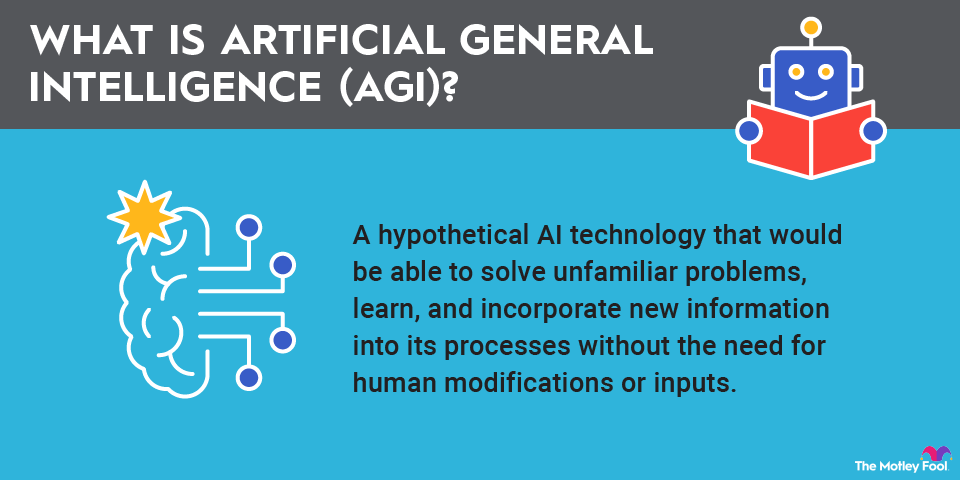
Agentic artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform industries, business operations, and capital markets in the years ahead. This reality could create a wealth of new opportunities for publicly traded companies and investors who own shares in those businesses.

Investors with an interest in the broader AI industry should also familiarize themselves with agentic AI. This sector appears to be the next evolutionary leap in the AI race that will move this technology beyond content generation to proactive, autonomous action. Here's what you should know about agentic AI, what it is, how it works, and more.
What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to autonomous artificial intelligence systems capable of independently planning, reasoning, and acting to achieve complex, multistep goals with limited human oversight. These systems go beyond responding to prompts.
Instead, they possess agency that allows them to learn and interact with other software and agents to complete sophisticated tasks, meaning they act more like a human employee. Unlike generative AI, which is reactive to content inputs, agentic AI systems can perceive their environments to reason, plan, act, and respond to a given scenario.
For example, a typical tool using generative AI could write a marketing email based on a prompt. But an agentic AI system could go several steps further to plan and execute an entire marketing campaign. It could draft the content, schedule the emails based on user data, track engagement, and automatically optimize the organization's marketing strategy based on real-time performance metrics.
How does agentic AI work?
Agentic AI works in a multipronged cycle to achieve its goals autonomously. It behaves similarly to how a human agent would work to complete a task or series of tasks.
First, the AI agent collects data from its surroundings, including user inputs, databases, or sensors, to gain an understanding of the current situation.
Next, using reasoning capabilities powered by large language models (LLMs), the agent analyzes the information to understand the goal, identify patterns, and formulate a strategy or a series of steps to achieve it. This often involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable subtasks.
The agent then executes the planned actions and analyzes the outcome while incorporating any feedback to improve its strategies for future tasks. An AI agent could use this process to complete practical tasks for virtually all types of organizations.
Why is agentic AI important?
Agentic AI could foreseeably tackle intricate challenges that are simply beyond the scope of current AI systems. Because agentic AI can manage nuanced problems and automate entire processes rather than just isolated tasks, its implementation could lead to significant increases in productivity and efficiency for businesses across a range of industries.
To offer just a few examples, an investment firm could deploy an AI agent to optimize investment recommendations for clients, or an e-commerce business could utilize an AI agent to oversee supply chain processes. But what would this look like in practice?
Well, a financial agent could analyze a client's history, current market data, and financial goals to create and manage a personalized investment strategy. It could even proactively monitor the market and autonomously execute trades or optimize clients' investments based on predefined parameters such as their preferences and risk tolerance level.
Similarly, instead of reacting to disruptions, an e-commerce company's agentic system could constantly monitor global weather, traffic, and supplier data to predict delays. It could then autonomously reroute shipments or adjust inventory levels to prevent bottlenecks from happening in the first place.
That combination of perception, decision-making, and autonomous action could allow agentic AI to drive transformative changes in virtually every sector in the years ahead.
Related investing topics
Agentic AI in the real world
Numerous public companies are actively developing and deploying agentic AI, especially large technology companies that specialize in software and automation. For example, Microsoft (MSFT -0.21%) is embedding agentic AI capabilities into its products and cloud services, such as Copilot.
Another major player in the AI race, Nvidia (NVDA -2.37%), provides the hardware and software that support agent development and deployment. Then there's Amazon's (AMZN -2.21%) cloud business, which offers services like Amazon Bedrock to help financial institutions and other clients build and manage autonomous AI agents.
Agentic AI is only in its nascent stages, but this technology looks poised to take off as these systems refine and improve. Organizations will also need to make substantial investments in the space to unlock agentic AI's full potential.