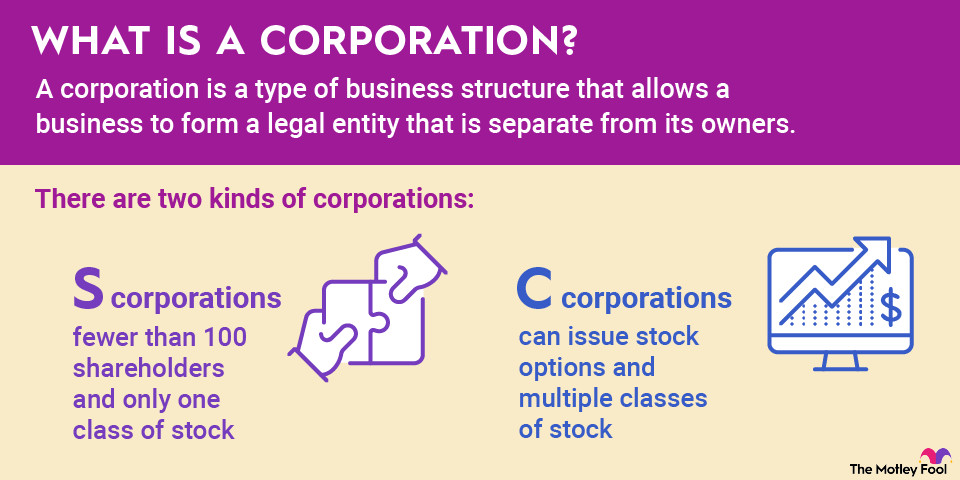
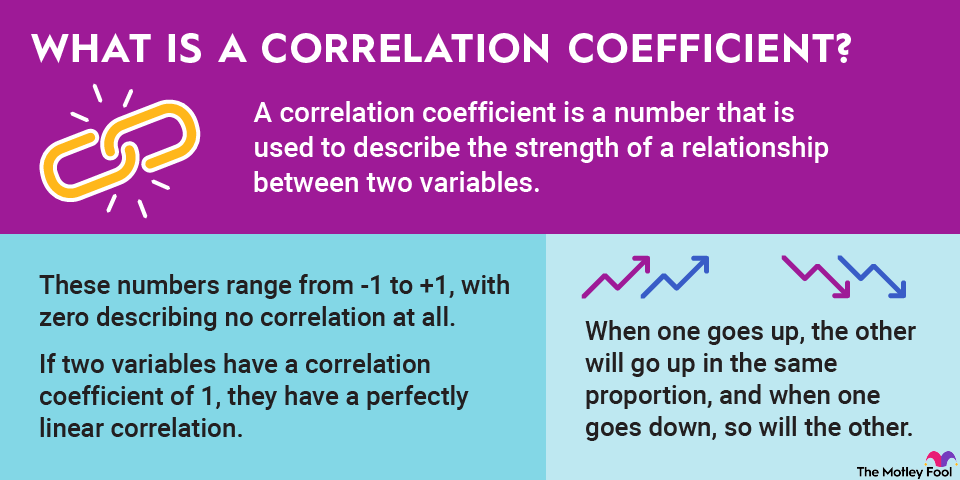
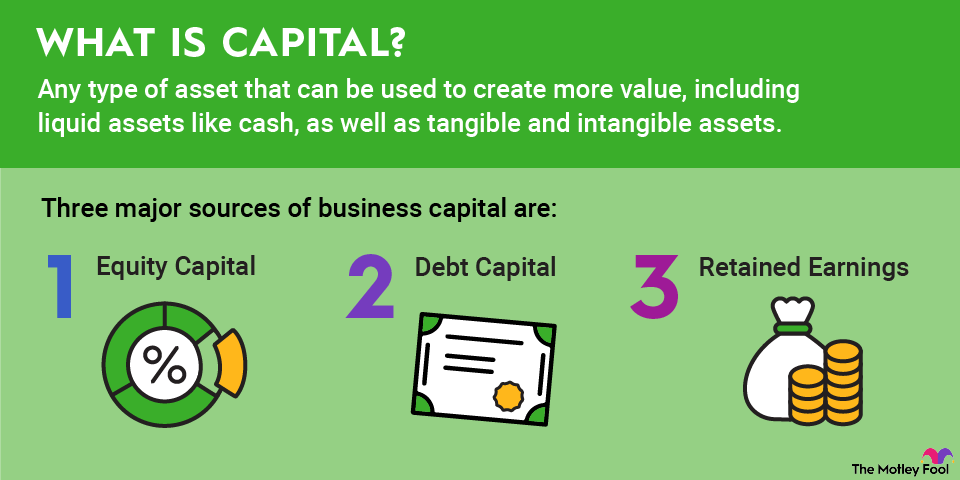
Regulating member banks
Central banks are in charge of policies regarding other types of banks, especially those that hold deposits. Capital requirements, reserve requirements, and deposit guarantees are all set by a central bank. They can also provide services to those banks and the government. You can think of them as the bank for banks.
Acting as lender of last resort
Once in a while, you may come across the phrase "lender of last resort." It's pretty much exactly what you imagine: A central bank is the last lender for seriously distressed institutions and governments. It can do things like purchase government debt obligations, providing an alternative to taxing people when funds are tight.
Does the U.S. have a central bank?
Although the U.S. founding fathers were initially opposed to the idea of a central bank, one was eventually created. The U.S. central bank is known as the Federal Reserve System (or the Fed), and it's governed by the Federal Reserve Board.
The Fed was established with the 1913 Federal Reserve Act to consolidate and stabilize the banking system, which was, at one time, primarily controlled by large banks in the country's more populous eastern portion (much to the chagrin of Americans in rural and western portions). By establishing the Fed, the U.S. finally had one currency, one institution over monetary policy, and one decentralized bank monitoring everything.