A product life cycle is the progression of an item or service from being made available to consumers to finally being taken off of the market. Effective product life-cycle management is crucial for businesses and can be the deciding factor in whether commercial projects succeed or fail.

What are the stages of a product life cycle?
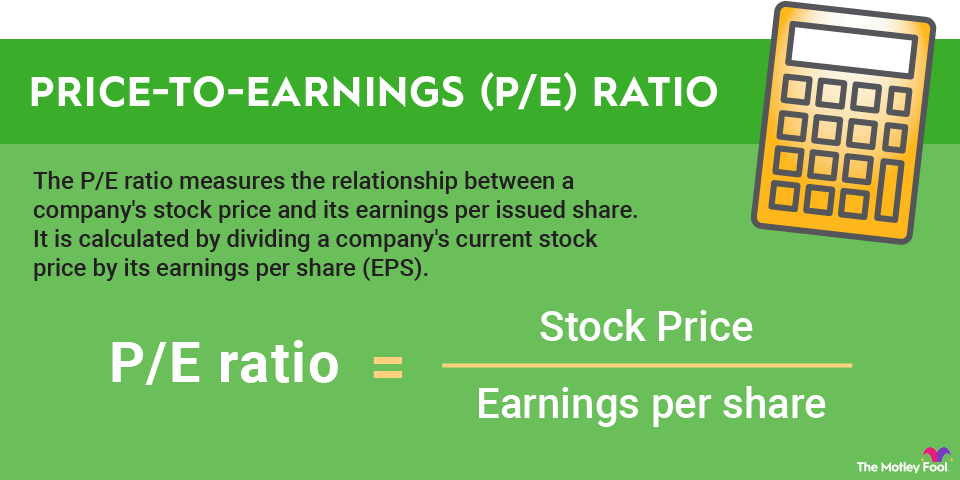
Product life cycles are most often broken down into four key stages. These stages are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
At the introduction stage, the product is first brought to market. From there, the product enters the growth stage of the cycle, which sees revenue increase and the item or service become more widely available. Once the product is no longer seeing substantial sales increases, it has reached the maturity stage. Market decline is the stage in the product life cycle that sees the revenue and profits generated by an item or service begin to fall. At the end of the decline stage, the product is no longer commercially viable and ceases to be produced and sold.
Revenue
Why are product life cycles important for businesses?
Successful products typically require high levels of planning and execution across each stage of their product life cycle. The progression of product life cycles is typically shaped by the level of interest from consumers and has a defining impact on whether commercial projects are successful.
If a product completely flops upon release, it never enters a meaningful growth stage and jumps almost immediately to maturation and decline. In this case, the business is likely to lose money and incur a substantial opportunity cost for not having delivered an item or service that was in line with the desires and demands of the market. While all products will eventually enter the decline stage, the goal is to generate healthy sales and profits before that occurs.
The transition from growth to maturity to decline
Growth stages can be cut short due to product shortcomings, the arrival of new innovations that make the item or service less desirable, or the entrance of similar, competing product offerings that eat into sales. If rival businesses notice a product is gaining traction and enjoying a strong growth phase or continued success in market maturity, they may choose to release their own competing alternative. This can shorten the original product’s growth stage or accelerate its transition from maturity to decline.
On the other hand, a product entering into market maturity isn’t necessarily a bad thing. While rapid sales growth is no longer occurring, the maturity stage is often the most profitable stage for a product because manufacturing and marketing expenses can be reduced, which leads to stronger operating margins. An item or service in decline can also continue to be profitable, but eventually it will hit a tipping point and no longer be worth producing or maintaining.
In most cases, having a longer product life cycle is beneficial because it means that customers continue to spend on the base product. This means there is less need to invest money in developing and marketing entirely new items or services. Alternatively, businesses will sometimes plan for relatively short life cycles and operate with the expectation that a new, follow-up product will quickly be ready to replace the previous iteration.
Related investing topics
An example of a product life cycle in action
The VHS tape was developed by Japanese electronics company JVCKenwood and was the primary medium for distributing home videos for more than two decades. The first VCR machines for VHS tapes were released in 1976, and the machines and video format enjoyed successful introduction periods and long growth phases. Sales for VHS tapes peaked in 1998, which was one year after the first movies were released on DVD in the U.S. The rapid rise of the DVD format meant that VCRs and VHS tapes quickly shifted from market maturity into the decline phases of their product life cycles.
In 2001, sales of DVD players eclipsed those of VCRs, and the following year saw DVD sales surpass VHS tape sales. Major movies stopped being released on VHS altogether in 2006, marking the end of the product life cycle for JVC’s videocassette format. The DVD format enjoyed its own growth and maturity stages before being pushed into decline by the rise of new high-definition optical formats and the rise of digital distribution and streaming media.