The deployment of 5G networks is still in the early phases, and a lot of money remains to be spent on the latest wireless technology as telecom carriers roll it out to more markets across the world. Not surprisingly, 5G infrastructure investments are expected to jump from $9.8 billion last year to $58 billion by 2026, clocking a compound annual growth rate of 29%, according to third-party estimates.
Ciena (CIEN 2.34%) and NVIDIA (NVDA 1.28%) are two ways investors can take advantage of that massive spurt in infrastructure spending. Both companies provide technologies that are critical to the efficient functioning of 5G networks. Let's see why these two could turn out to be top 5G stocks in the long run.

Image source: Getty Images.
1. Ciena can benefit from the backbone of 5G networks
Setting up 5G networks requires the deployment of optical fiber networks to support the massive increase in bandwidth, reduce latency, and reduce power consumption. Telecom operators reportedly spent over $144 billion to upgrade the legacy mobile backhaul network infrastructure to optical fiber between 2014 and 2019, as they made the shift to 4G.
Optical fiber networks are a necessity for 5G networks because they can offer unlimited bandwidth. Theoretically, 5G networks can support speeds up to 20GB per second as compared to 4G's peak speed of 1GB per second. As a result, the fiber optic cable market's revenue is expected to double from 2019 to 2025, according to third-party estimates, paving the way for Ciena to boost sales of its 5G networking solutions.
The company announced a range of 5G solutions earlier this year, such as 5G-optimized routers, 5G network automation software, and transport networks to hook up cell sites with each other and the core network, as well as to data centers. The good part is that Ciena is already working with leading telecom operators around the world. Its clients include top Indian telecom operators such as Reliance Jio, Bharti Airtel, and Vodafone-Idea.
In the U.S., Ciena has helped Verizon quadruple its fiber capacity to support 5G networks. Telefónica U.K. has also decided to use Ciena's packet transport solution to upgrade its legacy network to support 5G. All of this indicates that Ciena is right in the middle of the 5G revolution, and things should get better as deployments gather pace.
Even more importantly, Ciena controls nearly a quarter of the optical network hardware market, and it has consistently increased its share over the years. So it's in a nice position to take advantage of the market's secular growth as 5G networks come online across the world, which should allow Ciena to sustain the impressive top- and bottom-line growth it has clocked of late.
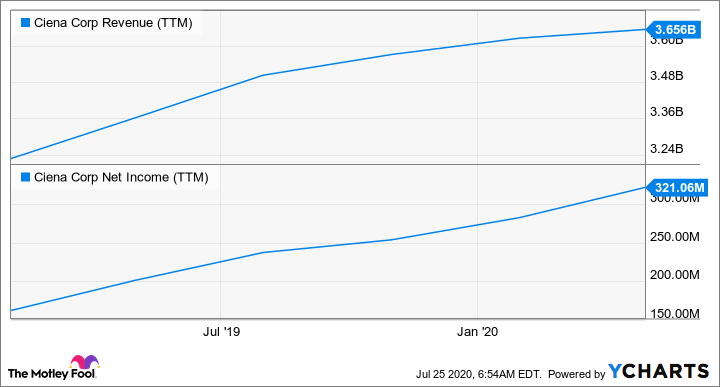
CIEN Revenue (TTM) data by YCharts
And finally, Ciena's valuation is another reason to go long. Its price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio of 26 is lower than the five-year average multiple of nearly 56, which makes it an attractive 5G bet considering the potential acceleration in earnings as seen in the chart above.
2. NVIDIA is solving a crucial problem
NVIDIA specializes in graphics cards that power computers and data centers, as well as speed up 5G networks. In October of last year, NVIDIA announced that it is partnering with telecom giant Ericsson to make 5G networks more efficient and smarter with the help of GPUs (graphics processing units). More specifically, the two companies are looking to "build high-performing, efficient, and completely virtualized 5G radio access networks (RAN)."
NVIDIA aims to use this partnership to plug gaps in the current network infrastructure where carriers are unable to deploy bandwidth according to real-time requirements. A 4G network that's aimed to work at peak capacity to ensure seamless voice and data access with the help of dedicated hardware runs the risk of underutilization if there aren't enough users in that area.
The bandwidth wastage could be much higher in the case of a 5G network, which is why networks will have to be made more intelligent. This is where NVIDIA's GPUs come into play. They can help telecom carriers deploy software-defined virtual radio access networks (vRAN) that run on virtual machines.
The advantage of vRAN is that applications that are running on a virtual machine can be moved to another machine if needed. This allows telecom operators to intelligently transfer bandwidth from one place to another, thereby reducing both operating and capital expenses substantially. Not surprisingly, the vRAN market is expected to grow at an annual pace of 128% through 2024, according to third-party estimates.
Moreover, 5G is expected to create the need for smaller data centers to ensure low latency and faster processing times. This could boost demand for data center GPUs because they will play a key role in accelerating workloads locally for applications such as self-driving cars and the Internet of Things.
NVIDIA's data center business supplied 37% of its total revenue last quarter and grew nearly 80% year over year. The rollout of 5G can give NVIDIA a nice shot in the arm and may turn out to be yet another catalyst for this high-flying tech giant that's already growing at a terrific pace.