NYSEMKT: UNG
Key Data Points
The fund makes it easy to bet on the thesis that the price of natural gas in the U.S. will move meaningfully in the short term. Traders can make this gamble without needing to open a commodity futures account and learn how to trade futures. They also don't need to risk investing in a natural gas stock that might underperform the price of gas in the near term.
However, the United States Natural Gas Fund also has serious drawbacks. The costs of rolling natural gas futures contracts forward (and the fund's expense ratio) eat into its returns over the long term, so this fund is only suitable for a short-term trade.
This guide will show you everything you need to know about the United States Natural Gas Fund and teach you how to invest in ETFs for beginners.
Expense Ratio
What is the United States Natural Gas Fund?
The United States Natural Gas Fund is an exchange-traded security similar to an exchange-traded fund (ETF). It primarily invests in natural gas futures contracts. The fund will also hold other natural gas-related futures contracts, forwards, and swap contracts. It collateralizes these contracts with cash, cash equivalents, and U.S. Treasury bonds with remaining maturities of less than two years.
The fund aims to track the daily price movements of natural gas. It benchmarks its returns against futures contracts traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) that expire in the next month and have at least two weeks until expiration.
The fund has a couple of notable benefits. It provides investors exposure to natural gas without knowing how to invest in futures contracts. It also enables them to bet directly on natural gas instead of investing in a natural gas stock, which might not move in the same direction as gas prices.
However, it also has some major drawbacks. The fund needs to roll its futures contracts forward as they near expiration, which eats into returns (expiring contracts tend to have a lower price than those with more time until expiration). In addition, fees (from rolling contracts and fund management costs) eat into the fund's returns.
Because of these issues, this fund is unsuitable for long-term investment. It's best for making a short-term trade to potentially profit from an expected near-term rally in the price of natural gas.
How to buy the United States Natural Gas Fund
One of the benefits of the United States Natural Gas Fund is that you don't need a futures trading account to make a trade on natural gas prices. This fund trades just like any stock, enabling anyone to buy shares in their regular brokerage account. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you add the energy ETF to your portfolio.
- Open your brokerage app: Log in to your brokerage account where you handle your investments.
- Search for the stock: Enter the ticker or company name into the search bar to bring up the stock's trading page.
- Decide how many shares to buy: Consider your investment goals and how much of your portfolio you want to allocate to this stock.
- Select order type: Choose between a market order to buy at the current price or a limit order to specify the maximum price you're willing to pay.
- Submit your order: Confirm the details and submit your buy order.
- Review your purchase: Check your portfolio to ensure your order was filled as expected and adjust your investment strategy accordingly.

Should I invest in the United States Natural Gas Fund?
Investing is a very personal endeavor. You should invest in things that align with your risk tolerance and return objectives. With that in mind, here are some reasons you might want to invest in the United States Natural Gas Fund:
- You have a thorough understanding of how this fund works.
- You're very bullish about natural gas due to a pending near-term catalyst.
- You're comfortable with the risks of investing in this fund, including the fact that it could lose significant value if natural gas doesn't deliver a meaningful rally in the short term.
- You're a very disciplined investor who will sell if your thesis doesn't play out as expected.
- You're seeking a sector ETF or mutual fund focused on the natural gas industry.
On the other hand, here are some reasons you might decide against investing in this fund:
- You don't understand how this fund works.
- You don't have a short-term bullish thesis on natural gas.
- You're seeking a lower-risk way to invest in natural gas.
- You want to make a longer-term investment in natural gas.
- You're seeking a lower-cost way to invest in natural gas.
- You want to invest in a dividend ETF to generate passive income.
Does the United States Natural Gas Fund pay a dividend?
The United States Natural Gas Fund does not pay a dividend. The fund invests primarily in natural gas futures contracts expiring in a month, which don't generate any income. The fund's purpose is as a short-term investment vehicle to make a bet on the near-term price movement of natural gas.
What is the United States Natural Gas Fund's expense ratio?
Fund managers charge fees, known as the expense ratio, to execute their investment strategy on behalf of investors. This fund has a total expense ratio of 1.01%. That's a very high expense ratio due in part to the management oversight required to roll futures contracts forward each month.
To put the expense ratio into a different context, every $1,000 invested in the fund would cost $10.10 annually. The fee would really add up over the long term, which has contributed to its poor historical performance.
Historical performance of the United States Natural Gas Fund
Futures trading is very challenging. That's evident in the performance of this fund over the years:
Fund | 1-Year | 5-Year | 10-Year |
|---|---|---|---|
United States
Natural Gas Fund | 46.07% | (15.41%) | (20.45%) |
Benchmark
Futures Contract | 41.65% | (16.41%) | (20.83%) |
The sole factor driving those poor long-term returns is the fund's expenses (expense ratio and the cost of rolling natural gas futures contracts). Given its underperformance, this fund is unsuitable as a long-term investment.
However, the fund does a much better job of tracking the movement in the price of natural gas in the short term. For example, gas prices have surged in the past year, driving a big increase in the value of this fund:
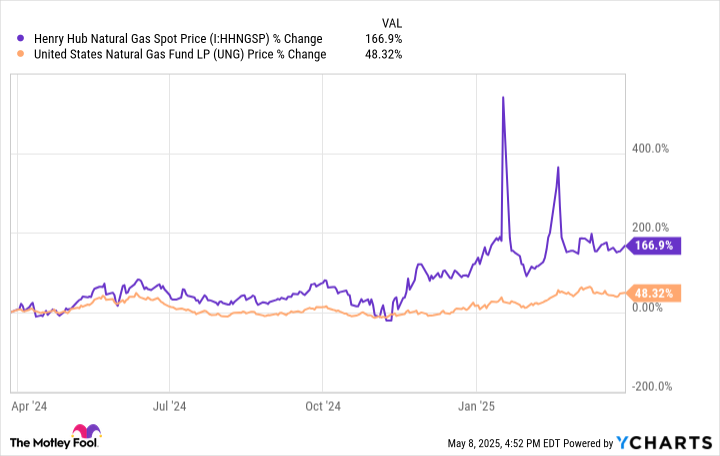
Given this dynamic, investors should buy this fund only when they firmly believe the price of natural gas will spike over a short period (due to a winter storm or other catalyst).
Related investing topics
The bottom line on the United States Natural Gas Fund
The United States Natural Gas Fund is a specialized fund. It enables anyone to make a short-term bet on natural gas prices without opening a futures account. It's imperative that investors use this fund only as a short-term trading vehicle. The fund's costs eat into its returns over the long term, which has contributed to its poor historical performance.