Since cryptocurrencies are decentralized and not under the control of financial institutions, they need a way to verify transactions. One method many cryptos use is proof of stake (PoS).
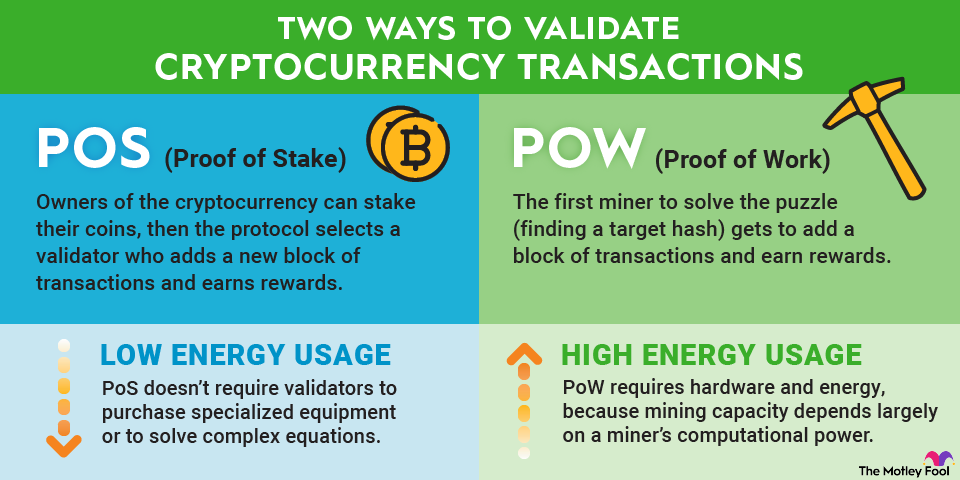
Proof of stake is a type of consensus mechanism used to validate cryptocurrency transactions. With this system, owners of the cryptocurrency can stake their coins, which gives them the right to check new blocks of transactions and add them to the blockchain.
This method is an alternative to proof of work, the first consensus mechanism developed for cryptocurrencies. Since proof of stake is much more energy-efficient, it has gotten more popular as attention has turned to how crypto mining affects the planet.
Understanding proof of stake is important for those investing in cryptocurrency. Here's a guide to how it works, its pros and cons, and examples of cryptocurrencies that use it.

Mining power in proof of stake
Mining power in proof of stake depends on the amount of coins a validator is staking. Participants who stake more coins are more likely to be chosen to add new blocks.
Each proof-of-stake protocol works differently in how it chooses validators. There's usually an element of randomization involved, and the selection process can also depend on other factors such as how long validators have been staking their coins.
Although anyone staking crypto could be chosen as a validator, the odds are very low if you're staking a comparatively small amount. If your coins make up 0.001% of the total amount that has been staked, then your likelihood of being chosen as a validator would be about 0.001%.
That's why most participants join staking pools. The staking pool's owner sets up the validator node, and a group of people pool their coins together for a better chance of winning new blocks. Rewards are split among the pool's participants. The pool owner may also take a small fee.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Energy-efficient. | Not as proven in terms of security as proof of work. |
Provides fast and inexpensive transaction processing. | Validators with large holdings can have excessive influence on transaction verification. |
Doesn't require special equipment to participate. | Some proof-of-stake cryptocurrencies require locking up staked coins for a minimum amount of time. |