Insurance stocks can make a great addition to any investor’s stock portfolio. Not only does the insurance business have the potential to produce excellent long-term returns, but it’s also a business that works in good times and bad.
With that in mind, here’s an overview of how the insurance business works, some important concepts to know, and three insurance stocks that investors should keep on their radar in 2025 and beyond.

Three top insurance stocks for 2025
| Name and ticker | Market cap | Dividend yield | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| MetLife (NYSE:MET) | $52.2 billion | 2.83% | Insurance |
| Markel Group (NYSE:MKL) | $23.9 billion | 0.00% | Insurance |
| Kinsale Capital Group (NYSE:KNSL) | $10.5 billion | 0.15% | Insurance |
1. MetLife

NYSE: MET
Key Data Points
MetLife (MET -0.50%) is a great option for investors who want some insurance exposure with low volatility. It’s the largest U.S. life insurer, and it also has a huge retirement solutions business.
MetLife has an easy-to-understand business model and a history of strong returns on equity. For context, it has produced a 127% total return for investors over the past five years (about 18% annualized). Plus, the company pays one of the highest dividend yields of its peer group, which can significantly boost total returns over time.
2. Markel

NYSE: MKL
Key Data Points

NYSE: KNSL
Key Data Points
Warren Buffett chose the insurance industry as the backbone of his empire.
How insurance companies make money
One of the most important things to understand before buying any stock is how the company makes its money. This sounds simple, but it’s frequently misunderstood when it comes to the insurance industry.
The obvious way that insurance companies can make money is by selling insurance policies and bringing in more money in premiums than they pay out in claims. This is known as an underwriting profit.
The second, and more important, way insurance companies make money is by investing the money they take in before it is paid out for claims. This money is known as the float. Most insurers invest their float in safe places, such as high-quality bonds, but some choose to be a little more adventurous and buy other types of investments (like Markel does).
Obviously, this is a simplified explanation. Insurance companies have other ways to generate revenue, and two of the companies discussed in this article have substantial non-insurance operations, as well. But this is the main idea behind how the business works.
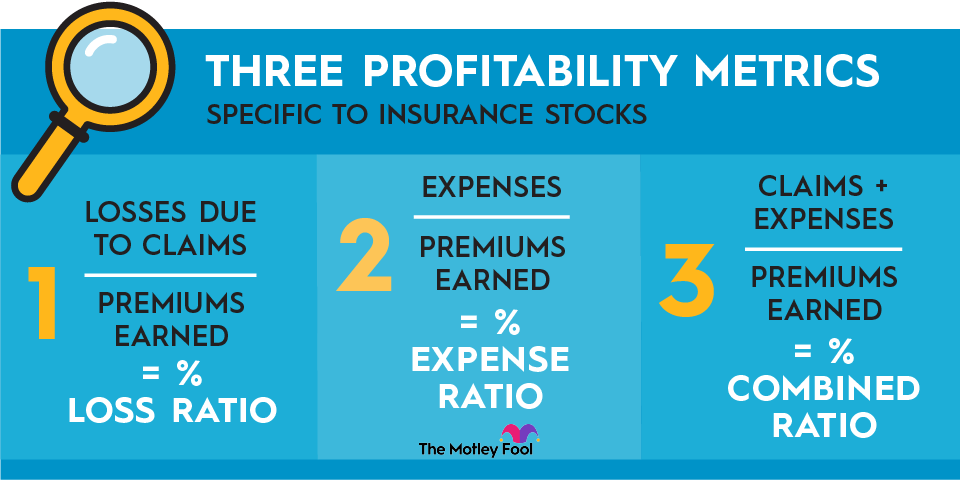
Three important metrics for insurance investors to know
To analyze insurance stocks, most standard metrics work, such as return on equity (ROE) and net margin. However, there are three insurance-specific profitability metrics that you should know before getting started:
- Loss ratio: This is the percentage of an insurer’s premiums paid out as claims. For example, if an insurer collects $100 million in premiums and pays out $70 million for claims, the insurer has a loss ratio of 70%.
- Expense ratio: This is the percentage of premiums that an insurer spends to run its business. For example, expenses might include employee salaries and office equipment. An insurer with $100 million in collected premiums and $20 million in expenses would have a 20% expense ratio.
- Combined ratio: This is the combination of the loss ratio and the expense ratio. An insurer with $100 million in premiums and $90 million in losses and expenses would have a combined ratio of 90%. A combined ratio of less than 100% shows an underwriting profit and is a sign of good risk management.
Types of insurers
Like most industries, insurance companies can be divided into subcategories, so here’s a quick explanation of the main types of insurers and what they do:
- Property and casualty: Property and casualty (P&C) insurers write insurance policies that cover property damage and provide liability protection. Auto and homeowners insurance are two common forms. Renters insurance and pet insurance are two other common examples. P&C insurance is typically the easiest type to understand and analyze, especially for beginners.
- Life: Life insurance provides money to a designated beneficiary upon the death of the insured person.
- Health: As the name implies, health insurance helps cover healthcare expenses for the insured. Health insurance products vary dramatically in type and scope and have their own unique risks, particularly when it comes to regulatory issues.
- Specialty: Specialty insurance, also known as the excess and surplus (E&S) lines, includes anything that cannot be covered by a standard insurance company. This includes difficult-to-assess situations and can also include high-risk versions of the other types of insurance. For example, liability insurance for a demolition business could fall under the category of specialty insurance.
- Reinsurance: This is insurance for insurance companies. To protect themselves from catastrophic losses, insurers often purchase reinsurance policies that will cover losses above a certain amount. This can be extremely important in the event of natural disasters or mass casualty events.
Benefits and risks of investing in insurance stocks
Insurance stocks can be a great way to build wealth over time without excessive risk. Since insurance companies make money not only from profitable underwriting but from investments as well, they can be excellent total return investments. This is especially true with companies like Markel, which branches out into stock and venture capital investing with its float.
Of course, there's no such thing as a risk-free stock investment, and insurance stocks aren't an exception. By nature, insurance has an element of unpredictability -- after all, the definition of insurance is transferring risk from one party (customers) to another (the insurance company). For example, if there's a particularly bad natural disaster, it can be potentially devastating to insurance company profits.
How to invest in insurance stocks
The process of investing in insurance stocks is pretty straightforward:
- Open your brokerage app: Log in to your brokerage account where you handle your investments.
- Search for the stock: Enter the ticker or company name into the search bar to bring up the stock's trading page.
- Decide how many shares to buy: Consider your investment goals and how much of your portfolio you want to allocate to this stock.
- Select order type: Choose between a market order to buy at the current price or a limit order to specify the maximum price you're willing to pay.
- Submit your order: Confirm the details and submit your buy order.
- Review your purchase: Check your portfolio to ensure your order was filled as expected and adjust your investment strategy accordingly.
Related investing topics
A recession-resistant business with excellent return potential
Insurance companies have highly attractive economics. Other people give them money to hold onto until a claim needs to be paid, and the insurer can invest this money for its own benefit in the meantime. This is why Warren Buffett is so attracted to insurance and chose it as the backbone of Berkshire Hathaway’s empire.
Insurance is a recession-resistant business as well. During tough times, people still need to maintain auto and homeowners coverage, for example. In short, insurance is a business that can produce excellent long-term returns without too much volatility.

