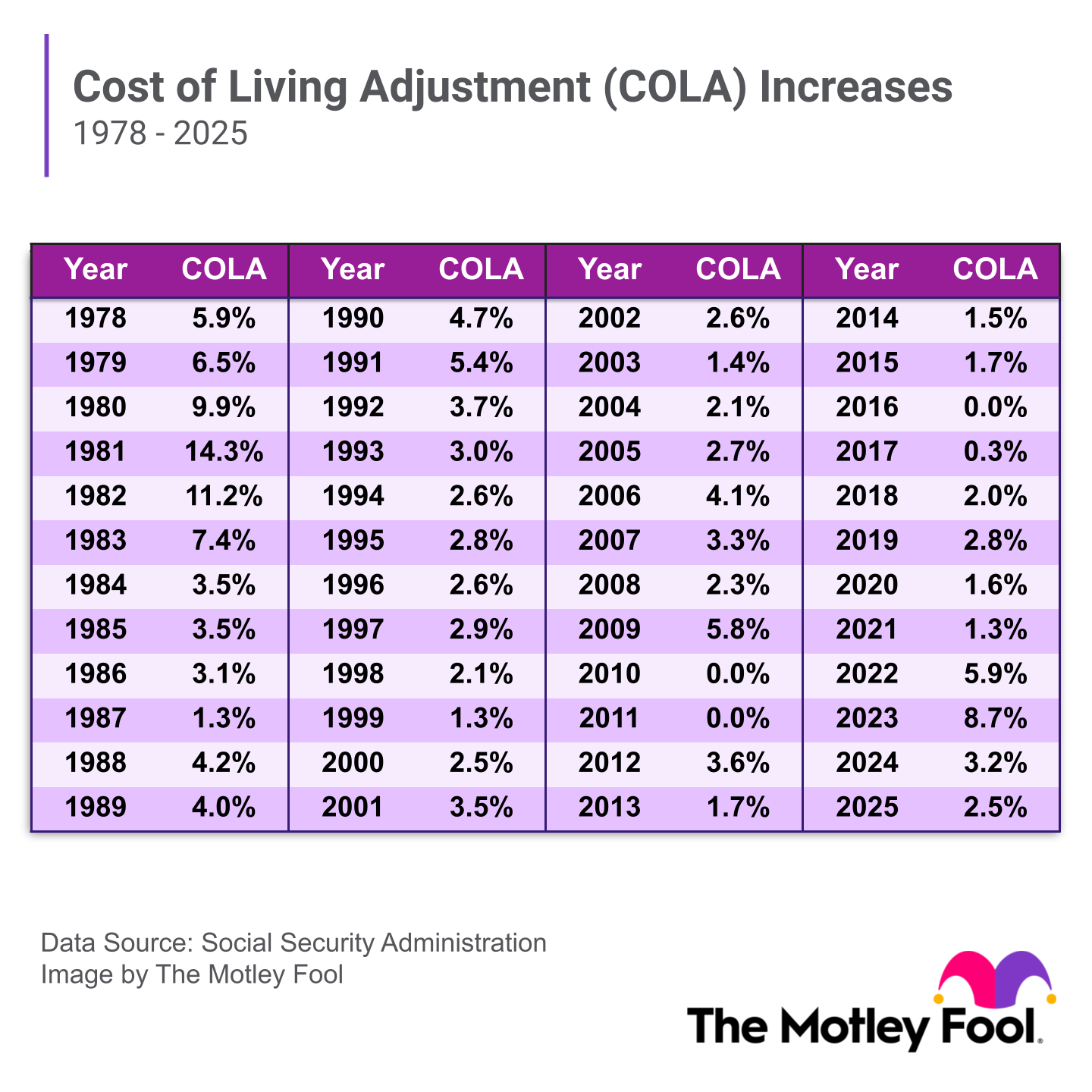
Learning how to maximize your Social Security can make a big difference in your retirement planning. Social Security makes up about 30% of income for people 65 and older. But increasing your Social Security requires careful planning.

Taxable Income
2. Work at least 35 years
The Social Security benefits formula uses an inflation-adjusted average of your 35 highest years of earnings. If you only work 32 years, you'll have three years with $0 in earnings, which would drag down your benefit. Working at least 35 years will help you maximize your benefit -- and working additional years could increase your benefit if you're replacing lower-earning years with higher-earning ones.
3. Delay as long as possible
You won't be eligible for your primary insurance amount until you reach full retirement age (FRA), which is 67 if you were born in 1960 or later. It's possible to start Social Security at age 62, but your benefit will be about 30% lower.
If you truly want to score the maximum Social Security benefit, though, you'll want to delay past FRA. You'll earn an extra 8% in delayed retirement credits for every year you wait, up to age 70, which is when your benefit maxes out.
4. If you're working, avoid collecting a check until FRA
In 2023. if you claim Social Security while working and haven't reached FRA, Social Security imposes limits on how much you can earn before it withholds part of your benefit:
- Until the year you reach FRA, Social Security withholds $1 for every $2 you earn above $21,240. That threshold will increase to $22,320 in 2024.
- From the year you reach FRA to the month you're eligible for your full benefit, Social Security withholds $1 for every $3 you earn above $56,520. That threshold will increase to $59,520 in 2024.
Once you reach FRA, Social Security won't withhold part of your benefit, no matter how much you earn. Note that even if you collect benefits early and continue working, Social Security will recalculate your benefit when you reach FRA to give you credit for the amount it withheld. Your benefit will increase as a result.

5. Collect spousal or survivor benefits
If your current or former spouse earned significantly more than you, you may get a bigger benefit by collecting based on their work record. Spousal benefits are paid to current spouses, as well as ex-spouses (if the marriage lasted at 10 least years).
The maximum benefit is 50% of their primary benefit. Collecting early will reduce your benefit more, but you can't earn delayed retirement credits for waiting past FRA. Your benefit will max out at age 67, not 70.
If you're a widowed spouse (or if your ex-spouse of at least 10 years has died), you could be eligible for survivor benefits. Survivor benefits are up to 100% of the late spouse's benefit (if they were already claiming) or up to 100% of their primary insurance amount (if they weren't taking benefits yet).
You can claim as early as age 60, rather than 62, for a reduced amount. As with spousal benefits, survivor benefits max out at age 67. Note that Social Security doesn't let you claim multiple benefits. You can collect your own retirement benefit or a spousal or survivor benefit, but not both.
6. Get a one-time do-over
If you've already started receiving Social Security but now wish you'd held out for a larger benefit, you may have two options for increasing your checks:
- If it's been fewer than 12 months since you were approved for benefits: You can withdraw your application for benefits and reapply later, but you'll need to repay all benefits you received, as well as any money withheld for taxes and Medicare premiums.
Medicare
- If you're already FRA but haven't turned 70 yet: You can request that Social Security suspend your benefits to earn delayed retirement credits, and then reinstate them later. Once you're 70, Social Security will automatically restart your payments if you haven't already had them reinstated.
7. Save for retirement in a Roth account
You technically won't get bigger Social Security payments if you opt for a Roth IRA or a Roth 401(k) over traditional accounts, but you will get to keep more of your benefit. Withdrawals from Roth accounts are generally tax-free in retirement because you've already paid taxes on that money. However, with traditional retirement accounts, you get a tax break on your contributions but have to pay taxes on withdrawals.
Related investing topics
The bottom line
One of the biggest myths about Social Security is that increasing your payments is easy. But as you can see, maximizing your Social Security benefit requires you to work more, earn more, or delay benefits you may need well before age 70.
While Social Security is a lifeline for seniors in the U.S., retirement is difficult when your benefit is your only source of income. That's why it's essential to invest for retirement as early as possible. But if you're behind on saving, then working longer and delaying benefits are two good strategies for maximizing your Social Security.