Helping to facilitate transparency about people and organizations working in the financial services industry, the Central Registration Depository (CRD) is a program that assists with the licensure of individuals working in the U.S. securities industry, as well as its regulators. Access to the CRD is available through the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), which oversees the program.

What is the CRD?
To support FINRA's efforts at promoting confidence that individuals and organizations operating in the financial industry are on the up-and-up, the CRD assumes a variety of responsibilities such as maintaining the registration records of brokerage firms, branch offices and their associated individuals. These records include their qualifications, as well as employment and disclosure histories. The CRD also manages the processing of form filings, fingerprint submissions, and registration-related fees from qualification exams and continuing education sessions.
Many of the records that the CRD collects are available to the public. This attempts to provide an extra layer of safety for investors, giving them the ability to research financial professionals. One tool in particular that is offered to the public with information from the CRD is BrokerCheck, which FINRA characterizes as a free tool that can help people research the professional backgrounds of investment professionals, brokerage firms and investment adviser firms.
The importance of the CRD
The CRD serves an important role in the financial services industry by ensuring that individuals can trust their stock brokers, insurance agents, and other financial professionals. The CRD also is essential to fostering confidence in the financial industry by helping FINRA and the Securities and Exchange Commission ensure that individuals and firms comply with industry rules and standards.
After its creation in 1981, the CRD received a major update in 1999, when many of its services became available on the internet. According to the North American Securities Administrators Association, which helped develop the CRD with the National Association of Securities Dealers (now FINRA), the CRD has a database of the licensing and disciplinary histories for more than 630,000 securities professionals and 3,800 securities firms.
Further insights into the CRD
Though it'd be nice to believe that everyone offering their services to help you mange your personal wealth has your best intentions at heart, bad actors are out there. To help protect people seeking assistance with their financial planning from these untrustworthy individuals, the CRD provides a valuable tool: BrokerCheck.
BrokerCheck provides a variety of information, such as summaries of the investment professionals and their credentials. In addition, the reports provide overviews of their employment histories for individuals over the past 10 years, including work experiences in and out of the securities industry. The reports also include individuals' current registrations and licenses. Perhaps most importantly, they also contain a disclosure section that details information regarding customer disputes, disciplinary actions, criminal matters, and pending actions or allegations.
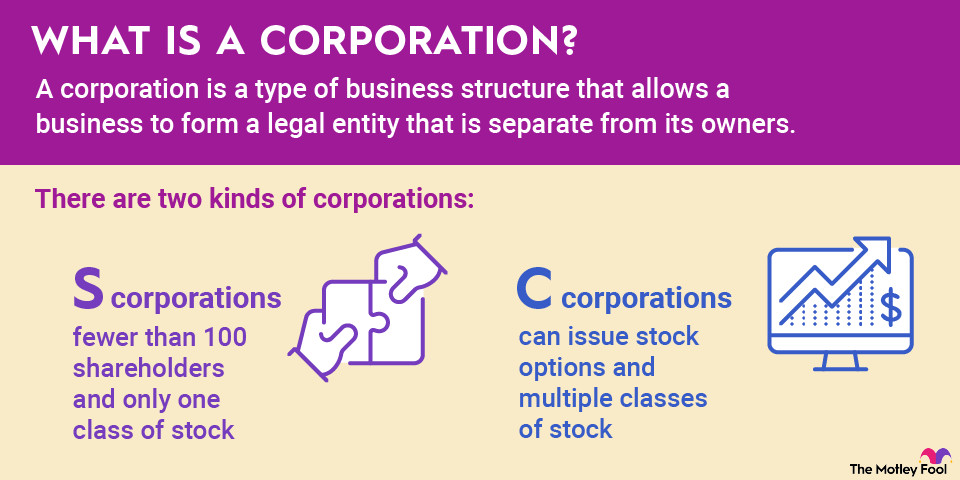
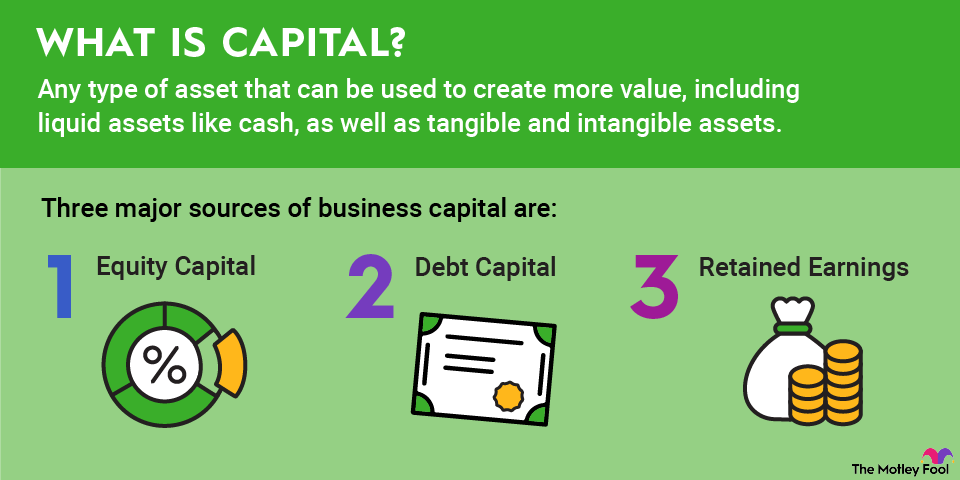
Related investing topics
The poster boy for financial advisor misconduct
From small-time crooks to those bilking clients out of millions of dollars, there are no limits to disingenuous individuals interested in taking advantage of unsuspecting marks. One of the most recognizable fraudsters in recent history was Bernie Madoff, who was responsible for a multi-billion Ponzi scheme that came to an end with his arrest in 2008. In late 2024, the Department of Justice announced the final disbursement of compensation to Madoff's victims, contributing to a total of $4.3 billion that had been returned to his victims.
Although Madoff died in 2021, individuals can still obtain a BrokerCheck report on him.