Dividend stocks can be a great way to generate passive income. The best ones consistently increase their dividends per share each year.
However, not all companies can routinely increase their dividends. One differentiating factor is the dividend payout ratio. Here's a closer look at this crucial metric for dividend investing.
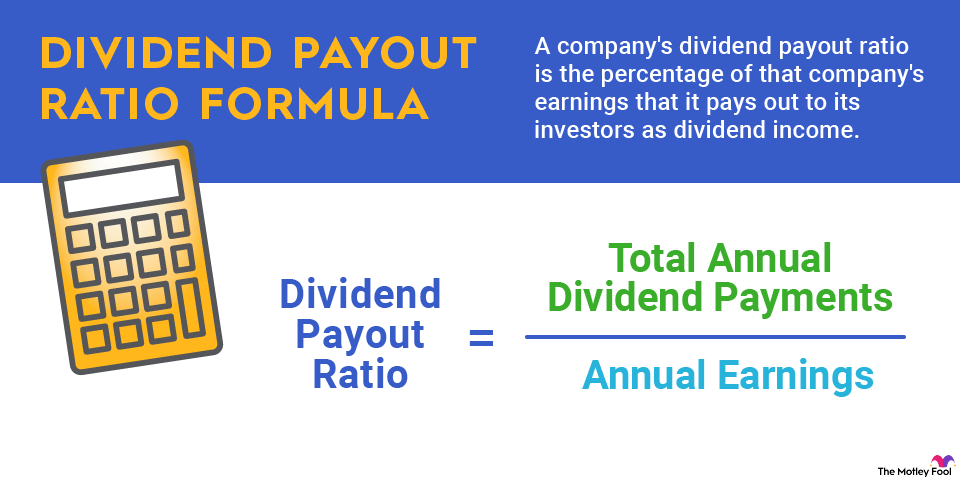
Dividend payout ratio formula
A company's dividend payout ratio is the percentage of that company's earnings that it pays out to its investors as dividend income. The dividend payout ratio formula is:
Total Annual Dividend Payments ÷ Annual Earnings = Dividend Payout Ratio
Say a company earns $100 million this year and makes $50 million in dividend payments to its shareholders. In this case, its dividend payout ratio would be 50%. You can also use per-share amounts to get the same result. This can be simpler since companies report dividends and earnings in per-share amounts.
How to use the dividend payout ratio
Let's use Apple (AAPL -0.54%) to demonstrate how to calculate the dividend payout ratio using per-share information. As of October 14, 2025, Apple had earned $6.58 per share over the previous four quarters. Its most recent quarterly dividend was $0.25per share, which works out to $0.96 per share annually. Using the dividend payout ratio formula above, we have:
$0.96 Annual Dividend Payments ÷ $6.58 Earnings Per Share = 15% Dividend Payout Ratio
What is a good dividend payout ratio?
Dividend payout ratios tend to vary by industry. Companies that operate in mature, slower-growing sectors that generate lots of relatively steady cash flow may have higher dividend payout ratios. They don't need to retain as much money to fund their business for things like opening new stores, building another factory, or on research and development for new products. For financially strong companies in these industries, a good dividend payout ratio may approach 75% (or higher in some cases) of their earnings.
However, companies in fast-growing sectors or those with more volatile cash flows and weaker balance sheets need to retain more of their earnings. Ideally, it should be less than 50%.
What is a safe dividend payout ratio?
When you calculate dividends, you'll also want to calculate the dividend payout ratio. A safe dividend payout ratio varies by industry and a company's overall financial profile. For example, one company operating in a stable sector might safely maintain a high dividend payout ratio of 75% of its earnings because it has a strong balance sheet. On the other hand, a competitor in that same industry that has a weaker financial profile might not be able to sustain its dividend if it had a payout ratio that high.
Historically, the safest dividend payout ratio has been around 41%, according to research by Wellington Management and Hartford Funds. More dividend stocks with a payout ratio averaging around that level have outperformed exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the S&P 500 than those with other payout levels. That's because they can pay an attractive dividend yield while also retaining a significant amount of cash to expand their business. They can also use it on other shareholder-friendly activities such as share repurchases and debt repayment.
Dividends Per Share
Is a high dividend payout ratio good?
A mistake many beginning investors make is to buy stocks with the highest dividend yields they can find. They assume that the higher yield will enable them to earn greater returns.
Unfortunately, that's not always the case. Many stocks with high yields also have a high dividend payout ratio. That potentially puts them at risk of cutting the dividend if business conditions deteriorate. They're also less likely to increase the amount of dividends paid since they have lower retained earnings. That gives them less wiggle room to increase their payout ratio.
A better approach is to buy stocks with a lower payout ratio, even if it means sacrificing potential yield to ensure that you own companies that can continue to pay dividends. These companies have more financial flexibility to invest in expanding their earnings, which will enable them to increase their dividends.
This is evident in the historical performance of dividend stocks:
Grouping | Annual Average Returns (1973-2022) |
|---|---|
Dividend growers and initiators | 10.24% |
Equal-weighed S&P 500 Index | 7.68% |
No change in dividend policy | 6.6% |
Dividend cutters and eliminators | 3.95% |
As the table shows, companies that made no change to their dividend policy (i.e., they maintained their payout level) and those that either cut or eliminated their dividends have underperformed the S&P 500 over the past several decades.
On the other hand, companies that recently initiated a dividend and those that have consistently increased their dividends -- such as Dividend Achievers and Dividend Kings -- have outperformed the S&P 500 over the long term. That's why investors should seek out companies with a lower dividend payout ratio instead of a higher yield since they're more likely to increase their payouts.
Related investing topics
Don't overlook the dividend payout ratio
The dividend payout ratio is a vital metric for dividend investors. It shows how much of a company's income it pays out to investors. The higher that number, the less cash a company retains to expand its business and its dividend.
Given the significant outperformance of dividend growth stocks, investors can use the dividend payout ratio to find companies with the flexibility to routinely reward them with more dividend income in the future.