You may have heard quite a bit in 2024 about whether the U.S. economy would be able to make a “soft landing” from the aftereffects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although the economy is far from out of the woods on a possible recession in 2025, it appears that the Federal Reserve pulled off the rare feat of engineering a recovery that didn’t involve a recession or high inflation.
What is a soft landing?
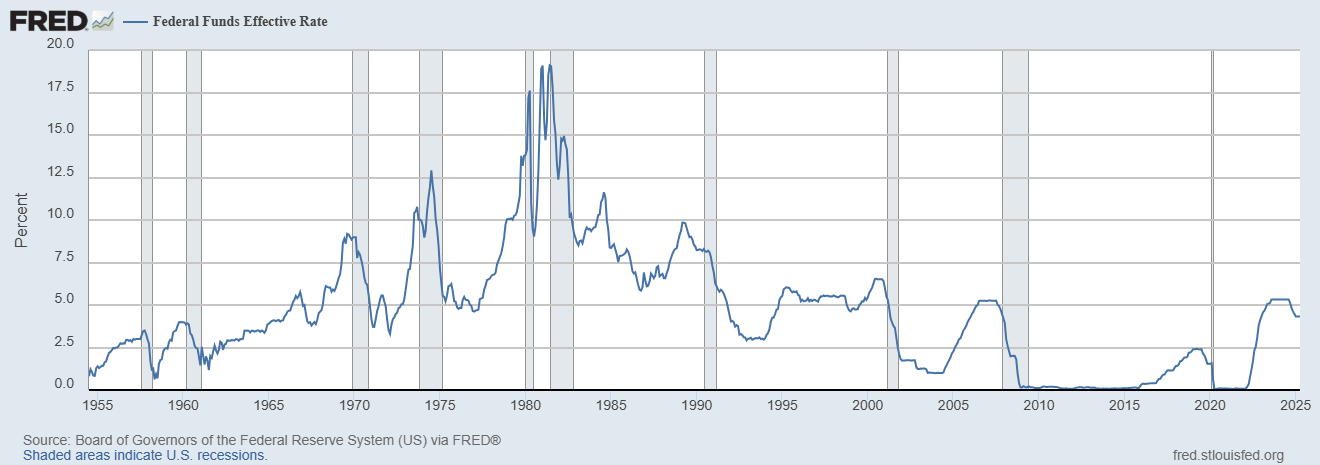
A soft landing is a recovery from an economic downturn that doesn’t involve a deeper recession or high inflation. It’s generally determined by interest rates, which are set in the United States by the Federal Reserve when it adjusts the federal funds rate, the rate at which banks use when lending money to each other.
Engineering a soft landing requires impeccable timing, which is no small feat in an economy with a gross domestic product (GDP) of about $30 trillion. If interest rates are too high, business investment can dry up, leading to high rates of unemployment and a recession. If interest rates are too low, inflation can soar, causing higher prices and eroding purchasing power for consumers and businesses.
Soft and hard landings
There’s only been one definitive example of a soft landing over the last half-century. After a booming 1994 during which the Fed raised interest rates seven times in 12 months, from 3.25% in February 1994 to 6%, a number of red flags appeared.
Near the end of 1995, business investment, government outlays, and consumer spending all slowed amid fears of a recession. Over the next six months, the Fed cut interest rates from 6% to 5.25%, and Americans escaped without a recession.
A much less successful attempt at a soft landing occurred in the wake of the 2008-09 financial crisis. As the global economy teetered on the brink of collapse, the Fed cut interest rates sharply, from 5.25% in September 2007 to zero by December 2008.
According to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), the Great Recession officially lasted from September 2007 until June 2009. Key economic indicators, however, told the story of an extremely hard and bumpy landing, with real GDP not climbing past pre-recession levels until 2011 and unemployment not fully recovering until 2016.
Most recently, the Fed was being given credit for steering the economy to a soft landing in early 2025. A brief recession caused by the 2020-23 COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc on supply chains and household incomes, pushing inflation to its highest levels since the early 1980s.
The Fed began raising interest rates in March 2022, raising them from 0.25% in March 2022 to 5.5% by July 2023. Meanwhile, the unemployment rate failed to rise significantly with higher interest rates, even as companies including Intel (INTC -2.81%), Tesla (TSLA -0.16%), and Cisco (CSCO -0.08%) laid off thousands of workers in the tech sector. As inflation eased, the Fed cut interest rates to 4.5% by late 2024.
Although a recession had been predicted (and indicated by metrics such as an inverted yield curve), leading experts, including Nobel laureate Paul Krugman and former Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, claimed a soft landing had occurred.
The soft landing also spurred optimism in the investment community amid a record-setting bull market. In a December 2024 note, State Street (STT -6.05%), one of three major index fund managers, observed that “the soft landing outcome has propelled stocks to all-time highs in 2024. Meanwhile, credit spreads are historically tight, and most measures of market volatility are tranquil. Solid corporate profits are forecast to accelerate throughout 2025, especially in the US.”
The jury, however, may still be out, as global tariffs imposed by the Trump administration have placed the Fed in a potentially difficult situation. As has been the case during previous potential downturns, the Fed would be able to cut interest rates to boost employment, risking inflation, or increase interest rates to dampen inflation, risking greater unemployment.