Semiconductors are at the heart of major technology trends, including artificial intelligence (AI) and next-generation communication systems. An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is a type of semiconductor that has been specifically designed to carry out a singular function with very high efficiency.
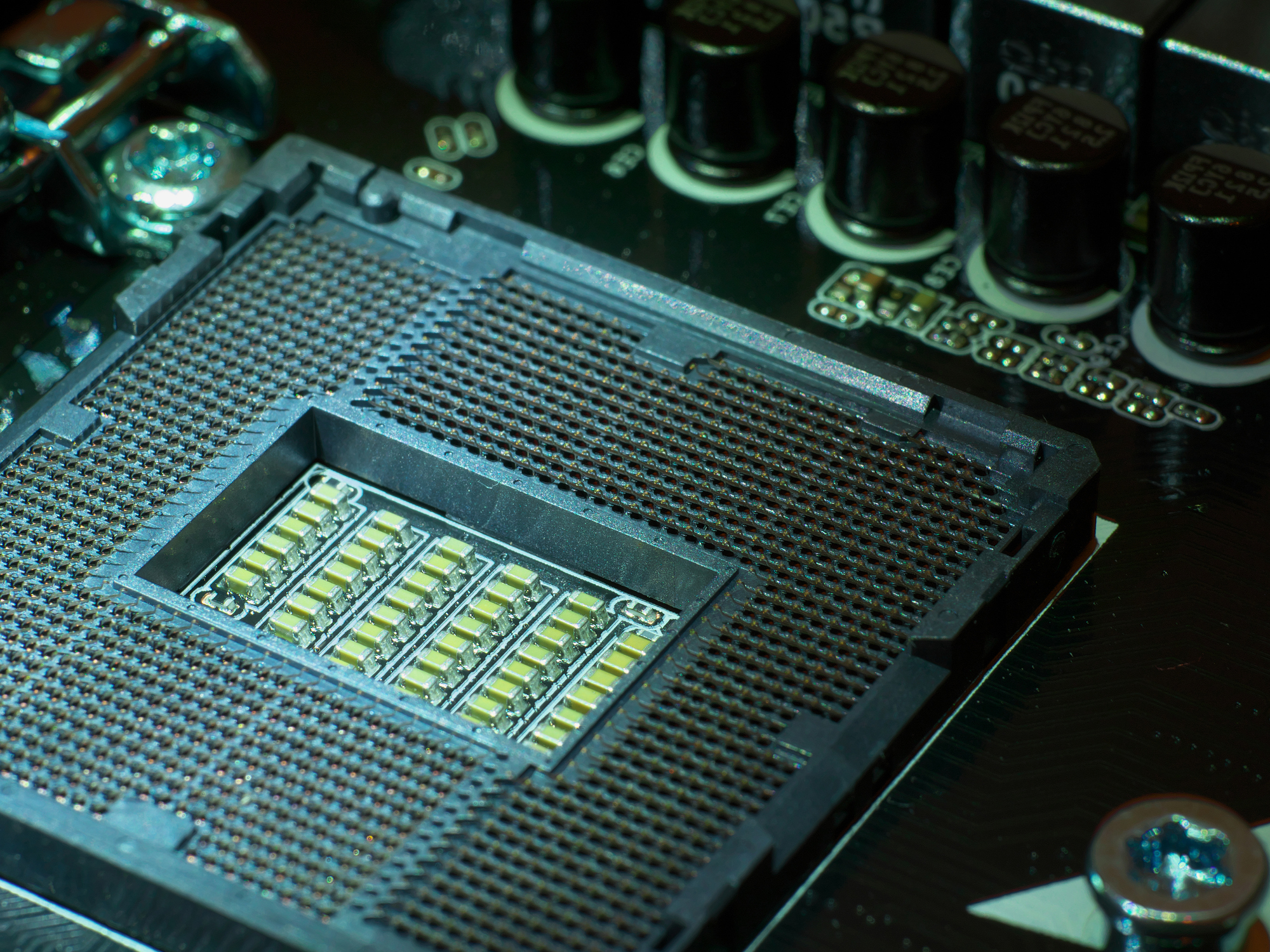
Understanding ASICs
Semiconductors, including central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs), are built to handle a variety of potential use cases. ASICs, on the other hand, are designed with one specific purpose in mind.
This focus on serving one particular function can allow ASICs to deliver superior performance and lower energy usage for their purpose-built tasks, compared to chips with broader, less-specialized capabilities. Within the ASIC category, there are two core types of designs.
ASICs that use the gate-array approach are semi-customized designs that offer the benefits of easier development and reduced costs by utilizing non-specialized transistors, layer architecture, and other hardware. Full-custom ASICs are fully specialized designs that can deliver better performance than semi-customs but come with the trade-off of higher development and manufacturing costs.
Why ASICS are important
Application-specific integrated circuits are less versatile than standard semiconductors. However, using chips that have been designed for specialized workloads can deliver a variety of benefits for hardware companies.
Even though there is a greater risk that an ASIC will become obsolete as technologies change, many leading hardware companies are willing to accept this risk and shoulder relatively high development costs because proprietary task-specific chips can help them stand out from the competition and deliver hardware that paves the way for stronger sales and margins over the long term.
ASICs are already widely used in consumer tech devices, telecommunications, and networking hardware, including switches and routers, vehicles, and cryptocurrency miners. They have also been gaining favor in the artificial intelligence (AI) processing space.
What are the practical benefits of ASICs?
In addition to improving performance and reducing energy consumption for a given computing task, ASICs can help reduce the overall size of hardware and free up processing power for other chips in the device.
For example, a task being handled by an ASIC is one that doesn't need to be performed by a CPU. Application-specific integrated circuits can help lower hardware failure rates because they rely on fewer components to complete a function.
Using ASICs can also allow hardware manufacturers to reduce costs, protect their intellectual property, and establish and protect competitive advantages. Application-specific integrated circuits typically have higher up-front development costs compared to chips built with more generalized capabilities in mind, but they can offer big advantages for hardware makers at scale.
Related investing topics
An example of ASICs in action
Nvidia (NVDA -2.94%) has been dominating the AI hardware space with its GPUs, but other leading tech players are looking to ASICs as a potential technological alternative. Companies like Alphabet (GOOGL -0.75%)(GOOG -0.87%) and Amazon (AMZN -2.61%) are turning to internally designed ASICs as a way to reduce their reliance on Nvidia's hardware and cut down on AI infrastructure costs.
Given the high hardware costs and highly energy-intensive nature of relying on artificial intelligence infrastructure centered around GPUs, ASICs could continue to play a growing role in reducing costs and power consumption and pushing the broader AI revolution forward.