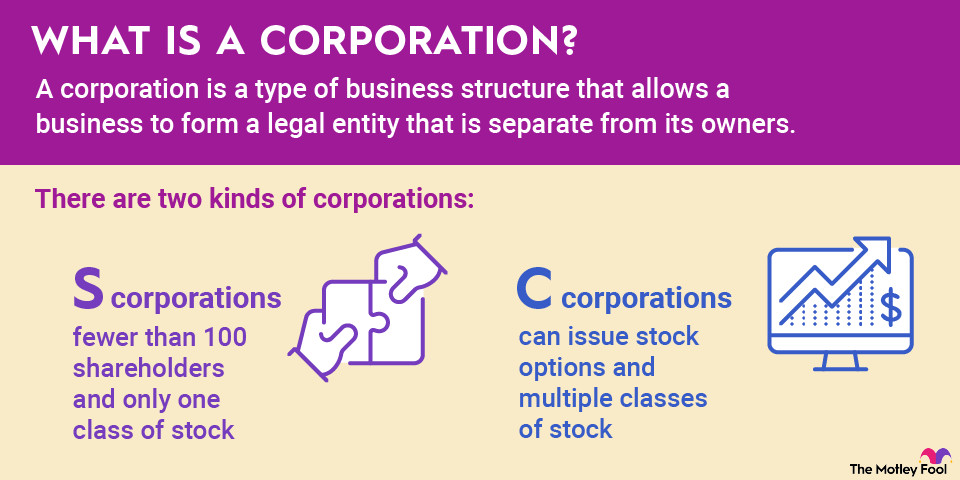
When the enemy is at your door, having a moat can help protect your castle from rival kingdoms, and the same is true for businesses. A competitive moat is just one type of moat that can help keep your competition at arm's length and your sales strong.

What is a competitive moat?
A competitive moat (Warren Buffet calls these "economic moats") is a major advantage you have over your direct competition. That's pretty vague, but there are so many potential things that could make up your moat that it's hard to be too specific. If there's something that's giving your company a business advantage in your market, it could be your competitive moat.
A very basic example would be a manufacturing company that has developed a proprietary technology that allows it to produce its products with just as much quality but for 30% less than the competition. That proprietary tech is its competitive moat, keeping the competition at bay since they don't have access to that same tool.
Monopoly
Resource moats
Resource moats are about what you own or the collection you've established. This is often in the form of intellectual property or regulatory good fortune. If you have a whole catalog of exceptional patents, for example, that's a resource moat, as would be simply being in the right place at the right time when regulations changed, giving you an accidental monopoly or leg-up when you happened to be in compliance and no one else in your industry was.
Related investing topics
Why competitive moats matter to investors
Competitive moats are a stock investor's favorite thing. Because competitive moats give a company an untouchable advantage, they're likely to be companies that can last over the long term. If you're working a buy-and-hold strategy, finding companies with wide moats is like finding chunks of gold in your potting soil mix.
There are lots of great companies for shareholders to buy into, but those with healthy competitive moats are absolute no-brainers when it comes time to choose your investments. There's no such thing as a perfectly safe bet, but these companies are generally about as safe as it gets.