Setting up a workplace retirement plan for your small business can help ensure your and your employees' retirement while attracting higher-quality talent. But not all retirement plans are created equal. If you're trying to decide between a SIMPLE IRA and a 401(k) plan for your small business, this article will give you the basics to get you started down the right path.
The basics of SIMPLE IRAs
The SIMPLE IRA is, as the name implies, simple, at least relative to other workplace retirement plans. SIMPLE is a backronym for Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees, and IRA stands for Individual Retirement Account.
Any employer with 100 or fewer employees is eligible to establish a SIMPLE IRA plan, assuming they don't have any other workplace retirement plan. It's very easy to establish, with most financial institutions offering boilerplate plans for free.
Any employee who earned at least $5,000 in the previous two years and expects to earn $5,000 this year is eligible to contribute to a SIMPLE IRA account. Employers can establish less restrictive rules if they choose, but they cannot add further restrictions.
Employees can generally elect to contribute up to $16,500 in 2025, or $17,000 in 2026. If the employee is 50 or older, they can contribute an additional $3,500 in 2025 or $4,000 in 2026. There are a few exceptions, though:
- If the business has 25 or fewer workers, employees can contribute up to $17,600 in 2025 or $18,100 in 2026. Workers 50 and older can make catch-up contributions of up to $3,850 in both years, for a maximum contribution of $21,450 in 2025 or $21,950 in 2026.
- Employers with 26 to 100 workers can also allow these higher limits -- but they must offer higher contribution rates of either a flat 3% of employee salaries or a 4% match.
- Starting in 2025, employees between the ages of 60 and 63 can make higher catch-up contributions of up to $5,250. This limit will remain the same in 2026.
The employer withholds the amount the employee elects from each paycheck and deposits it in their designated SIMPLE IRA account.
In addition to the employee's contribution, the employer also contributes. The employer contribution can either be a dollar-for-dollar matching contribution of 3% of the employee's compensation or a non-elective contribution equal to 2% of each employee's compensation. The higher matching contribution percentage could result in the employer contributing more if its employees are motivated to save for retirement.
SIMPLE IRAs vs 401(k)s
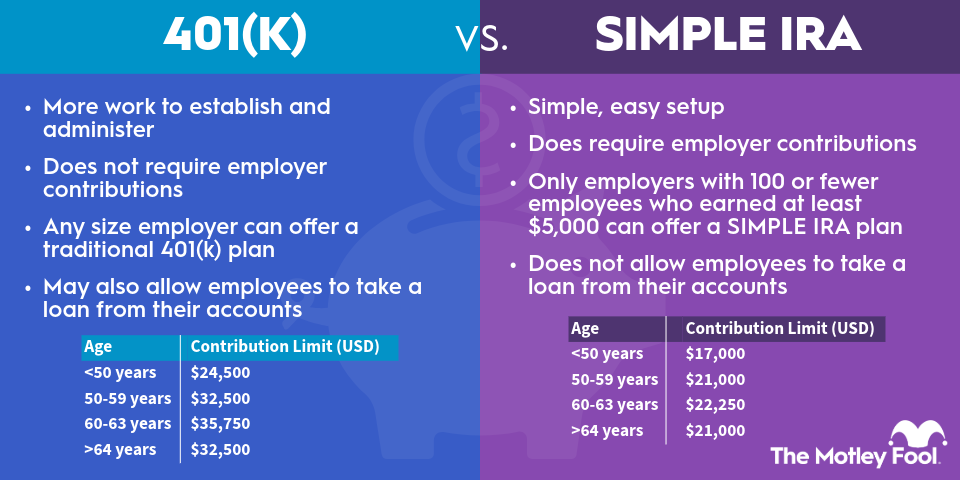
A SIMPLE IRA has its advantages and disadvantages versus a 401(k). First, 401(k) plans require significantly more work to establish and administer, which means they are more expensive for the business owner. 401(k) plans also require nondiscrimination testing and annual tax reporting at the plan level.
Additionally, 401(k) plans may restrict investment options for participants to facilitate easier administration and ensure plan compliance. It's possible to establish self-directed 401(k) accounts, but SIMPLE IRA plans are more typically self-directed, allowing account holders to invest in a broad range of options, including individual stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
On the other hand, 401(k) plans allow employees to contribute more to their retirement than a SIMPLE IRA if they choose. The contribution limit for employee salary deferrals into 401(k)s is $23,500 in 2025 and $24,500 in 2026. Individuals aged 50 to 59 or 64 and older can contribute up to $31,000 in 2025 or $32,500 in 2026. Those aged 60 to 63 can set aside up to $34,750 in 2025 or $35,750 in 2026.
There's also more flexibility for the employer contribution. Employers can contribute anywhere from 0% to 25% of an employee's compensation, as long as they offer the same employer contribution terms to all participants. Additionally, matching contributions don't have to be dollar-for-dollar like in a SIMPLE IRA.
An employer can also implement vesting periods for the employer contribution in a 401(k). That means the employee needs to continue working to receive the benefit of the matching contribution. That can keep employees around longer. SIMPLE IRA employer contributions vest immediately.
401(k) plans may also allow employees to take a loan from their accounts. That can allow them to temporarily access their retirement funds for a big purchase or emergency spending, making them more appealing to employees.
Which is better for you?
The value of offering an employer-sponsored retirement plan lies in its ability to attract and retain top employees. So what's best for you, as a business owner, is also what's best for your employees.
If your business offers higher salaries, it's more likely you'll want to invest in the more expensive 401(k) plan. Employees with higher salaries are more likely to want to save more of their earnings for retirement. In addition, the more flexible matching contribution of a 401(k) may allow you to save more versus the compulsory employer contributions of a SIMPLE IRA. (Although a good 401(k) employer match is a key benefit employees look at when comparing jobs.)
If you offer lower salaries, a SIMPLE IRA will likely suffice for your employees. $17,000 (or $18,100) is still a high contribution limit when compared to retirement savings options outside of the workplace, especially for employees on an average salary. Keep in mind that a SIMPLE IRA or 401(k) won't prohibit employees from also contributing to their own IRAs outside of work, but it may restrict their deductible contribution if their income is too high.
The primary benefit of a SIMPLE IRA is its lower setup and administration costs. If a SIMPLE IRA meets the needs of your employees, it's a much better choice than a 401(k). But if you need more flexibility and higher contribution limits, a 401(k) is worth the expense.