Stock market performance
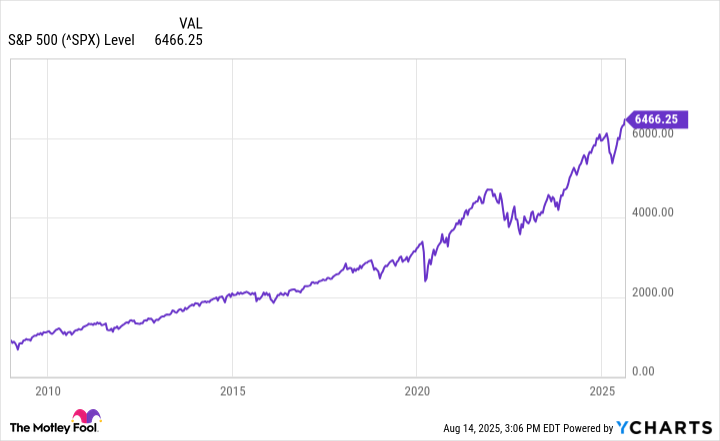
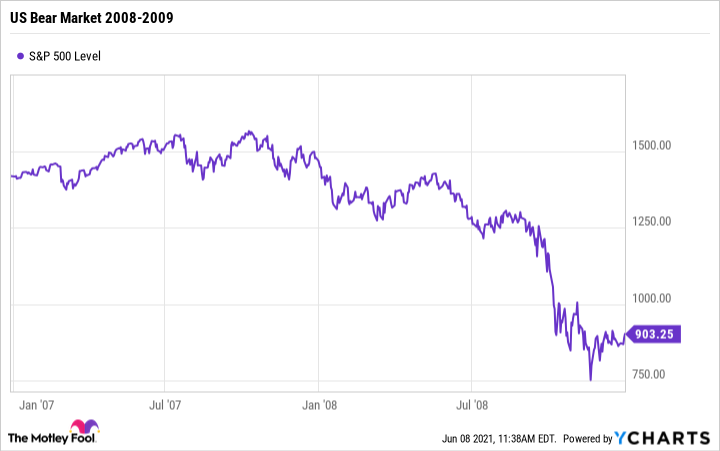
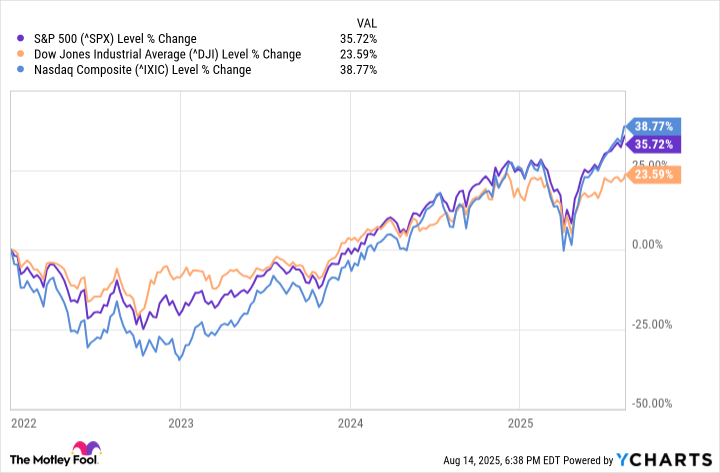
Stock prices are rising in a bull market and declining in a bear market. The stock market under bullish conditions is consistently gaining value, even with some brief market corrections. The stock market under bearish conditions is losing value or holding steady at depressed prices.
Change in GDP
Rising GDP denotes a bull market, while falling GDP correlates with a bear market. GDP increases when companies' revenues increase and employee pay rises, which enables increased consumer spending. GDP decreases when companies' sales are sluggish and wages are stagnant or declining.
Bear markets are closely linked with economic recessions and depressions. Recessions are formally declared when GDP decreases for two consecutive quarters, while depressions occur when GDP decreases by 10% or more and the downturn lasts for at least two years.
Unemployment rate changes
A declining unemployment rate is consistent with a bull market, while a rising unemployment rate occurs during a bear market. During bull markets, businesses are expanding and hiring, but they may be forced to lower their headcounts during bear markets. A rising unemployment rate tends to prolong a bear market since fewer people are earning wages, which results in reduced revenue for many companies and in turn, more people selling shares or not buying into companies.