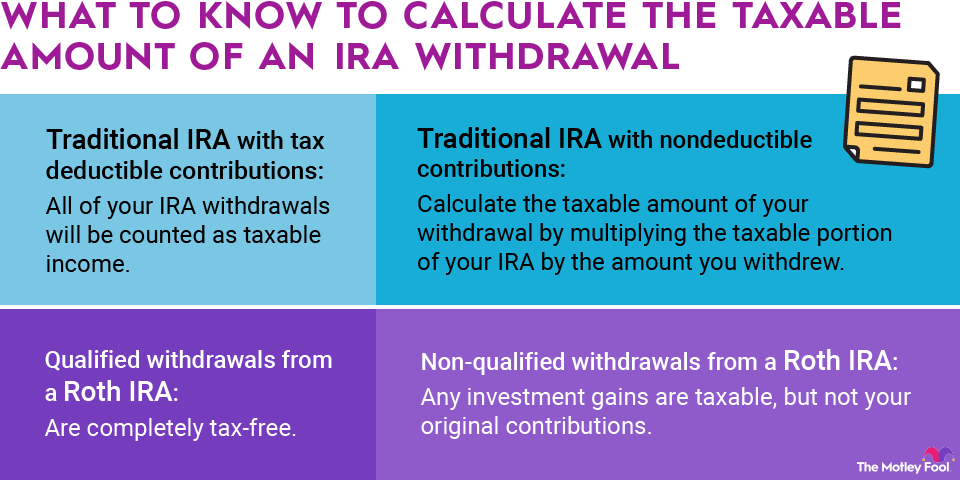
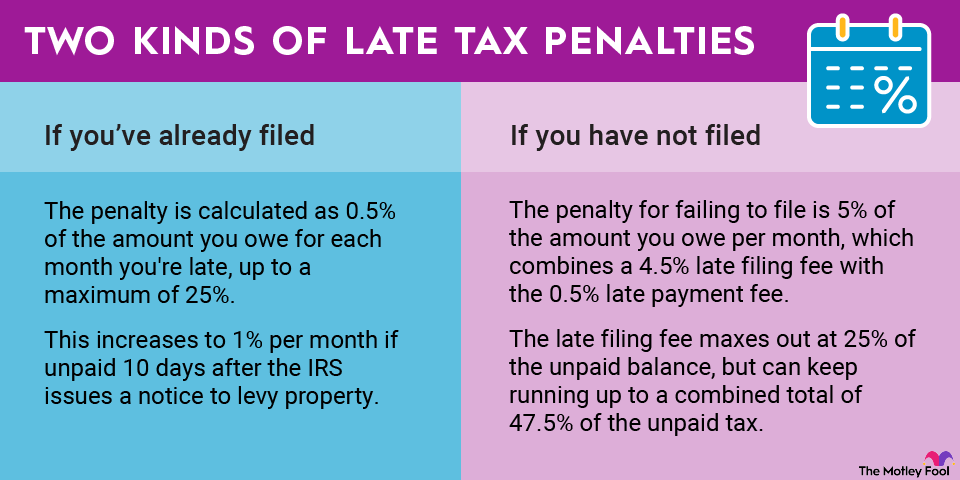
There are several ways of evaluating the profitability of a business, and one of the simplest ways is with the total margin ratio. This ratio shows a company's profitability relative to the total revenue it produces. Here is how you can calculate it, as well as what it means.

Calculating the total margin ratio
First, determine the business' net income, which can be found by subtracting its total expenses from its total revenue.
Net income = Total revenue - Total expenses
It's important to emphasize that you need to account for all revenue, including operating revenue and nonoperating revenue, such as investment income. Similarly, be sure to account for all expenses, even interest and taxes, which are left out of some other profitability metrics. You can find the net income listed separately on the income statement, but it's important to know where it comes from.
Then, divide the net income by the total revenue, and multiply by 100 to express the result as a percentage. This will give you the company's total margin ratio.
Total margin = (Net income ÷ Total revenue) × 100
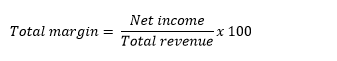
A positive percentage represents a profitable business, and a negative percentage tells you the business is losing money. Certain businesses operate at total margins of 10%, 20%, or more, while other types of businesses regularly operate at much narrower profit margins, as we'll see in the example below. For this reason, this metric is most useful when comparing similar businesses -- it wouldn't be too useful if you're trying to compare, say, a retail business and a tech company.
Why it's useful
Total margin ratio is useful for assessing and comparing the overall profitability of businesses and is also useful for tracking a business' profitability over time. Because of its simplicity, total margin ratio is not enough by itself to evaluate a potential investment, but it can be a good starting point.