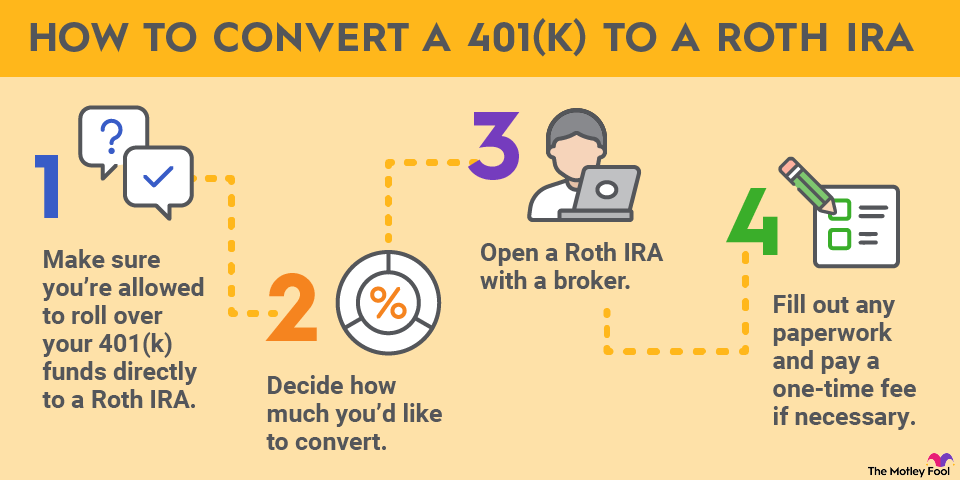
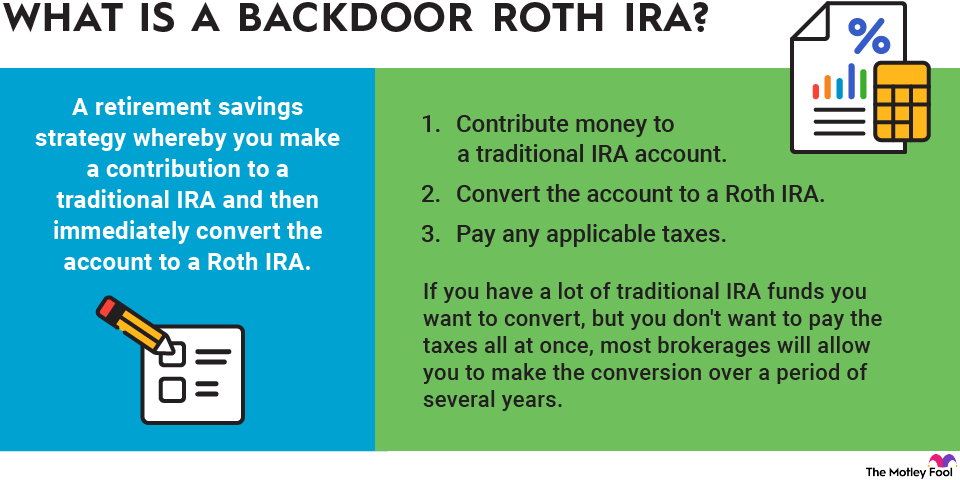
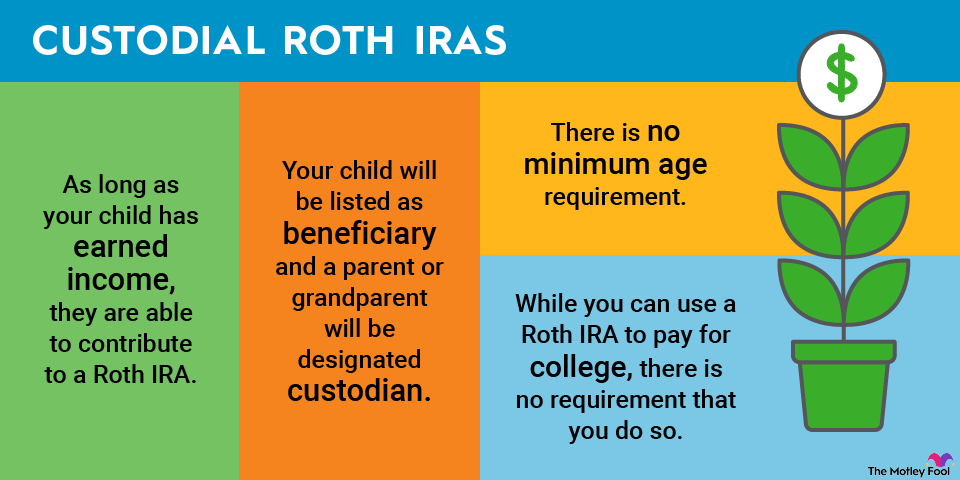
RMDs on inherited Roth IRAs
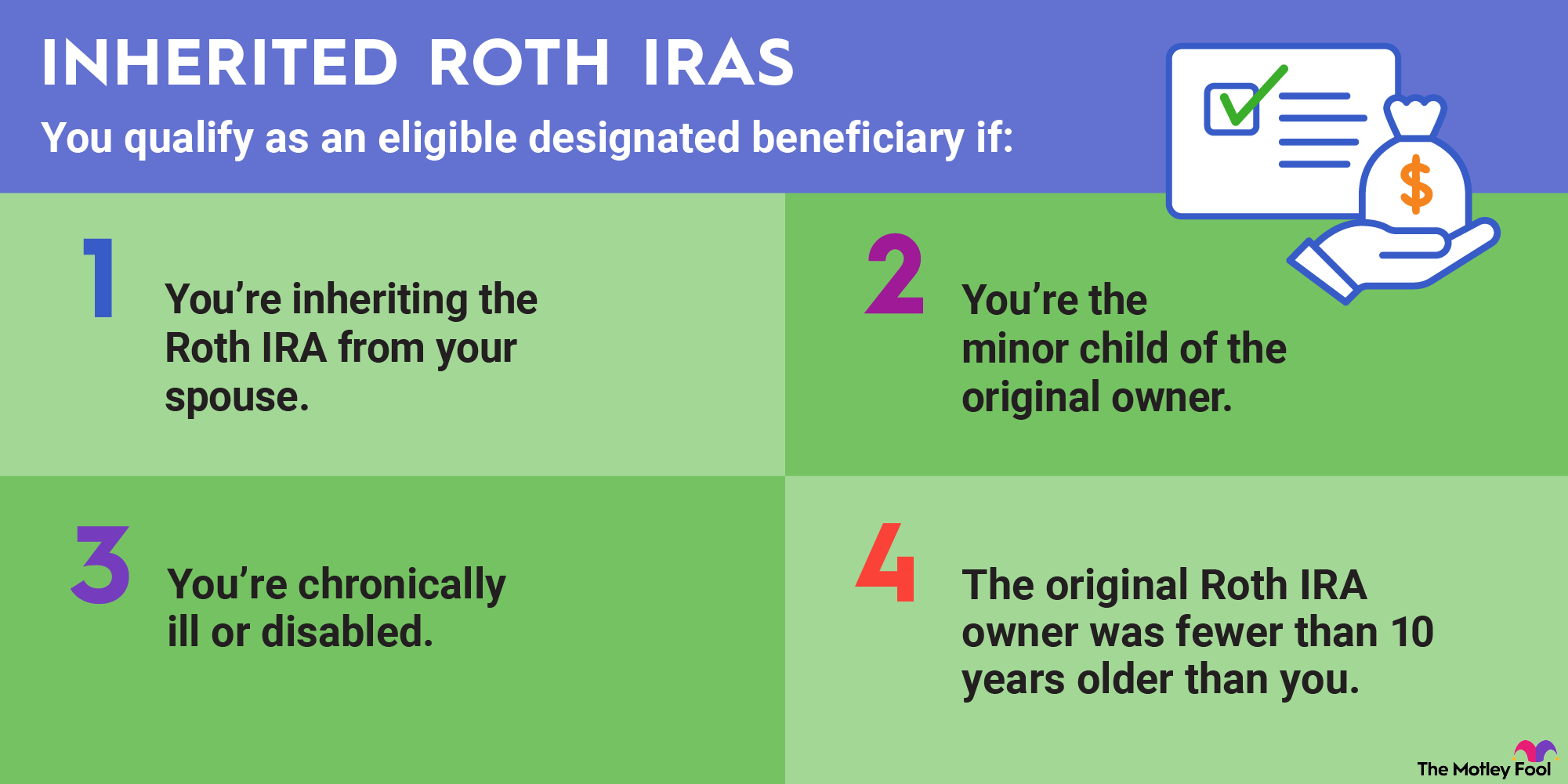
The distribution rules for Roth IRAs change once you pass away. The exact withdrawal requirements depend on who inherits your Roth fund. For example, your spouse can roll over the Roth assets into their own Roth IRA. The IRS does not impose RMDs on those inherited funds while your spouse is living.
Non-spouse beneficiaries, including children, don't have that rollover option. Those types of beneficiaries can either withdraw the funds immediately or transfer them to an inherited Roth IRA. Generally, moving the money to an inherited Roth IRA is the better choice because it allows the money to continue growing tax-deferred.
Inherited Roth IRAs have specific withdrawal requirements, and to further complicate matters, these distribution rules have recently changed. For Roth IRAs inherited before Jan. 1, 2020, beneficiaries may take RMDs over their lifetimes (based on IRS life expectancy tables). However, following the passage of the SECURE Act in 2019, most beneficiaries no longer have the option of receiving lifetime RMDs for IRAs bequeathed after 2019.
The exceptions are beneficiaries who are younger than the original account owner by 10 years or less, beneficiaries who are chronically ill or disabled, and minor children. Minor children can take RMDs until they reach legal adulthood. Thereafter, they have 10 years to withdraw the remaining funds. Students may have the option to delay the start of the 10-year window until they reach age 26.
10-year rule for inherited Roth IRAs
If you inherit a Roth IRA in 2020 or later, then you must withdraw all funds from the account within 10 years of the original owner's death. Withdrawals are tax-free if the funds have been in the account for five years or more.
Because a Roth IRA has no RMDs for the original owner, it's a powerful tool for building wealth and a financial legacy. Your beneficiaries, too, will enjoy years of tax-deferred earnings growth after inheriting the account.