Artificial intelligence (AI) is quietly transforming the real estate industry — from how homes are priced and marketed to how properties are managed and maintained. What was once a slow-moving, relationship-driven business is increasingly powered by data, algorithms, and automation.
Real estate generates massive amounts of information, making it a natural fit for AI. Machine-learning models now help estimate property values, identify investment opportunities, and streamline transactions, while generative AI enables virtual tours and 3D property models that let buyers explore homes from anywhere. Behind the scenes, AI-powered smart-home and property-management systems are improving efficiency, reducing costs, and flagging issues before they become expensive problems.
In this article, we’ll break down eight practical ways AI is being used in real estate today — and what these innovations mean for homeowners, investors, landlords, and the companies building the technology.
Understanding AI
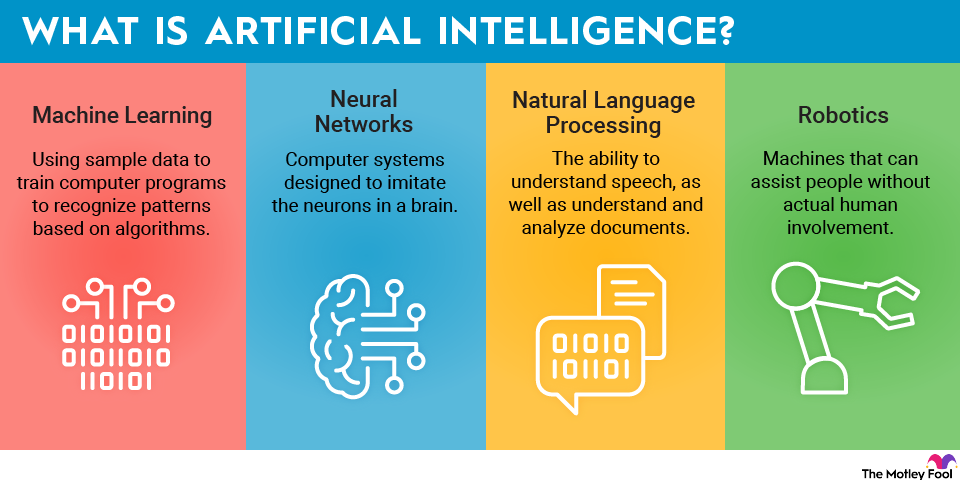
AI is generally understood as the ability of computers and machines to handle tasks that require human intelligence. Machine learning, one of the most common applications of AI, involves training machines with large amounts of data to recognize patterns, analyze data, and run forecasts and algorithms.
These applications are common in real estate. More broadly, AI technology includes computer vision in autonomous vehicles, robotics, neural networks, voice recognition, and natural language processing. Keep reading to see eight ways AI is used in real estate.
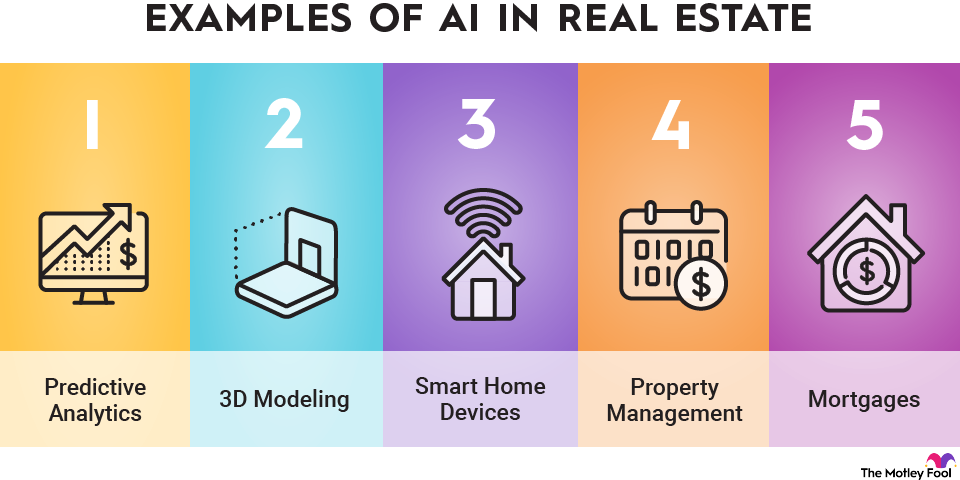
Eight uses of AI in real estate
1. Predictive analytics
Perhaps the most common and practical use of AI in real estate is predictive analytics. When you see an estimate on the value of a property, it's generally based on predictive analytics from AI.
Zillow, the leading online real estate marketplace, uses AI for its Zestimates -- the proprietary valuation estimates it provides -- as well as for personalized recommendations, floor plans, and photos. Rival Redfin, now owned by Rocket Companies, uses AI for similar estimates and offers users an AI-powered tool to enhance and redesign listing photos.
Forecasting is important, especially when investing in commercial real estate. Investors, agencies, and economists use AI to predict where the real estate market is headed, hoping to get an edge on the competition and buy at the right price.
2. 3D modeling/virtual tours
Visual representations have become increasingly important in the real estate industry. It's one of a number of industries taking advantage of digital twins: AI-based, computer-generated images that enable users to explore a space digitally.
Matterport, now owned by CoStar (CSGP -15.45%), is considered a leader in the technology. It creates 3D virtual tours of properties, allowing potential buyers to use augmented reality and other features to explore a property before visiting in person. Matterport's proprietary AI, Cortex AI, is a neural network that utilizes computer vision, image processing, and deep learning to automate 3D-image construction.
Nvidia's (NVDA -2.82%) Omniverse technology, which enables the creation of digital twins, is often used for virtual tours, allowing prospective buyers to immerse themselves in the property. This technology can also be used for virtual staging, allowing real estate agents to virtually show a property fully furnished or with different layouts.
The technology helps increase the pool of potential buyers since anyone with a connected device can get a good look at the property. It also helps buyers, sellers, and agents save money by screening potential buyers to ensure they're interested.
Some start-ups are developing similar technologies that show renderings of properties that don't exist yet. Some of them focus on assisting architects and offer tools that can provide cost estimates based on different design options.
3. Smart home devices
Real estate is a massive industry, and property tech might be an overlooked corner of it. However, property tech, or proptech, represents a fast-growing niche in the real estate industry.
Proptech focuses on devices that enable landlords and homeowners to monitor properties remotely. These include smart home devices, such as smart doorbells, locks, thermostats, and cameras, that help notify people of any problems that might occur inside the property.
AI enables devices to learn user preferences and adjust their settings accordingly. They can help save money on utilities, improve tenant satisfaction, and help the landlord stay up to date and avoid major repairs.
4. AI in property management
Property management is another important subsector of the real estate industry. AI assists managers in screening tenants, collecting rent, and scheduling maintenance.
AI chatbots can play a role in tenant screening, much like their uses in customer service across other industries. They can answer questions about rental rates and availability and guide customers through the application process, alleviating some of the work required of human agents.
AI automation can assist with processing payments, managing workflows, performing market analytics, and managing collections. Additionally, AI assistants can generate reports to track leasing performance, helping improve occupancy and operational efficiency.
5. Mortgages
Artificial intelligence is also gaining increasing adoption in financing, including mortgages. In underwriting, AI is used to analyze borrower information, including credit scores, income, and employment history, to evaluate the borrower's risk profile and find the best rate to charge.
AI tools help detect and prevent fraud and can automate loan servicing tasks, such as payment processing and customer communication. Some mortgage lenders, such as Rocket Companies (RKT +7.96%), use AI to deliver near-instant decisions on mortgage applications.
For instance, the company offers mortgage approvals in as little as eight minutes. In April 2024, it launched Rocket Logic, an AI-driven platform designed to simplify the mortgage application process for homebuyers and deliver approvals faster.
6. Risk assessment and fraud detection
Risk assessment and fraud detection are other ways AI can benefit real estate agents and potential sellers. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large amounts of data to find suspicious patterns and potentially fraudulent behavior.
In this sense, cybersecurity plays a role in AI and real estate, and large landlords use platforms like CrowdStrike's (CRWD -3.86%) Falcon endpoint security program for threat detection. Commercial real estate services firm Cushman & Wakefield relies on the Crowdstrike platform for protection from fraud and other cybersecurity challenges.
7. Automated property valuation
AI is also being used for automated property valuations. These automated valuation models utilize algorithms and datasets to determine a property's estimated value, using comparable sales, tax assessments, other listings, and records to determine a value.
Automated valuations offer some advantages over traditional methods, including speed, scalability, data-driven analysis, and real-time valuations. While they're not designed to be a full replacement for a comparative market analysis (CMA), they are a good starting point for valuation estimates and gathering information.
8. Personalized property recommendations
Finally, AI is being used for personalized property recommendations. Instead of just analyzing properties, AI can review customer data, including purchasing history, browsing patterns, and preferences, such as size, budget, and amenities, to make recommendations for customers.
Much like with automated property valuations, this technology is designed to complement a human real estate agent, who can work with nuances and desires that would be beyond a typical AI function.
Related investing topics
Benefits and risks of AI in real estate
Like any other technology, there are both benefits and risks to using AI in real estate.
Among the benefits are:
- AI can help a prospective homebuyer get a lot of information quickly, especially about a large area or number of homes, saving time on research and collecting that information.
- Predictive analytics is another useful tool that AI can provide in real estate. AI-powered systems can help predict trends so you'll know which markets or neighborhoods have the most potential for appreciation.
- Computer vision is also a benefit in real estate, and is being used through tools like digital twins to monitor real estate holdings, or virtual tours to show a home online.
Some of the risks in AI in real estate include:
- AI-based estimates for real estate values can sometimes give a false sense of certainty. Zestimates, for example, aren't based on perfect information, and can't see what's inside a home.
- Another major risk of AI is that the results can be biased, as it's only as good as the data it is fed. If you're screening applicants, for example, you'll want to make sure you test your results for bias so you're not violating any anti-discrimination laws in housing.
- AI can help with real estate paperwork, but it's a mistake to rely on it in place of a human, especially for something like a lease negotiation, or when context or nuance is key.
Will AI change the world of real estate?
Real estate is a massive, fragmented industry that is typically slow to change. However, the examples above show that AI is already affecting areas such as predictive analytics, property estimates, smart home devices, mortgages, and others. As AI improves, it's likely to become an even bigger part of the real estate industry.
If you're an investor searching for exposure to AI, consider AI stocks or AI exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or learn more about real estate investing to discover more opportunities to use AI in real estate. Keep your eye out -- more real estate companies are set to embrace AI in the future.