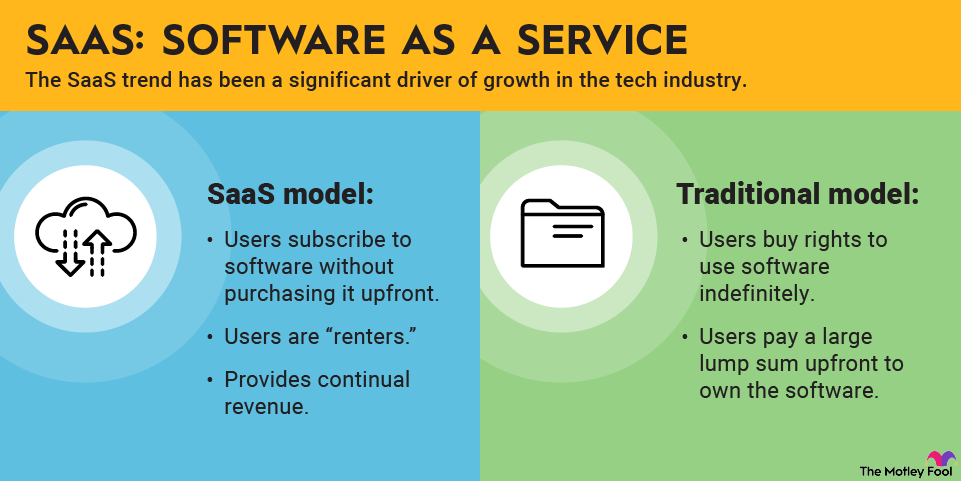
Semiconductor stocks are shares of companies that produce the microchips and electronic components used in everything from smartphones to cars.
They are part of the technology sector but are also manufacturing businesses, which means their businesses are cyclical, like any industrial business.
Semiconductor
Picking top-performing semiconductor stocks in the industry can be tricky, and their performance is highly volatile since sales volumes ebb and flow.
But the semiconductor sector is growing rapidly as the world rapidly embraces its critical role in artificial intelligence (AI) development and applications.
Some of the best-performing stocks throughout 2023-25, like Nvidia (NVDA +2.98%), have hailed from the semiconductor industry.
Different types of semiconductor stocks
The Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS), a system used by investors and index providers to categorize public companies by sector and industry group, places semiconductor stocks under the information technology sector. Within this sector, GICS breaks down semiconductor-related firms into two main categories.
Semiconductor equipment
These companies provide the tools, machines, and services required to manufacture chips. This includes firms that make lithography systems, wafer inspection tools, or etching equipment used by chipmakers. These companies tend to be critical suppliers for the production process, but don’t produce chips themselves.
Semiconductor companies
These are the ones that actually design and manufacture the chips that power computers, smartphones, cars, appliances, and more. These chips can range from basic memory to high-performance processors or specialized sensors.
Other classification methods
Beyond this GICS classification, semiconductor stocks can also be sorted by geography, such as U.S.-based versus international companies, or by business model.
Some are fabless, meaning they design chips but outsource the manufacturing to third-party foundries. Others operate fabs, or fabrication plants, and handle the manufacturing process in-house.
Each of these distinctions can affect how the company earns revenue, manages costs, and scales operations.
What trends drive semiconductor stocks?
Computer chips have many uses, but up-and-coming semiconductor companies will likely focus on two areas of growth in the decade ahead:
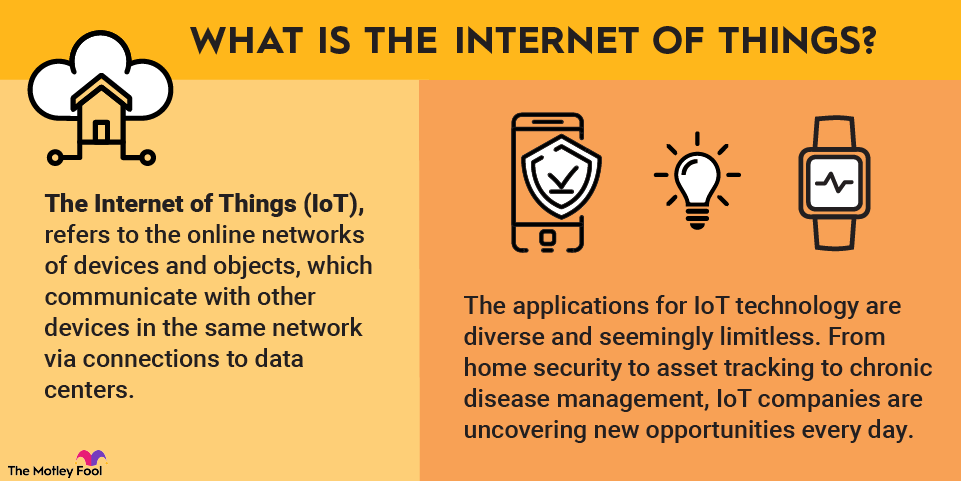
1. The Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data with each other.
This technology is set to revolutionize various industries by enabling smarter homes, cities, and consumer goods.
Semiconductors are crucial in IoT devices since they provide the processing power and connectivity needed for these devices to function.
As IoT applications expand, the demand for advanced, energy-efficient chips that can handle the diverse and high-volume data processing requirements will surge.
Emerging semiconductor companies focusing on IoT will need to innovate to create smaller, more efficient, and more powerful chips to meet the evolving needs of this market.
2. Generative AI
Generative AI, which includes technologies like machine learning and neural networks, is another significant growth driver for semiconductor companies.
These AI systems require immense computational power to process complex algorithms and vast amounts of data.
As generative AI becomes more integrated into applications such as search engines, autonomous vehicles, and advanced robotics, the demand for high-performance chips will increase.
Semiconductor companies that develop graphics processing units (GPUs) and other specialized AI hardware are poised to benefit immensely from this trend. Innovations in chip architecture to improve speed, efficiency, and processing capabilities will be essential to support the growing AI industry.
Another important long-term catalyst to watch in the U.S. was the CHIPS and Science Act, signed into law in August 2022. The legislation was designed to significantly bolster domestic semiconductor manufacturing and research via billions in funding and significant tax credits.
Best semiconductor stocks to buy in 2025
Here are four top picks for semiconductor industry secular growth trends:
1. Qualcomm

NASDAQ: QCOM
Key Data Points
Qualcomm (QCOM +1.49%) is the longtime leader in mobile chip design. Historically, Qualcomm has been a key Apple (AAPL +0.39%) supplier, having profited from the smartphone boom and Apple's ecosystem over the past decade.
Recently launched flagship Android devices powered by Qualcomm's Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 are seeing strong demand globally, especially in China.
In premium and high-tier smartphones, Qualcomm's Snapdragon Mobile platforms are also enabling generative AI capabilities.
Today, Qualcomm has also pivoted to a strong automotive focus via its Snapdragon X platforms. These platforms aim to transform vehicles with advanced connectivity and autonomous driving features.
In the PC market, Qualcomm has expanded its computer portfolio with the Snapdragon X Plus Platform, tailored towards upcoming launches of next-generation AI PCs.
Qualcomm’s appeal comes from its transition toward multiple long-term growth markets rather than relying solely on smartphones. Automotive, edge AI, and AI-enabled PCs are all early-cycle opportunities with stronger secular tailwinds.
The company has also positioned itself as a leader in on-device AI computing, which may become increasingly important as consumers and enterprises look for faster, more privacy-preserving AI capabilities without relying entirely on cloud infrastructure.
Qualcomm also offers a more mature profile compared to other fast-moving semiconductor names. Its dividend yield is higher than many peers, reflecting stable cash flows and a long history of returning capital to shareholders.
2. Nvidia

NASDAQ: NVDA
Key Data Points
Nvidia (NVDA +2.98%) has positioned itself as the platform for all types of AI, largely thanks to its portfolio and the powerful H100 Tensor Core GPU, putting it in a leading position to pursue new markets and expand revenue.
Beyond their GPUs and data centers, Nvidia also offers a variety of platforms to cater to the evolving AI landscape. Blackwell, for instance, is designed for trillion-parameter-scale generative AI. Spectrum-X is a new market offering aimed at scaling AI to Ethernet-only data centers.
Additionally, Nvidia's NIM (Nvidia Infrastructure Management) is a software solution that delivers enterprise-grade, optimized generative AI capable of running on CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) everywhere.
CUDA is Nvidia's parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) model, which allows developers to utilize Nvidia GPUs for general-purpose processing (an approach known as GPGPU, general-purpose computing on graphics processing units).
The case for Nvidia often comes down to one thing: It sits at the center of the largest technology cycle in decades. Demand for AI compute continues to explode, and Nvidia has both the hardware (H100, A100, upcoming Blackwell chips) and software ecosystem (CUDA, NIM, enterprise AI platforms) to capture that growth.
Beyond data centers, Nvidia is expanding into robotics, autonomous vehicles, digital twins, edge computing, and enterprise AI services—each of which represents a long runway for future revenue. Its gross margins remain industry-leading, and its pace of innovation gives it pricing power even in competitive markets.
Nvidia is also one of the most actively traded stocks in the world, which appeals to investors who want liquidity, tight spreads, and flexibility. For those who use options, Nvidia supports a wide range of strategies thanks to deep volume and robust open interest.
3. Intel
Intel Corp. (INTC +11.67%) is one of the most established names in the semiconductor industry, known for its legacy in PC processors and its large-scale manufacturing footprint.
While Intel has struggled in recent years with delays, market-share losses, and fierce competition, the company is now deep into a multi-year turnaround plan. This includes its “IDM 2.0” strategy, which aims to rebuild Intel’s manufacturing leadership, expand its foundry business, and strengthen its position in data centers and AI infrastructure.
Recent earnings show some early stabilization. Intel’s most recent quarter highlighted improving gross margins and positive operating cash flow, helped by restructuring and cost-savings initiatives. The company also raised revenue guidance for upcoming quarters, suggesting that PC demand and enterprise spending may finally be bottoming. Analysts remain divided, but the stock has seen periods of strong performance when sentiment improves around its manufacturing roadmap or government-supported domestic chip production.
Intel may be worth investing in if you believe in the long-term thesis of on-shore semiconductor manufacturing and Intel’s ability to regain competitiveness. A successful foundry buildout could unlock new revenue streams and diversify its business away from the volatile PC market. The risks are real -- execution remains the biggest variable -- but the upside could be meaningful if Intel delivers even part of its turnaround plan.
4. Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments (TXN +2.54%) takes a different approach from most high-profile chip companies. Rather than chasing cutting-edge processors or GPUs, TI dominates the world of analog and embedded semiconductors—chips used in power management, industrial automation, automotive electronics, and sensing applications. These markets grow more steadily and often deliver higher margins because customers rely on long product cycles and stable supply.
Recent news has been mixed. TI’s latest earnings commentary pointed to a slower-than-expected recovery in analog-chip demand, leading to cautious guidance and a sharp share-price reaction. Even so, the company continues to invest heavily in its future, committing more than $60 billion to expand U.S. manufacturing through new facilities in Texas and Utah. Analysts have noted that once the inventory correction normalizes, TI is well positioned to benefit from rising content in electric vehicles, factory automation, and long-duration industrial projects.
TI may be attractive for investors looking for a more stable semiconductor play. Its analog focus means it faces less volatility than high-end chipmakers tied to PCs or gaming. TI also generates reliable free cash flow, supports a long dividend-growth streak, and maintains a conservative balance sheet. The near-term softness could present an opportunity for patient investors who want lower-cyclicality exposure within the broader semiconductor sector.
Name & Ticker | Market Cap | Dividend Yield | Industry |
Nvidia (NVDA) | $5 trillion | 0.02% | Semiconductors / AI Chips |
Qualcomm (QCOM) | $189 billion | 2.04% | Mobile Chips & Telecom Semis |
Intel (INTC) | $170 Billion | 0% | CPUs, Foundry, Infrastructure |
Texas Instruments (TXN) | $148 billion | 3.47% | Analog & Embedded Semiconductors |
Best semiconductor ETFs to buy right now
If you prefer not to pick single stocks, you can also buy a semiconductor exchange-traded fund (ETF) to gain exposure to the overall sector
Two top semiconductor ETFs in terms of overall assets under management (AUM) are:
1. iShares Semiconductor ETF (SOXX)

NASDAQ: SOXX
Key Data Points
The iShares Semiconductor ETF (SOXX +3.20%) tracks 30 market-cap-weighted U.S. semiconductor stocks via the NYSE Semiconductor index. This ETF sported more than $16 billion in assets under management (AUM) in late 2025, charging a 0.35% expense ratio.
2. VanEck Semiconductor ETF (SMH)

NASDAQ: SMH
Key Data Points
The VanEck Semiconductor ETF (SMH +2.96%) tracks 25 market-cap-weighted, U.S.-listed semiconductor stocks via the MVIS US Listed Semiconductor 25 index. It had more than $37 billion in assets in late 2025 and charged a 0.35% expense ratio.
Benefits and risks of investing in semiconductor stocks
Benefits
- Exposure to long-term structural growth trends such as AI, cloud computing, automotive electronics, and 5G connectivity.
- High pricing power and strong margins in many segments, especially for companies producing differentiated or hard-to-replicate chips.
- Global demand for semiconductors continues to rise across consumer devices, data centers, industrial automation, and emerging technologies.
Risks
- The industry is cyclical, with earnings and valuations heavily influenced by global economic conditions and inventory cycles.
- Competition is intense, with technological leadership shifting quickly among companies like Nvidia, AMD (AMD +7.71%), Intel, and Qualcomm.
- High capital expenditures and long product development cycles mean mistakes or delays can materially set back growth and profitability.
Key factors to understand before investing in semiconductors
When looking for the best chipmakers and long-term undervalued semiconductor stocks to buy, consider these four key factors before you buy:
1. Sustainable revenue growth
Companies that gradually increase their sales over time are the best investments, but overall revenue growth matters even more for semiconductor stocks.
Revenue
Many companies in this sector struggle to cope with the industry's cyclical nature. Hardware, such as PC and laptop chips, tends to become a commodity as the years progress and more advanced chips come out. If a new market is growing quickly, other chipmakers might pile on with similar products. Supply swells, prices fall, and individual company sales decline.
If a semiconductor chip company isn't constantly innovating and finding new outlets or developing a robust pipeline for its hardware tech, weathering the cycle can be unsustainable.
That being said, some chip designers are able to protect their work with patents that are not easy to replicate by other means. This can create a type of competitive moat for the company's long-term growth, although it doesn't completely prevent up-and-down sales cycles.
2. Above-average profit margins
Sales need to translate to profits. Companies that cannot control their expenses have low profit margins, and companies with high profit margins have a greater ability to reinvest in research and improve their operations. High gross profit, operating profit, and free cash flow generation are also positive indicators that the company is operating efficiently.
Because of the very high amount of expense needed to get into the semiconductor business, established companies tend to be able to ramp up profit margins as revenue increases over time.
3. Attractive returns on invested capital
A company's return on invested capital (ROIC) indicates how well it's able to generate profit from the cash it raises via debt and equity it receives. A high ROIC means the company is likely innovating strategically, improving operations to increase efficiency, and targeting secular growth trends with new chip designs.
4. Strong balance sheet
Semiconductors are arguably the most complex things ever developed by humankind. Manufacturing chips is very expensive, so it's especially important to understand how semiconductor companies obtain the necessary financial resources to expand.
For example, take chip manufacturers such as the world's largest, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM -0.32%). For a chip business, the company has above-average debt compared to its revenue. However, it also has more cash and investments than it does debt, which signifies a healthy and profitable business that has no problems getting funding.
A company's balance sheet that has more cash than debt and low debt relative to operating profit is a key element to watch. Plenty of cash relative to debt means that a company is well positioned to pay interest and principal payments, even in a pinch. It can also mean the return of excess cash in the form of dividends and stock repurchases.
Related investing topics
How to invest in semiconductor stocks
- Open your brokerage app: Log in to your brokerage account where you handle your investments.
- Search for the stock: Enter the ticker or company name into the search bar to bring up the stock's trading page.
- Decide how many shares to buy: Consider your investment goals and how much of your portfolio you want to allocate to this stock.
- Select order type: Choose between a market order to buy at the current price or a limit order to specify the maximum price you're willing to pay.
- Submit your order: Confirm the details and submit your buy order.
- Review your purchase: Check your portfolio to ensure your order was filled as expected and adjust your investment strategy accordingly.