Shareholder value is the value delivered by a company to investors who own shares in the company. Shareholder value is created when a company's management team makes business decisions that enable the company to increase its earnings, dividends, or share price.
Why is shareholder value important?
Why is shareholder value important?
A company that focuses on maximizing shareholder value is more likely to generate attractive returns for investors. Executives of publicly traded companies are expected to prioritize shareholders' interests by making decisions that increase shareholder value.
While creating and increasing shareholder value is undoubtedly important, it's not unusual for disagreement to arise among shareholders and a company's management about which specific actions would increase shareholder value the most.
How to create shareholder value
How to create shareholder value
Establishing and boosting shareholder value is a primary goal of every publicly traded company. Management teams have a variety of ways to create and increase shareholder value:
Become profitable
Many growing companies are not yet profitable. If a company that has been operating at a loss begins posting profits, then shareholder value is created. Profitable companies trade at higher prices than companies that are still losing money.
Increase earnings per share
Profitable companies that increase their earnings per share (EPS) generally increase shareholder value since stock prices typically are strongly correlated with a company's earnings performance. A company that consistently increases its per-share earnings is consistently increasing shareholder value.
Increase sales
Companies can sometimes increase shareholder value by generating revenue that exceeds investors' expectations. Growth-focused companies often prioritize boosting sales over capturing profits because rapidly growing revenues can indicate strong future earnings potential. Shareholder value, in the form of a rising stock price, can be increased as a result of strong sales performance.
Increase free cash flow
Growth-oriented companies often generate negative free cash flows (FCFs), meaning that they have cash shortfalls after accounting for capital expenditures. Companies that have plenty of available cash are in the best position to pursue new opportunities or to repurchase shares.
A company that transitions from generating negative to positive FCF creates shareholder value, and companies that continue to increase their FCF continue to increase the value for shareholders.
Pay dividends
A company can create shareholder value by beginning to pay a dividend. It can further boost shareholder value by raising its dividend payout rate. As dividends are typically disbursed in cash, a shareholder can either receive the value of a dividend directly or arrange for all dividends received to be automatically reinvested. Reinvesting all dividends is the best way to maximize shareholder value from dividend payments since it enables you to harness the power of compounding interest.
Compound Interest
Repurchase shares
A company that repurchases its own stock can increase shareholder value because share buybacks usually have a beneficial effect on the company's stock price. Companies that buy back shares typically opt to retire those shares from circulation, resulting in a reduction of the company's outstanding share count. Fewer shares outstanding indirectly boosts shareholder value by increasing per-share earnings, even if a company's total earnings are essentially unchanged.
Merge with or acquire a company
A company can create shareholder value by purchasing or merging with another company. The combined entity can benefit from increased market share, may be better positioned to expand into new markets, and can likely cut costs by consolidating back-end operations. The new organization is also likely to generate greater EPS, thereby boosting the company's share price.
How to measure your shareholder value
How to measure your shareholder value
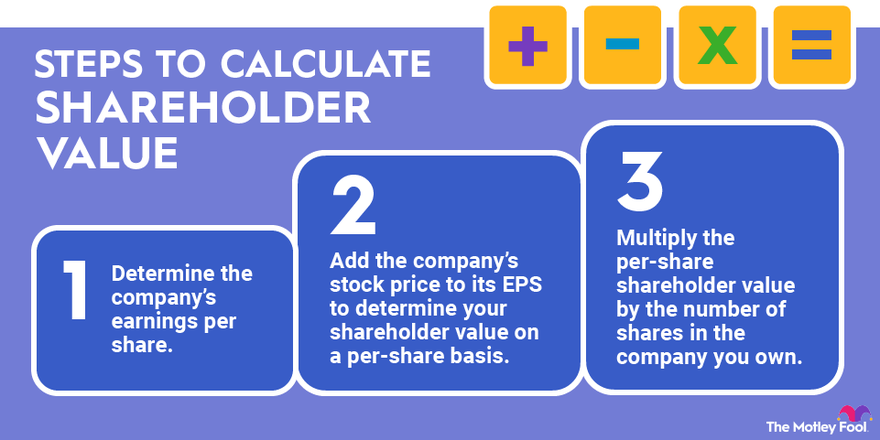
Your shareholder value is directly correlated with how many shares of a company you own. Here's how to compute your portion of shareholder value:
- Determine the company's earnings per share.
- Add the company's stock price to its EPS to determine your shareholder value on a per-share basis.
- Multiply the per-share shareholder value by the number of shares in the company you own.
If a company has EPS of $2 and a stock price of $40, then the shareholder value on a per-share basis is $42. If you own 10 shares of the company's stock, then your individual shareholder value is $420.
Related investing topics
How can companies maximize shareholder value?
How can companies maximize shareholder value?
Companies have a variety of options available to maximize shareholder value, but they cannot reasonably pursue every opportunity or initiative. Business decisions that maximize short-term shareholder value can jeopardize the long-term success of the company, while business decisions that prioritize only long-term outcomes can be detrimental to the short-term performance of a company's stock. The companies that best maximize shareholder value are those that balance short-term priorities with long-term needs.