What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average Stock Index?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (^DJI +0.22%) is a stock index that tracks 30 of the largest U.S. companies. Created in 1896, it is one of the oldest stock indexes, and its performance is widely considered to be a useful indicator of the health of the entire U.S. stock market.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average index is managed by S&P Dow Jones Indices, a joint venture majority-controlled by the financial information and analytics company S&P Global (SPGI +0.31%).

The Dow Jones Industrial Average includes not just industrial stocks but also stocks from most sectors and industries, except for utilities and transportation, which are measured by other indexes specific to those fields.
According to S&P Global, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is a "world-renowned gauge of the U.S. equity market." Most Dow Jones Industrial Average–listed companies trade on the New York Stock Exchange.
Can you buy Dow Jones stock?
You can't buy stock in the Dow Jones Industrial Average itself, but you can get exposure to the Dow and the companies included in the index. Your investment options include:
1. Buy shares of all 30 companies included in the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
With only 30 companies in the index, it's possible to directly purchase each stock in the Dow. Most brokers don't charge commissions on trades, and many allow fractional share investments, meaning you can buy partial shares.
This investment alternative requires you to manage 30 separate stocks and make changes to your portfolio whenever the index changes (although, historically, the index only changes every couple of years).
2. Buy shares in a Dow-focused ETF
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the Dow's performance, such as the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA +0.20%), will invest you in the 30 companies listed in the Dow. Buying shares in an ETF is simpler than investing in 30 separate companies, and you won't have to make changes to your portfolio when the companies listed by the Dow change.
As with most ETFs, an annual expense ratio -- a management fee -- is assessed by this ETF. The expense ratio of 0.16% works out to a fee of $1.60 per year for every $1,000 invested.
3. Invest in Dow options or futures contracts
You can buy Dow options contracts through the CBOE Global Markets options exchange and Dow futures contracts using the CME Group's (CME -0.85%) Chicago Mercantile Exchange. These types of securities are best suited for experienced investors since trading options and futures can be risky.
For novice investors who want portfolio exposure to a wide range of sectors through familiar large-cap stocks, the companies of the Dow Jones Industrial Average represent a good starting point for your research. That's especially true if you're seeking to invest in blue chip companies, which are generally the most stable and profitable on the market.
How is the value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average calculated?
Most stock market indexes are weighted by market capitalization -- equal to share price times the number of shares outstanding. But the Dow Jones Industrial Average is price-weighted.
The value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average is calculated by determining the average value of the stock prices of the 30 listed companies. However, calculating that average value is not as simple as totaling the 30 stock prices and dividing by 30.
Mergers, spinoffs, stock splits, and other developments complicate the arithmetic and require a committee to formally determine a "Dow divisor" -- the denominator by which the sum of the 30 share prices is divided. As of November 2024, the Dow divisor was 0.162684. Using this divisor, you can calculate the value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average by adding up the share prices of all 30 Dow companies and dividing that amount by 0.162684.
Any change in the share price of any Dow-listed company affects the value of the index equally, in accordance with Charles Dow's original vision. But it's important to realize that, on a percentage basis, the movements of the highest-priced stocks have the greatest impact on the index's value.
For example, the highest-priced stock on the Dow in late October 2025 was Goldman Sachs, trading at $769.59. The lowest-priced stock was Verizon, trading at $38.76. Since Goldman's stock price is about 20 times greater than Verizon's, Verizon's share price would have to change by 20% to have the same impact on the Dow as a change of just 1% in the price of Goldman stock.
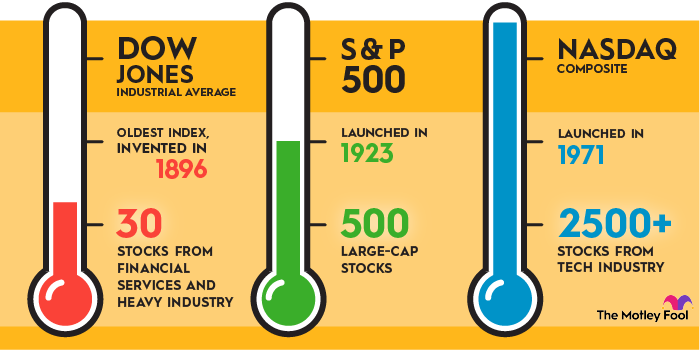
The Dow Jones Industrial Average vs. the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq Composite
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is just one of three major indexes that many investors use to measure the performance of the stock market. The other two are the S&P 500 (^GSPC +0.19%) and the Nasdaq Composite (^IXIC +0.31%).
The S&P 500 is an index of 500 large-cap stocks that are chosen using certain criteria, such as market cap and profitability, by a committee of the S&P Dow Jones Indices. The Nasdaq index tracks more than 2,500 stocks, or almost every stock traded on the Nasdaq Exchange.
Unlike the Dow, the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq are market capitalization–weighted, meaning that the most valuable companies influence index values the most. Both the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq are more heavily weighted toward technology stocks than the Dow, and the Nasdaq has the most tech exposure of all three indexes.
The stocks of tech giants such as Alphabet (GOOG +1.16%)(GOOGL +1.15%), Meta (META +1.80%), and Tesla (TSLA +0.09%) aren't included in the Dow, but they are major components of the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq.
The Dow underweights the tech sector and is more weighted than its peers toward cyclical sectors such as financial services and heavy industry. Despite the differences, the Dow and the S&P 500 tend to perform similarly.

