You can use your wallet to send and receive cryptocurrencies to other wallets or exchanges. Wallets also enable you to participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) activities like yield farming, staking, lending, and borrowing. Many wallets support multiple blockchains, allowing you to manage various cryptocurrencies from one interface.
Security is paramount when selecting the right crypto wallet for your needs. If you lose or forget your private key or seed phrase, you could lose access to your crypto.
Consider your needs and risk tolerance when choosing a wallet. In addition to robust security features and user-friendliness, the wallet's ability to support numerous cryptocurrencies and its compatibility with your devices are vital factors to consider.
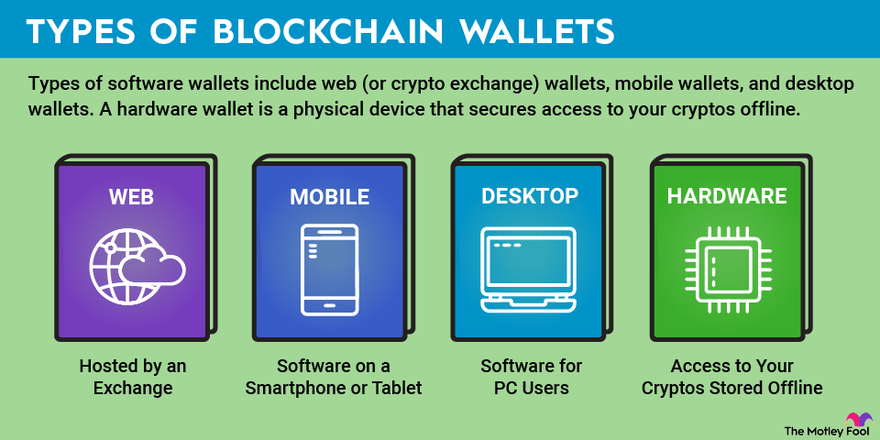
Types of crypto wallets
Crypto wallets come in several forms, broadly categorized as custodial and noncustodial. And each comes with its own pros and cons.
Custodial wallets, often associated with exchanges like Coinbase (COIN +15.31%), store your private keys on their servers. They offer convenience and potential recovery options but require trust in the custodian. Noncustodial wallets, like Ledger or Trezor, give you full control over your keys, ensuring ultimate ownership, but they also increase your responsibility for their security.